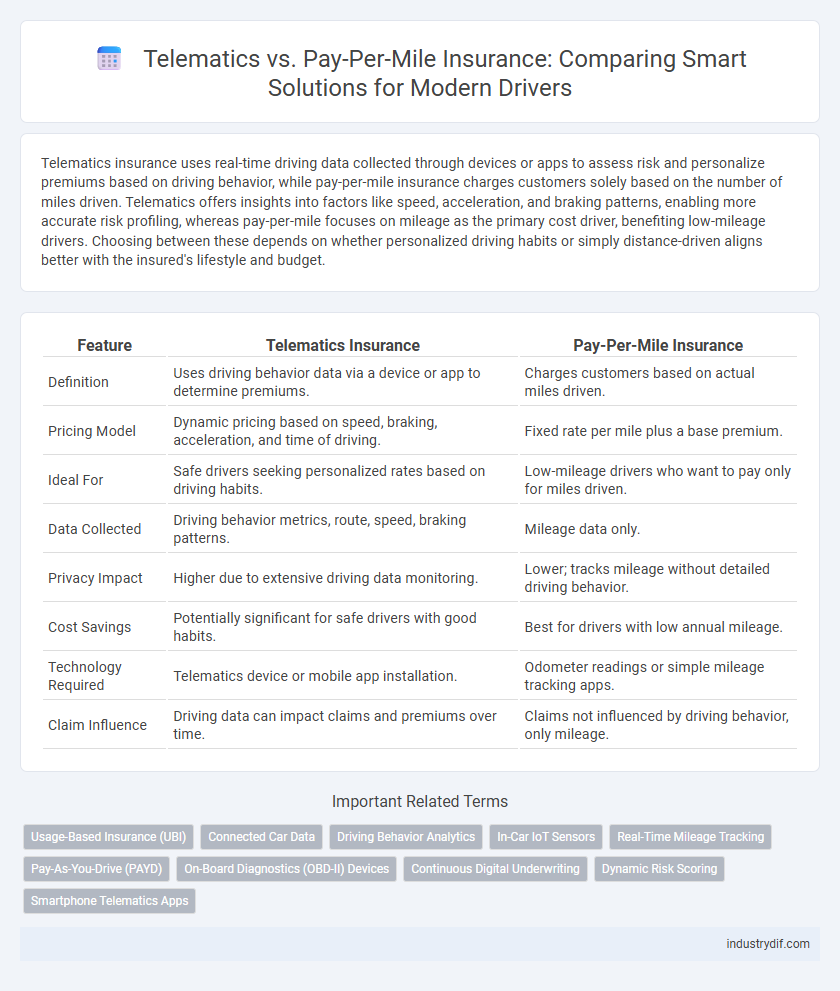
Telematics insurance uses real-time driving data collected through devices or apps to assess risk and personalize premiums based on driving behavior, while pay-per-mile insurance charges customers solely based on the number of miles driven. Telematics offers insights into factors like speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, enabling more accurate risk profiling, whereas pay-per-mile focuses on mileage as the primary cost driver, benefiting low-mileage drivers. Choosing between these depends on whether personalized driving habits or simply distance-driven aligns better with the insured's lifestyle and budget.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Telematics Insurance | Pay-Per-Mile Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses driving behavior data via a device or app to determine premiums. | Charges customers based on actual miles driven. |
| Pricing Model | Dynamic pricing based on speed, braking, acceleration, and time of driving. | Fixed rate per mile plus a base premium. |
| Ideal For | Safe drivers seeking personalized rates based on driving habits. | Low-mileage drivers who want to pay only for miles driven. |
| Data Collected | Driving behavior metrics, route, speed, braking patterns. | Mileage data only. |
| Privacy Impact | Higher due to extensive driving data monitoring. | Lower; tracks mileage without detailed driving behavior. |
| Cost Savings | Potentially significant for safe drivers with good habits. | Best for drivers with low annual mileage. |
| Technology Required | Telematics device or mobile app installation. | Odometer readings or simple mileage tracking apps. |
| Claim Influence | Driving data can impact claims and premiums over time. | Claims not influenced by driving behavior, only mileage. |
Understanding Telematics in Auto Insurance
Telematics in auto insurance leverages GPS and onboard diagnostics to monitor driving behavior, including speed, acceleration, braking patterns, and mileage. This data enables insurers to assess risk more accurately and offer personalized premiums based on actual driving habits. Unlike pay-per-mile insurance, which charges solely based on distance driven, telematics policies encompass a broader range of driving metrics to incentivize safer driving and reduce claims.
