Life insurance offers comprehensive financial protection with higher coverage amounts suited for long-term planning and wealth transfer, while microinsurance provides affordable, minimal coverage tailored to low-income individuals or those with limited access to traditional insurance markets. Microinsurance often features simplified application processes and lower premiums, making it accessible for protecting against specific risks. Choosing between life insurance and microinsurance depends on individual financial goals, risk exposure, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
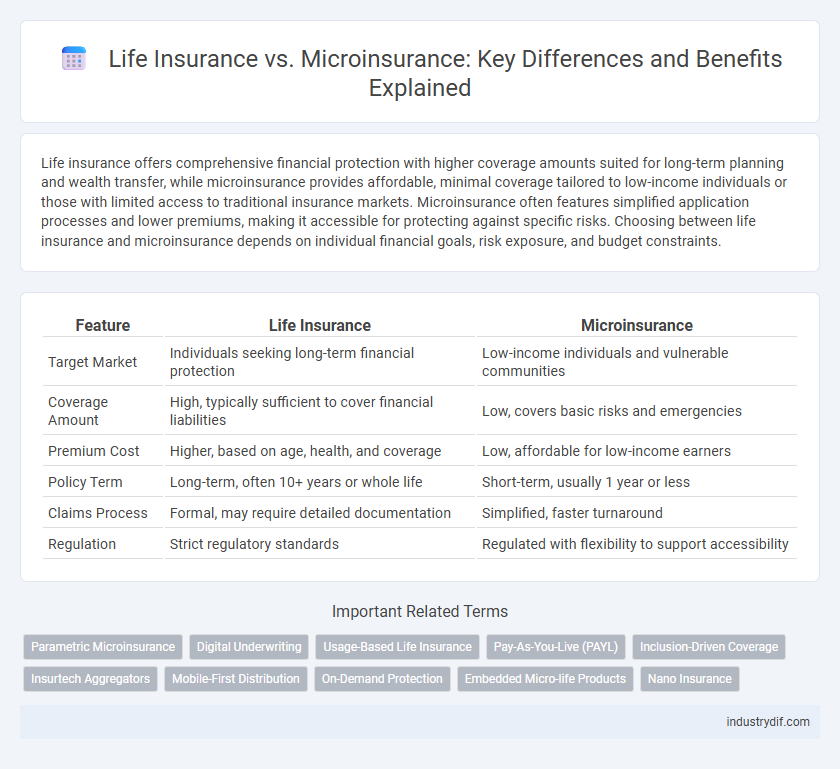
| Feature | Life Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Market | Individuals seeking long-term financial protection | Low-income individuals and vulnerable communities |
| Coverage Amount | High, typically sufficient to cover financial liabilities | Low, covers basic risks and emergencies |
| Premium Cost | Higher, based on age, health, and coverage | Low, affordable for low-income earners |
| Policy Term | Long-term, often 10+ years or whole life | Short-term, usually 1 year or less |
| Claims Process | Formal, may require detailed documentation | Simplified, faster turnaround |
| Regulation | Strict regulatory standards | Regulated with flexibility to support accessibility |
Understanding Life Insurance: Key Features and Benefits
Life insurance provides comprehensive financial protection by offering a death benefit to beneficiaries, ensuring long-term security and peace of mind. Key features include fixed premium payments, cash value accumulation, and policyholder dividends, which contribute to wealth building and retirement planning. This coverage typically supports mortgage payments, education costs, and income replacement, highlighting its role in safeguarding family financial stability.
What is Microinsurance? Definition and Scope
Microinsurance is a type of insurance designed to provide affordable and accessible coverage specifically for low-income individuals and families who are typically underserved by traditional life insurance. It covers risks such as health, life, property, and agriculture, with lower premiums and simplified processes to meet the financial constraints of vulnerable populations. Microinsurance is essential in emerging markets, promoting financial inclusion and risk protection in communities with limited access to conventional insurance products.
Coverage Differences: Life Insurance vs Microinsurance
Life insurance offers comprehensive coverage, including death benefits, critical illness, disability, and sometimes savings components, designed for long-term financial protection. Microinsurance provides limited, affordable coverage aimed at low-income individuals, focusing mainly on basic risks like accidental death or hospitalization with lower policy limits. The key difference lies in the scope and depth of coverage, with life insurance catering to broader financial needs and microinsurance targeting essential protection for underserved populations.
Target Markets: Who Needs Life Insurance vs Microinsurance?
Life insurance primarily targets middle to high-income individuals seeking comprehensive financial protection for dependents and estate planning, typically involving higher premiums and broader coverage. Microinsurance focuses on low-income populations and informal sector workers who require affordable, accessible policies with simplified benefits to mitigate everyday risks like health emergencies or crop failure. Understanding these distinct target markets helps insurers design products that meet specific financial capacities and risk profiles effectively.
Premium Structure Comparison
Life insurance premiums are typically higher due to extensive coverage, underwriting processes, and longer policy terms, often requiring medical evaluations and financial assessments. Microinsurance premiums are designed to be affordable and accessible, featuring lower amounts and simplified underwriting to serve low-income populations with limited documentation. The premium structure in microinsurance focuses on minimizing costs while maintaining basic coverage, enabling rapid enrollment and flexible payment options compared to traditional life insurance.
