Group health insurance provides comprehensive coverage through an employer or organization, offering cost-effective premiums and broader benefits for members. Peer-to-peer insurance operates on a community-based sharing model, where participants pool funds to cover claims, promoting transparency and potential savings. While group health insurance guarantees structured benefits and regulatory protection, peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes trust and personalized risk-sharing among peers.
Table of Comparison
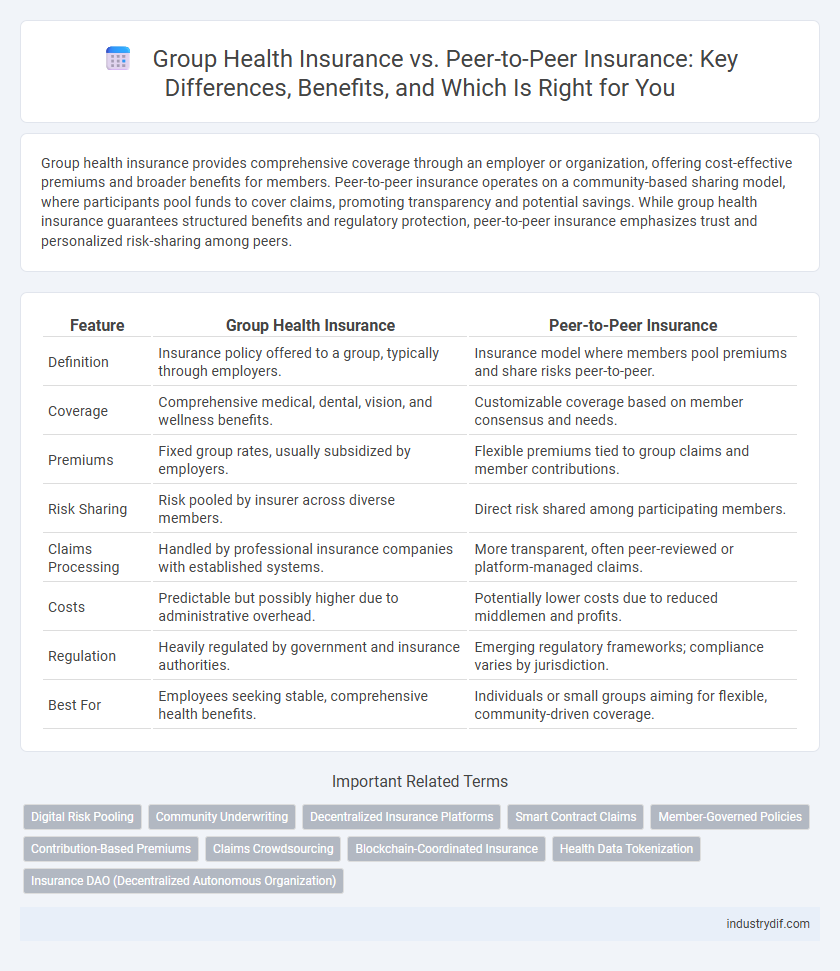
| Feature | Group Health Insurance | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance policy offered to a group, typically through employers. | Insurance model where members pool premiums and share risks peer-to-peer. |
| Coverage | Comprehensive medical, dental, vision, and wellness benefits. | Customizable coverage based on member consensus and needs. |
| Premiums | Fixed group rates, usually subsidized by employers. | Flexible premiums tied to group claims and member contributions. |
| Risk Sharing | Risk pooled by insurer across diverse members. | Direct risk shared among participating members. |
| Claims Processing | Handled by professional insurance companies with established systems. | More transparent, often peer-reviewed or platform-managed claims. |
| Costs | Predictable but possibly higher due to administrative overhead. | Potentially lower costs due to reduced middlemen and profits. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by government and insurance authorities. | Emerging regulatory frameworks; compliance varies by jurisdiction. |
| Best For | Employees seeking stable, comprehensive health benefits. | Individuals or small groups aiming for flexible, community-driven coverage. |
Overview of Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance provides coverage to a defined group of individuals, typically employees of a company, under a single policy that offers comprehensive medical benefits, including hospitalization, preventive care, and prescription drugs. Employers often subsidize premiums, making group health insurance more affordable and accessible compared to individual plans, while allowing risk pooling that helps stabilize costs across members. This type of insurance promotes employee well-being and retention by ensuring consistent access to healthcare services and reducing out-of-pocket expenses.