What Is Pay-Per-Mile Insurance?
Pay-per-mile insurance charges policyholders based on the actual number of miles they drive, providing a cost-effective option for low-mileage drivers. This model uses odometer readings or GPS tracking to calculate premiums, aligning insurance costs with individual driving habits. Unlike traditional insurance, pay-per-mile offers personalized rates that can lead to significant savings for infrequent drivers.
Key Differences Between Telematics and Pay-Per-Mile Insurance
Telematics insurance uses data from in-vehicle devices to monitor driving behavior, including speed, braking, and acceleration, to determine premiums. Pay-per-mile insurance charges customers based strictly on the number of miles driven, providing a straightforward cost model without behavioral data analysis. The key difference lies in telematics focusing on driving habits for risk assessment, while pay-per-mile bases cost solely on distance traveled.
Advantages of Telematics-Based Policies
Telematics-based insurance policies offer enhanced risk assessment by collecting real-time driving data, leading to more accurate premium pricing and personalized discounts. These policies incentivize safer driving behaviors through instant feedback and rewards, promoting reduced accident rates and overall road safety. Compared to pay-per-mile insurance, telematics provides a comprehensive view of driving habits beyond mileage, including speed, braking, and cornering patterns, improving insurer's ability to tailor coverage and manage risk effectively.
Benefits of Pay-Per-Mile Insurance Models
Pay-per-mile insurance models significantly reduce costs for low-mileage drivers by charging premiums based solely on the number of miles driven, promoting affordability and fairness. This approach encourages safer driving habits and decreased vehicle usage, leading to lower accident risks and reduced environmental impact. Insurers benefit from more accurate risk assessment and pricing, enhancing customer satisfaction through personalized premiums.
Data Collection and Privacy Concerns
Telematics insurance collects real-time driving data such as speed, acceleration, and braking patterns through a device installed in the vehicle or a smartphone app, raising concerns about continuous monitoring and potential misuse of personal information. Pay-per-mile insurance tracks only the miles driven, limiting data collection to distance rather than detailed driving behavior, which can alleviate some privacy worries but still requires trust in how mileage data is stored and used. Both models demand transparent data policies and robust cybersecurity measures to protect policyholders' sensitive information from unauthorized access or exploitation.
Pricing Structure Comparison
Telematics insurance uses real-time driving data collected via devices or smartphone apps to adjust premiums based on individual driving behavior, rewarding safe drivers with lower rates. Pay-per-mile insurance charges customers based solely on the number of miles driven, providing cost savings primarily for low-mileage drivers regardless of driving habits. Pricing structures differ as telematics combines mileage with driving quality metrics, while pay-per-mile relies exclusively on distance traveled, impacting cost effectiveness for varied driver profiles.
Who Should Choose Telematics Insurance?
Drivers who want personalized premiums based on detailed driving behavior should choose telematics insurance, as it uses real-time data from devices to monitor speed, braking, and mileage. This option benefits safe, low-risk drivers aiming to reduce premiums through improved driving habits. Urban commuters and families with variable driving patterns also gain from telematics insurance's tailored risk assessment and cost savings.
Ideal Customers for Pay-Per-Mile Insurance
Ideal customers for pay-per-mile insurance are low-mileage drivers who use their vehicles infrequently, such as retirees, urban residents, and remote workers. These customers benefit from significant cost savings as premiums directly correlate with the exact miles driven, offering a fairer pricing model compared to traditional coverage. Insurers targeting this market segment leverage telematics data to accurately track mileage, ensuring transparent and personalized premium calculations.
