Insurance policies explicitly list exclusions to clarify coverage gaps, yet silent cyber risks remain unaddressed as they are not specifically mentioned. Silent cyber refers to cyber-related losses arising in traditional policies without explicit cyber endorsements or exclusions. Insurers must carefully analyze policy language to manage exposure and avoid unexpected liability from these ambiguous cyber threats.
Table of Comparison
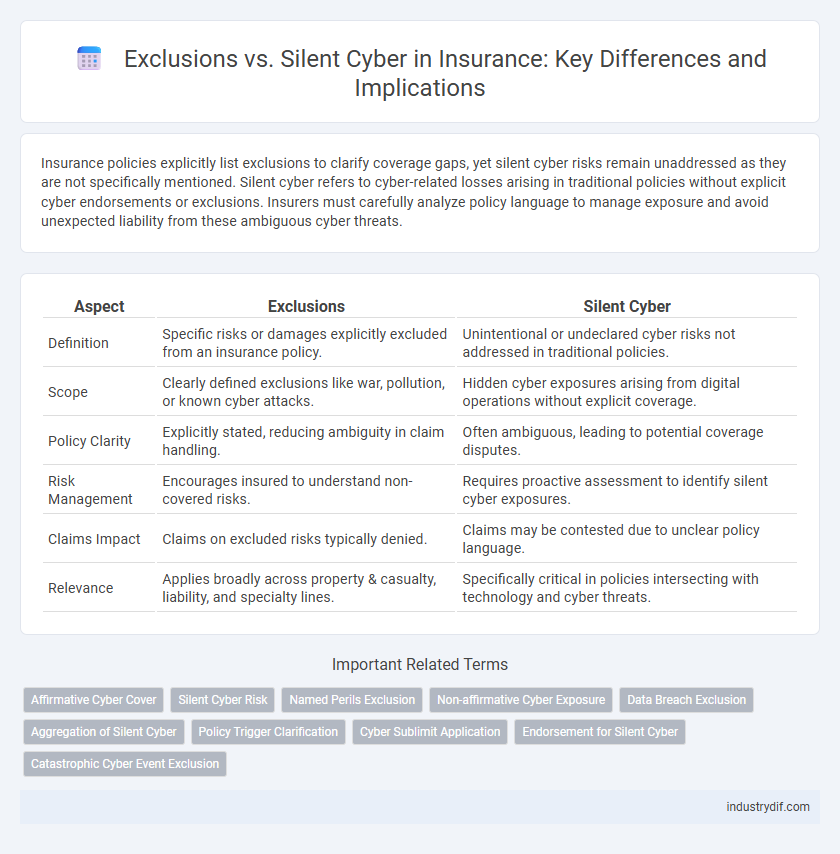
| Aspect | Exclusions | Silent Cyber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specific risks or damages explicitly excluded from an insurance policy. | Unintentional or undeclared cyber risks not addressed in traditional policies. |
| Scope | Clearly defined exclusions like war, pollution, or known cyber attacks. | Hidden cyber exposures arising from digital operations without explicit coverage. |
| Policy Clarity | Explicitly stated, reducing ambiguity in claim handling. | Often ambiguous, leading to potential coverage disputes. |
| Risk Management | Encourages insured to understand non-covered risks. | Requires proactive assessment to identify silent cyber exposures. |
| Claims Impact | Claims on excluded risks typically denied. | Claims may be contested due to unclear policy language. |
| Relevance | Applies broadly across property & casualty, liability, and specialty lines. | Specifically critical in policies intersecting with technology and cyber threats. |
Understanding Exclusions in Insurance Policies
Exclusions in insurance policies specifically outline risks and damages that are not covered, providing clarity on policy limits and insurer liabilities. Silent cyber refers to cyber-related risks that are unintentionally excluded because traditional insurance policies lack explicit cyber coverage language. Understanding these exclusions is crucial for businesses to identify coverage gaps and consider supplemental cyber insurance to mitigate potential financial losses from cyber incidents.
