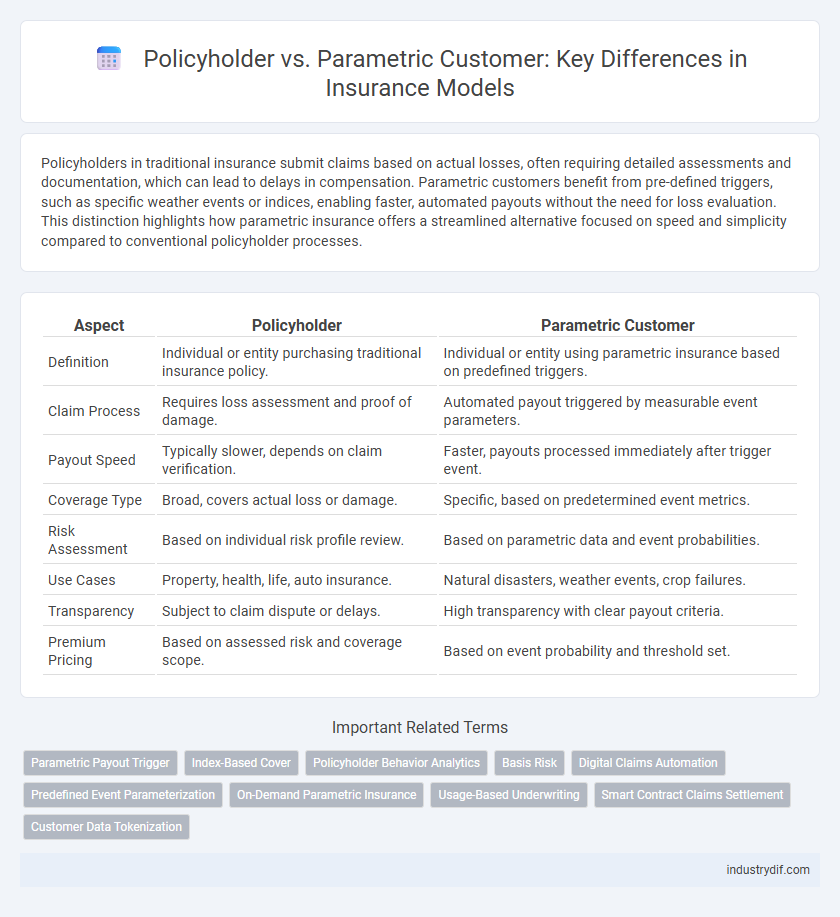
Policyholders in traditional insurance submit claims based on actual losses, often requiring detailed assessments and documentation, which can lead to delays in compensation. Parametric customers benefit from pre-defined triggers, such as specific weather events or indices, enabling faster, automated payouts without the need for loss evaluation. This distinction highlights how parametric insurance offers a streamlined alternative focused on speed and simplicity compared to conventional policyholder processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Policyholder | Parametric Customer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or entity purchasing traditional insurance policy. | Individual or entity using parametric insurance based on predefined triggers. |
| Claim Process | Requires loss assessment and proof of damage. | Automated payout triggered by measurable event parameters. |
| Payout Speed | Typically slower, depends on claim verification. | Faster, payouts processed immediately after trigger event. |
| Coverage Type | Broad, covers actual loss or damage. | Specific, based on predetermined event metrics. |
| Risk Assessment | Based on individual risk profile review. | Based on parametric data and event probabilities. |
| Use Cases | Property, health, life, auto insurance. | Natural disasters, weather events, crop failures. |
| Transparency | Subject to claim dispute or delays. | High transparency with clear payout criteria. |
| Premium Pricing | Based on assessed risk and coverage scope. | Based on event probability and threshold set. |
Understanding Policyholders in Traditional Insurance
Policyholders in traditional insurance engage in agreements that involve personalized risk assessments and claims processes based on actual losses, ensuring tailored financial protection. Unlike parametric customers who receive payouts triggered by predefined event parameters, policyholders provide detailed documentation and undergo thorough claim evaluations. This approach emphasizes a direct relationship between reported damages and compensation, fostering trust and customized coverage.
Exploring Parametric Insurance Customers
Parametric insurance customers benefit from pre-defined triggers based on measurable events such as weather conditions or natural disasters, enabling rapid claim settlements without the traditional loss adjustment process. These policyholders prioritize transparency and speed, valuing insurance products that mitigate coverage gaps through automated payouts. The rise of parametric insurance addresses the needs of clients seeking efficient risk transfer solutions in sectors like agriculture, travel, and catastrophe-prone areas.
Key Differences: Policyholder vs Parametric Customer
Policyholders purchase traditional insurance policies that involve claims assessments based on documented losses, while parametric customers receive payouts triggered by predefined parameters such as weather data or seismic activity, bypassing loss adjustment processes. The key difference lies in the claim process: policyholders undergo claims verification, whereas parametric customers benefit from faster, automatic disbursements triggered by objective data. This distinction impacts coverage speed, administrative costs, and transparency for each insurance approach.
Claims Process: Indemnity vs Parametric Approach
The claims process for policyholders typically follows the indemnity approach, requiring thorough loss assessment and documentation to determine the exact compensation based on incurred damages. In contrast, parametric customers benefit from a streamlined parametric approach where claims are triggered automatically once predefined event parameters, such as earthquake magnitude or rainfall levels, are met, enabling faster payouts. This shift reduces administrative delays and uncertainty, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency in insurance claims management.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting Practices
Policyholders undergo traditional risk assessment and underwriting practices involving detailed personal and historical data to determine coverage terms and premiums. Parametric customers benefit from predefined triggers based on measurable parameters, enabling faster claim settlements without extensive loss verification. This shift in underwriting focuses on objective data points, reducing subjective risk evaluation and streamlining policy management.