Future Trends in Usage-Based Car Insurance
Future trends in usage-based car insurance reveal significant advancements in telematics technology, enabling more precise data collection on driving behavior, vehicle usage, and environmental conditions. Pay-per-mile insurance models are evolving alongside telematics, offering customizable premiums based on actual mileage and driving patterns, promoting fairness and cost efficiency. Integration of AI and IoT devices is expected to enhance risk assessment accuracy and foster broader adoption of personalized insurance policies.
Related Important Terms
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics technology to monitor driving behavior, offering personalized premiums based on real-time data such as speed, acceleration, and braking patterns. Pay-Per-Mile insurance, a subset of UBI, calculates premiums primarily on the exact number of miles driven, providing cost savings for low-mileage drivers by directly correlating insurance costs with vehicle usage.
Connected Car Data
Telematics insurance leverages real-time connected car data such as driving behavior, speed, and braking patterns to personalize premiums, while pay-per-mile insurance calculates costs strictly based on the number of miles driven without detailed behavioral insights. Connected car data in telematics provides deeper risk assessment and encourages safer driving habits, offering more precise pricing compared to the distance-focused pay-per-mile model.
Driving Behavior Analytics
Telematics insurance leverages driving behavior analytics by using real-time data from GPS and onboard sensors to monitor acceleration, braking, and cornering, enabling personalized risk assessments and premium adjustments. Pay-per-mile insurance primarily charges based on distance driven but may incorporate limited behavior data, offering cost savings for low-mileage drivers without comprehensive driving pattern analysis.
In-Car IoT Sensors
In-car IoT sensors enable telematics insurance to collect real-time driving data such as speed, braking patterns, and acceleration, allowing for personalized risk assessment and dynamic pricing. Pay-per-mile insurance primarily uses odometer data to charge premiums based on distance driven, resulting in simpler, cost-effective coverage without detailed behavior analysis.
Real-Time Mileage Tracking
Telematics insurance uses real-time data from in-vehicle devices to monitor driving behavior and mileage continuously, enabling precise risk assessment and personalized premiums. Pay-per-mile insurance charges based solely on actual miles driven, often using GPS tracking or odometer readings, but lacks the comprehensive behavioral insights provided by telematics systems.
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD)
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD) insurance calculates premiums based on actual miles driven, offering cost savings for low-mileage drivers by aligning costs with road usage. Unlike general telematics, which assess driving behavior and risk factors, PAYD focuses solely on distance, making it a straightforward, mileage-based pricing model.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) Devices
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) devices enable telematics insurance to monitor comprehensive driving behavior, including speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, providing insurers with detailed risk profiles beyond mere mileage tracking. Pay-Per-Mile insurance primarily utilizes OBD-II data to measure distance driven, offering a simplified pricing model focused on actual road usage rather than driving habits.
Continuous Digital Underwriting
Continuous digital underwriting in telematics insurance leverages real-time driving data to dynamically assess risk and adjust premiums, enhancing personalization and accuracy. Pay-per-mile insurance, while usage-based, relies primarily on mileage tracking without the comprehensive behavioral insights that telematics provides for continuous risk evaluation.
Dynamic Risk Scoring
Telematics insurance utilizes continuous data collection for dynamic risk scoring by analyzing driving behavior in real-time, enabling personalized premium adjustments based on actual risk exposure. Pay-per-mile insurance calculates costs primarily on distance traveled, lacking the granular driving behavior insights that dynamic risk scoring in telematics offers for more accurate risk assessment.
Smartphone Telematics Apps
Smartphone telematics apps offer real-time driving behavior monitoring by leveraging GPS and sensor data to provide personalized insurance rates, enhancing the accuracy over traditional pay-per-mile insurance that charges solely based on distance traveled. These apps enable insurers to assess risk dynamically through factors like speed, braking patterns, and trip times, leading to more tailored premiums and improved driver safety incentives.
Telematics vs Pay-Per-Mile Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com