What Is Silent Cyber?
Silent Cyber refers to cyber-related risks that insurance policies implicitly exclude without explicitly stating them, leaving coverage gaps for cyber incidents. Traditional insurance policies, such as property, liability, and professional indemnity, often do not clearly address cyber threats, resulting in ambiguity over whether losses from cyber events are covered. This lack of explicit exclusion or inclusion creates uncertainty for policyholders and insurers when cyber risks materialize.
Key Differences Between Exclusions and Silent Cyber
Exclusions in insurance specifically deny coverage for cyber-related incidents by explicitly listing them in the policy, while Silent Cyber refers to the unintentional exposure to cyber risks that are neither clearly included nor excluded in traditional insurance contracts. Key differences include the clarity and scope of coverage: exclusions provide precise boundaries by explicitly forbidding cyber claims, whereas Silent Cyber creates ambiguity by leaving cyber risk coverage uncertain. Understanding these distinctions helps insurers and policyholders manage cyber risk exposure and negotiate appropriate premiums and coverage terms.
Common Types of Policy Exclusions
Common types of policy exclusions in insurance often explicitly omit coverage for cyber risks, leaving gaps known as Silent Cyber. These exclusions typically include acts of war, intentional acts, and known prior incidents, which can obscure coverage for cyberattacks not specifically referenced in the policy. Understanding the distinction between explicit exclusions and silent cyber risks is crucial for businesses seeking comprehensive cyber insurance protection.
How Silent Cyber Exposures Arise
Silent cyber exposures arise when traditional insurance policies unintentionally cover cyber risks without explicit cyber endorsements or exclusions, creating gaps in coverage understanding. These exposures occur as policies written before the recognition of cyber threats do not address subtle cyber-related losses, such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, or system failures caused by malicious software. Insurers face challenges in identifying silent cyber risks due to the evolving nature of cyber threats and the lack of standardized policy language addressing cyber incidents.
Industry Challenges: Managing Silent Cyber Risk
Silent cyber risk presents a significant challenge for the insurance industry as traditional policies often lack explicit cyber exclusions, leading to ambiguous coverage in the event of a cyber incident. Insurers must navigate the complexities of silent cyber exposures by clarifying policy language and incorporating specific cyber exclusions to mitigate unintended liabilities. Effective management of silent cyber risk requires continuous collaboration between underwriters, risk managers, and cybersecurity experts to address evolving threats and regulatory demands.
Regulatory Approaches to Exclusions and Silent Cyber
Regulatory approaches to insurance exclusions and silent cyber risks emphasize the need for clear policy language to address potential cyber-related losses without creating coverage gaps. Regulators advocate for explicit cyber exclusions or affirmative cyber coverages to ensure policyholders understand the scope of protection against silent cyber exposures. This clarity supports market stability by reducing litigation risks and aligning insurer risk management with evolving cyber threat landscapes.
Impact on Claims and Coverage Decisions
Exclusions in insurance policies explicitly deny coverage for specific cyber risks, leading to straightforward claim denials when those risks materialize. Silent cyber exposures arise from traditionally non-cyber policies that unintentionally cover cyber incidents, causing ambiguity in claims handling and coverage decisions. Insurers face challenges balancing clear contract language with evolving cyber threats, impacting claim outcomes and risk management strategies.
Best Practices for Addressing Silent Cyber in Policies
Insurers should explicitly define cyber risk exclusions and incorporate affirmative cyber coverage to address silent cyber exposure effectively. Regular policy reviews and updates ensure alignment with emerging cyber threats and clarify coverage scope, reducing ambiguity for both insurers and policyholders. Collaboration with cyber risk experts and implementation of clear risk assessment protocols improve underwriting accuracy and risk management in silent cyber exposures.