Understanding Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages a decentralized model where individuals pool funds directly to cover shared risks, reducing reliance on traditional insurers and lowering administrative costs. This model fosters transparency and trust among members, as claims are either paid from the communal pool or reimbursed collectively, minimizing conflicts of interest. Unlike group health insurance, which involves employer-sponsored plans with fixed premiums and coverage limits, peer-to-peer insurance offers flexible, community-driven protection tailored to the participants' specific needs.
Key Differences Between Group and P2P Insurance
Group health insurance provides coverage through employers or organizations, offering standardized plans with pooled risk and established underwriting processes. Peer-to-peer insurance operates on a decentralized model where members pool funds directly to cover claims, promoting transparency and potential cost savings by reducing administrative expenses. Unlike group insurance, P2P relies heavily on trust and community engagement, impacting claim management and risk distribution.
Coverage Features: Group vs. Peer-to-Peer Models
Group health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage plans that include preventive care, hospitalization, and prescription drugs, benefiting from negotiated rates and pooled risk among members of an organization. Peer-to-peer insurance models emphasize transparency and member control, often providing customizable coverage options with potential cost savings through shared risk within smaller, trusted communities. The group model excels in stability and broad risk distribution, while peer-to-peer models offer flexibility and stronger alignment of incentives among participants.
Cost Structure and Premiums Comparison
Group health insurance typically offers lower premiums due to risk pooling among a large number of employees, spreading costs evenly across the group. Peer-to-peer insurance often allows members to share premiums within smaller, more homogenous groups, potentially reducing expenses through transparency and reduced administrative fees. Cost structures in group plans rely heavily on employer contributions, while peer-to-peer models emphasize member-driven claims management and cost savings.
Risk Sharing Mechanisms in Each Model
Group health insurance pools risk among a large number of members, spreading potential costs evenly across the group to stabilize premiums and provide financial protection. Peer-to-peer insurance decentralizes risk by enabling small groups of individuals to share potential losses directly, often using technology platforms to enhance transparency and reduce administrative costs. The risk-sharing in group health insurance relies on collective underwriting by insurers, whereas peer-to-peer models leverage community-based risk mutualization with minimal intermediary involvement.
Claims Process: Group Health vs. Peer-to-Peer
Group health insurance provides a structured claims process managed by a central insurer, ensuring standardized claim submissions, quick approvals, and clear coverage guidelines. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages a decentralized claims system where members collectively review and approve claims, promoting transparency but potentially causing delays in settlement. The predictability and efficiency of group health insurance claims contrast with the community-driven, trust-based approach of peer-to-peer models.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance offers advantages like cost efficiency through pooled risk and benefits tailored to employee needs, fostering workforce retention and satisfaction. However, it may present drawbacks such as limited plan flexibility, mandatory employer contributions, and potential coverage restrictions based on group size or industry. Employers must weigh these factors against organizational goals and employee demographics to determine optimal insurance solutions.
Benefits and Limitations of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-Peer Insurance offers benefits such as enhanced transparency, reduced administrative costs, and a stronger sense of community trust by pooling premiums among members with similar risk profiles. Limitations include potential coverage gaps if the pool claims exceed the collective contributions, limited regulatory oversight compared to traditional group health insurance, and challenges in scalability for larger or diverse populations. This model suits members seeking lower premiums and greater control but requires careful risk management to ensure adequate protection.