Policy Accessibility: Application and Documentation
Life insurance typically requires extensive documentation, including medical reports, proof of income, and identity verification, which can prolong the application process. Microinsurance offers streamlined policy accessibility with minimal paperwork, often using simplified forms and mobile-based applications tailored for low-income populations. This ease of application enhances accessibility, making microinsurance a practical choice for underserved communities with limited documentation resources.
Claims Process in Life Insurance vs Microinsurance
The claims process in life insurance typically involves extensive documentation, medical records, and beneficiary verification, which can extend processing times but ensures thorough risk assessment. Microinsurance claims are designed for simplicity and speed, often leveraging mobile technology and minimal paperwork to provide rapid payouts for low-income clients. Efficient claims handling in microinsurance increases accessibility and trust among underserved populations compared to traditional life insurance claims.
Limitations and Exclusions
Life insurance policies typically have higher coverage limits but come with stringent underwriting requirements and may exclude pre-existing conditions or risky activities. Microinsurance offers lower coverage tailored for low-income individuals, often with simplified claims processes but limited benefit amounts and exclusions on certain diseases or high-risk occupations. Both types may exclude coverage for suicide within an initial period and losses due to war or criminal acts.
Role in Financial Inclusion
Life insurance provides long-term financial security for individuals and families, often requiring higher premiums and extensive underwriting processes. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, simplified coverage, enhancing accessibility and enabling broader participation in formal financial systems. Both play complementary roles in financial inclusion by addressing diverse risk protection needs across socioeconomic groups.
Choosing the Right Product: Factors to Consider
When choosing between life insurance and microinsurance, consider factors such as coverage amount, premium affordability, and duration of protection tailored to individual financial needs. Life insurance typically offers higher sums assured and long-term benefits, while microinsurance provides accessible, low-cost coverage for essential risks, often catering to low-income groups. Assessing personal goals, risk exposure, and budget constraints ensures selection of the right product aligned with financial security objectives.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers a streamlined, data-driven approach by triggering payouts based on predefined parameters such as weather events or crop yields, unlike traditional life insurance which relies on claims assessment after events occur. This innovative model enhances financial inclusion by providing rapid, transparent compensation to low-income populations vulnerable to specific risks.
Digital Underwriting
Digital underwriting in life insurance leverages advanced data analytics and AI algorithms to assess risk profiles efficiently, enabling tailored policy pricing and faster approvals. Microinsurance utilizes simplified digital underwriting processes with minimal data requirements to provide affordable coverage for low-income populations, ensuring accessibility and scalability in underserved markets.
Usage-Based Life Insurance
Usage-based life insurance leverages telematics and wearable devices to tailor premiums based on real-time health data and lifestyle behaviors, offering personalized coverage in contrast to traditional microinsurance products that target low-income populations with simplified policies and limited benefits. This dynamic underwriting approach enhances risk assessment accuracy and encourages healthier habits, bridging the gap between comprehensive life insurance and affordable microinsurance solutions.
Pay-As-You-Live (PAYL)
Pay-As-You-Live (PAYL) models in life insurance offer flexible premiums that adjust based on real-time lifestyle data, making coverage more affordable and personalized compared to traditional life insurance. Microinsurance under PAYL frameworks enables low-income individuals to access vital life insurance protection by aligning costs with daily habits and risk exposure, promoting financial inclusion.
Inclusion-Driven Coverage
Life insurance offers comprehensive financial protection primarily for middle to high-income individuals, while microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, smaller coverage tailored to their specific risks. Inclusion-driven coverage through microinsurance enhances access to essential financial security for underserved communities, promoting economic resilience and social stability.
Insurtech Aggregators
Insurtech aggregators streamline access to both life insurance and microinsurance by offering comparative digital platforms that simplify policy selection and enhance customer experience. These aggregators leverage AI-driven analytics to tailor coverage options, optimize pricing for diverse socioeconomic segments, and boost insurance penetration in underserved markets.
Mobile-First Distribution
Mobile-first distribution enhances accessibility for life insurance by enabling personalized policy management through apps and digital platforms, while microinsurance leverages mobile technology to deliver affordable, low-premium coverage tailored for low-income populations with simpler claims processes. Both models utilize mobile integration to increase customer engagement, streamline transactions, and expand market reach in underserved regions.
On-Demand Protection
Life insurance provides comprehensive coverage tailored for long-term financial security, while microinsurance offers affordable, on-demand protection designed for low-income individuals facing immediate risks. On-demand microinsurance enables policyholders to activate coverage instantly for specific events, enhancing flexibility and accessibility compared to traditional life insurance plans.
Embedded Micro-life Products
Embedded micro-life insurance products offer accessible, low-cost coverage integrated into everyday purchases, making life insurance more affordable and convenient for low-income populations. These products drive higher penetration rates by simplifying enrollment and leveraging digital platforms, tailored to meet the financial inclusion goals within emerging markets.
Nano Insurance
Nano insurance offers ultra-low premium life insurance policies tailored for low-income individuals, bridging the gap between traditional life insurance and microinsurance by providing accessible, affordable coverage with simplified underwriting processes and quick claims settlement. This innovative model leverages mobile technology and data analytics to deliver personalized protection, enhancing financial inclusion and risk management for underserved populations.
Life Insurance vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com