Future Trends: Evolving Exclusions and Cyber Coverage
Insurance policies increasingly adapt to cyber risk complexities by refining exclusions around silent cyber exposure, where traditional coverage gaps exist despite underlying cyber threats. Future trends indicate insurers will develop more explicit cyber-related exclusions while simultaneously expanding dedicated cyber insurance products to address evolving digital vulnerabilities. This shift aims to balance clarity in policy language with comprehensive coverage, responding to the surge in cyber incidents impacting businesses globally.
Related Important Terms
Affirmative Cyber Cover
Affirmative cyber cover explicitly includes protection against cyber risks, addressing gaps created by traditional insurance exclusions that often omit silent cyber exposures. By providing clear coverage for cyber incidents, affirmative cyber insurance mitigates financial losses from data breaches, ransomware, and other digital threats overlooked in standard policies.
Silent Cyber Risk
Silent cyber risk refers to potential cyber-related losses that are not explicitly covered or excluded within traditional insurance policies, creating gaps where insurers might unknowingly assume cyber exposure. Unlike clear policy exclusions, silent cyber risks arise from ambiguous language or outdated clauses, highlighting the need for insurers to explicitly address cyber perils to prevent unintentional coverage gaps.
Named Perils Exclusion
Named Perils Exclusion specifically restricts coverage to risks explicitly listed in the policy, often excluding cyber incidents unless explicitly included, which contrasts with Silent Cyber exposure where cyber risks are neither clearly covered nor excluded. Understanding the distinction between Named Perils Exclusion and Silent Cyber risk is essential for insurers to accurately assess and price policies amidst growing cyber threats.
Non-affirmative Cyber Exposure
Non-affirmative cyber exposure arises when traditional insurance policies exclude cyber risks without explicitly addressing them, creating coverage gaps for cyber incidents. Insurers must clarify exclusions and consider silent cyber policies to manage ambiguous liability arising from non-affirmative cyber exposures effectively.
Data Breach Exclusion
Data breach exclusions explicitly exclude coverage for losses arising from unauthorized access to or disclosure of sensitive information, creating significant gaps in traditional insurance policies. Silent cyber refers to unintentional exposure to cyber risks within standard policies not designed to address cyber incidents, often leaving businesses vulnerable without clear coverage for data breaches.
Aggregation of Silent Cyber
Aggregation of silent cyber risks in insurance refers to the unintentional accumulation of cyber-related exposures that are not explicitly excluded in traditional policies, potentially leading to significant aggregate losses. Insurers face challenges in quantifying these risks due to unclear policy language, increasing the importance of clear exclusions to manage silent cyber aggregation effectively.
Policy Trigger Clarification
Exclusions explicitly deny coverage for specific cyber risks, while silent cyber refers to unintentional exposure to cyber risks under traditional insurance policies without clear policy trigger language. Clarifying policy triggers involves defining whether a claim arises from a cyber event directly excluded or from non-cyber perils that inadvertently include cyber-related damage.
Cyber Sublimit Application
Cyber sublimit application often excludes certain cyber risks from standard insurance policies, creating gaps in coverage known as silent cyber exposure. Understanding the distinctions between explicit exclusions and silent cyber risks is essential for accurately assessing the financial impact and ensuring adequate protection against cyber threats.
Endorsement for Silent Cyber
Silent Cyber endorsements explicitly clarify coverage gaps by addressing cyber-related risks not covered under traditional property and casualty policies, reducing ambiguity in claims related to cyber events. These endorsements help insurers manage exposure to silent cyber risks by defining the scope of coverage for cyber perils excluded from standard policies.
Catastrophic Cyber Event Exclusion
Catastrophic cyber event exclusions explicitly eliminate coverage for large-scale cyber incidents causing widespread damage, contrasting with silent cyber risks that arise from ambiguous policy language lacking clear cyber-specific terms. Understanding these distinctions is critical for insurers managing cyber liability exposures amid increasing frequency and severity of cyberattacks on critical infrastructure and enterprise networks.
Exclusions vs Silent Cyber Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com