Suitability and Choosing the Right Model for Organizations
Group health insurance offers comprehensive coverage designed for organizations seeking standardized plans that ensure employee access to a wide network of healthcare providers, making it suitable for companies prioritizing stability and regulatory compliance. Peer-to-peer insurance provides a decentralized alternative emphasizing community-based risk sharing, appealing to organizations that value transparency, cost-efficiency, and fostering trust among employees. Choosing the right insurance model depends on the organization's size, risk tolerance, administrative capacity, and desired level of employee engagement in managing health benefits.
Related Important Terms
Digital Risk Pooling
Group Health Insurance typically pools risk across a defined employee group, offering collective bargaining power and standardized benefits, while Peer-to-Peer Insurance leverages digital platforms to create decentralized risk pools that enable personalized coverage and lower costs through direct member interactions. Digital risk pooling in Peer-to-Peer models enhances transparency and efficiency by automating claims and risk sharing using blockchain and smart contracts, differentiating it from traditional group insurance frameworks.
Community Underwriting
Group health insurance pools risk across a predefined set of members, typically employees of a company, allowing premiums to be based on the overall health profile of the group rather than individuals. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages community underwriting by enabling members within a network to share risk and claims directly with each other, fostering transparency and potential cost savings through mutual accountability.
Decentralized Insurance Platforms
Decentralized insurance platforms leverage blockchain technology to create transparent, peer-to-peer insurance models that directly connect policyholders without intermediaries, reducing costs and enhancing trust. Group health insurance, traditionally managed by centralized insurers, offers pooled risk and negotiated premiums, but lacks the flexibility and real-time claim processing provided by decentralized platforms.
Smart Contract Claims
Group health insurance leverages centralized underwriting and claim processing, often resulting in slower settlements and potential disputes, while peer-to-peer insurance utilizes blockchain-based smart contract claims that automate verification and payouts, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Smart contracts in peer-to-peer models execute claims instantly when predefined conditions are met, minimizing administrative costs and ensuring trust among participants.
Member-Governed Policies
Group Health Insurance relies on employer-sponsored plans where risk is pooled across all members, ensuring stable premiums and comprehensive coverage options. Peer-to-Peer Insurance operates on member-governed policies that emphasize transparency and community control, allowing insured members to share claims and reduce administrative costs collaboratively.
Contribution-Based Premiums
Group health insurance offers contribution-based premiums where employees and employers share costs, promoting affordability and risk pooling across a large member base. Peer-to-peer insurance relies on collective member contributions to fund claims directly, often resulting in lower premiums by minimizing administrative expenses and leveraging trust within smaller communities.
Claims Crowdsourcing
Group health insurance pools risks among a defined member base, enabling predictable claims management and cost distribution, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages claims crowdsourcing by allowing members to directly evaluate and approve claims, increasing transparency and potentially reducing fraud. Claims crowdsourcing within peer-to-peer insurance enhances collective decision-making and fosters trust, contrasting with traditional insurer-driven claims processing in group health plans.
Blockchain-Coordinated Insurance
Blockchain-coordinated group health insurance streamlines claims processing and enhances transparency by securely recording member data and transactions on a decentralized ledger, reducing administrative overhead and fraud. In contrast, peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain to create autonomous, community-driven pools where participants directly share risks and payouts without traditional intermediaries, fostering trust and cost efficiency.
Health Data Tokenization
Group Health Insurance leverages centralized data management systems, whereas Peer-to-Peer Insurance utilizes blockchain to enable secure health data tokenization, enhancing privacy and transparency. Tokenization converts sensitive health information into encrypted digital assets, reducing fraud risk and empowering policyholders with greater control over their personal data.
Insurance DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
Insurance DAOs leverage blockchain technology to create decentralized group health insurance models, enhancing transparency, reducing administrative costs, and enabling peer-to-peer risk sharing without traditional intermediaries. By utilizing smart contracts, these platforms automate claims processing and foster community-driven governance, positioning Insurance DAOs as innovative alternatives to conventional group health insurance and peer-to-peer insurance schemes.
Group Health Insurance vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com