Benefits for Policyholders in Conventional Models
Policyholders in conventional insurance models benefit from comprehensive coverage tailored to specific risks, enabling personalized claim assessments based on documented losses. These policies often include detailed terms and conditions that provide clarity and legal protection, fostering trust and financial security. Traditional models also allow for claim adjustments and negotiations, offering flexibility in handling complex or unforeseen circumstances.
Advantages for Parametric Insurance Customers
Parametric insurance customers benefit from faster claim settlements due to predefined triggers based on measurable parameters like weather data or earthquake intensity, eliminating lengthy damage assessments. This streamlined process reduces administrative costs and enhances transparency, providing certainty and speed that traditional policyholders may lack. Parametric coverage also offers customizable and scalable protection, aligning closely with specific risk exposures for improved financial resilience.
Customer Experience and Satisfaction Metrics
Policyholders typically engage with traditional insurance models involving claims processing and detailed documentation, which can sometimes delay settlements and impact satisfaction scores negatively. Parametric customers benefit from predefined triggers and automated payouts, significantly enhancing customer experience by offering faster, transparent, and more predictable claim resolution. Satisfaction metrics for parametric insurance often reflect higher Net Promoter Scores (NPS) and reduced Customer Effort Scores (CES), highlighting improved engagement and loyalty compared to conventional policyholder experiences.
Use Cases: When to Choose Policyholder or Parametric Solutions
Policyholder insurance is ideal for traditional coverage needs such as liability, property, or health risks where precise claim assessment and indemnity are essential. Parametric solutions suit situations requiring rapid payouts, such as agriculture, travel disruption, or natural disaster insurance, where pre-defined triggers like weather data or seismic activity enable swift compensation. Choosing between policyholder and parametric insurance depends on the desired balance between claim complexity, payout speed, and the type of risk exposure involved.
Future Trends: Policyholders and Parametric Insurance Evolution
Emerging trends indicate a shift from traditional policyholders to parametric customers who favor insurance products with predefined triggers and instantaneous payouts, enhancing transparency and efficiency. Advances in IoT and data analytics drive this evolution, enabling more accurate risk assessment and customized parametric solutions. The future insurance landscape will prioritize seamless integration of digital platforms, fostering greater customer empowerment and streamlined claims processing.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Payout Trigger
Parametric payout triggers in insurance activate automatic payments based on predefined objective parameters like weather data or seismic activity, providing faster and more transparent claims processing for parametric customers. Unlike traditional policyholders who require loss assessment, parametric insurance uses these triggers to minimize disputes and accelerate compensation.
Index-Based Cover
Policyholders with traditional insurance policies receive payouts based on assessed losses, while parametric customers benefit from index-based cover that triggers automatic payments when predefined parameters, such as weather events or seismic activity indices, are met. This index-based approach streamlines claims processing, reduces underwriting costs, and offers faster financial relief by bypassing loss verification.
Policyholder Behavior Analytics
Policyholder behavior analytics leverages data-driven insights to predict claim frequency, policy renewals, and risk profiles, whereas parametric customers engage with insurance products based on predefined triggers such as weather events. Understanding the distinct behavioral patterns of policyholders enables insurers to customize pricing models, enhance underwriting accuracy, and improve customer retention strategies.
Basis Risk
Policyholder insurance typically involves indemnity-based coverage where claims are paid based on actual losses, whereas parametric customers benefit from predefined triggers that activate payouts, minimizing claims processing time. Basis risk arises in parametric insurance when the payout does not fully correspond to the actual loss, creating a potential gap between the event parameter and the policyholder's incurred damages.
Digital Claims Automation
Policyholders typically undergo traditional claims processes involving manual assessments and documentation, whereas parametric customers benefit from digital claims automation that triggers instant payouts based on predefined event parameters such as weather data or natural disaster indices. Digital claims automation enhances efficiency, reduces fraud risk, and improves customer experience by enabling seamless, real-time claim settlements for parametric insurance products.
Predefined Event Parameterization
Policyholders rely on traditional insurance models requiring claims assessment after loss occurrence, while parametric customers benefit from predefined event parameterization that triggers automatic payouts based on measurable, predefined criteria such as rainfall levels or earthquake magnitude. This approach reduces claim processing time and increases transparency by establishing clear payout conditions in insurance contracts.
On-Demand Parametric Insurance
On-demand parametric insurance offers policyholders rapid, transparent payouts triggered by predefined events, differing from traditional parametric customers who typically rely on fixed coverage parameters. This model enhances flexibility and efficiency by using real-time data to automatically indemnify losses without the need for lengthy claims assessments.
Usage-Based Underwriting
Usage-based underwriting tailors insurance premiums by analyzing real-time data from policyholders' behaviors, enhancing risk assessment accuracy compared to traditional methods. Parametric customers benefit from predefined trigger events and automated payouts, streamlining claims and reducing processing times in usage-based insurance models.
Smart Contract Claims Settlement
Policyholders experience traditional insurance claims processes involving manual verification and adjustable payouts, whereas parametric customers benefit from automated Smart Contract claims settlement triggered by predefined parameters, ensuring faster and transparent payouts. Smart contracts enhance parametric insurance by eliminating claims disputes through real-time data oracles, reducing administrative costs and improving overall efficiency.
Customer Data Tokenization
Policyholder data tokenization securely replaces sensitive insurance information with unique identifiers, minimizing risk of data breaches while enhancing privacy compliance. Parametric customers benefit from tokenized data by enabling faster, automated claim settlements based on pre-defined event triggers, ensuring streamlined and transparent coverage.
Policyholder vs Parametric Customer Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com