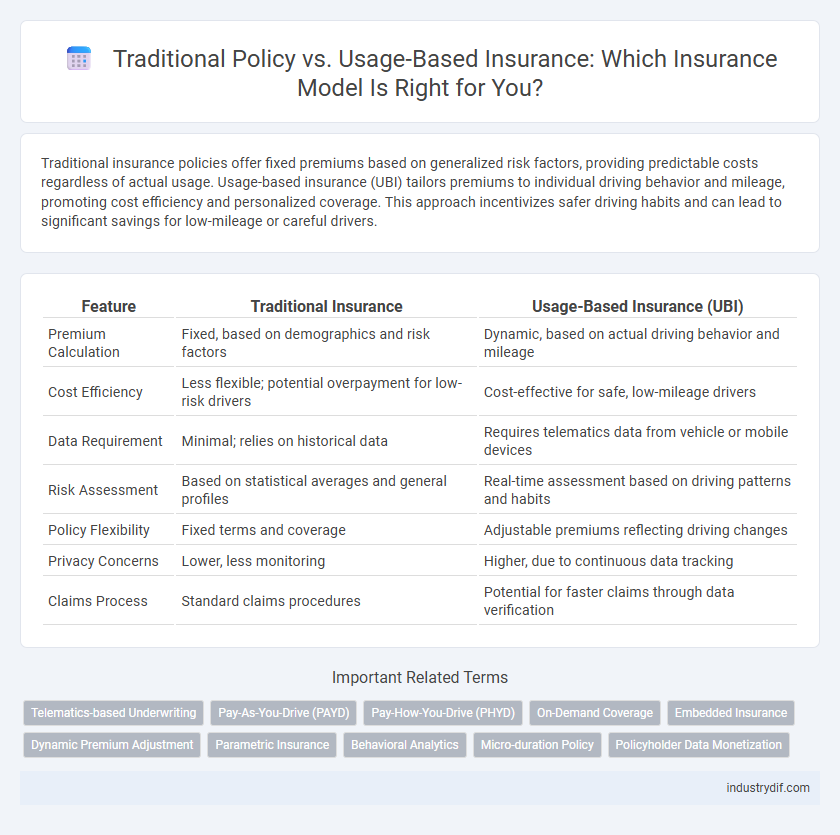
Traditional insurance policies offer fixed premiums based on generalized risk factors, providing predictable costs regardless of actual usage. Usage-based insurance (UBI) tailors premiums to individual driving behavior and mileage, promoting cost efficiency and personalized coverage. This approach incentivizes safer driving habits and can lead to significant savings for low-mileage or careful drivers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Calculation | Fixed, based on demographics and risk factors | Dynamic, based on actual driving behavior and mileage |
| Cost Efficiency | Less flexible; potential overpayment for low-risk drivers | Cost-effective for safe, low-mileage drivers |
| Data Requirement | Minimal; relies on historical data | Requires telematics data from vehicle or mobile devices |
| Risk Assessment | Based on statistical averages and general profiles | Real-time assessment based on driving patterns and habits |
| Policy Flexibility | Fixed terms and coverage | Adjustable premiums reflecting driving changes |
| Privacy Concerns | Lower, less monitoring | Higher, due to continuous data tracking |
| Claims Process | Standard claims procedures | Potential for faster claims through data verification |
Overview of Traditional Insurance Policies
Traditional insurance policies offer fixed premiums based on factors such as age, location, and driving history, providing predictable costs for policyholders. Coverage typically remains constant regardless of actual usage, making it suitable for drivers with consistent mileage and risk profiles. These policies emphasize long-term stability and broad protection without real-time data integration.
Understanding Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics technology to monitor real-time driving behavior, enabling personalized premiums based on factors such as mileage, speed, and driving patterns. Unlike traditional policies that use generalized risk profiles and static data, UBI provides dynamic risk assessment, offering cost savings for low-risk drivers. This data-driven approach enhances transparency and encourages safer driving habits while optimizing insurance costs for both providers and policyholders.
Key Differences Between Traditional and UBI Models
Traditional insurance policies rely on fixed premiums based on demographic factors and historical data, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages real-time driving behavior and mileage tracked via telematics devices. UBI models offer personalized risk assessment and potentially lower costs for safer drivers by analyzing specific metrics such as acceleration, braking patterns, and driving hours. Traditional policies often lack the dynamic pricing flexibility and immediate feedback that UBI provides, resulting in more generalized risk pools and pricing structures.
Premium Calculation Methods: Fixed vs. Variable
Traditional insurance policies calculate premiums using fixed rates based on demographics, vehicle type, and historical risk factors, resulting in predictable but less personalized costs. Usage-based insurance (UBI) employs variable premium calculation methods by analyzing real-time driving data such as mileage, speed, and driving behavior, allowing for more accurate risk assessment and potentially lower costs. Variable premiums in UBI incentivize safer driving habits, while fixed premiums in traditional policies provide straightforward budgeting without consideration of individual usage patterns.
Policyholder Eligibility and Customization
Traditional insurance policies often require standardized eligibility criteria based on demographic factors and fixed risk assessments, limiting customization options for policyholders. Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics and real-time driving data to offer tailored coverage, enabling personalized premiums and flexible policy terms aligned with individual behavior. This data-driven approach enhances risk accuracy while expanding eligibility to a broader range of drivers beyond conventional underwriting constraints.
Impact of Telematics and Data Collection
Telematics and data collection revolutionize traditional insurance policies by enabling usage-based insurance (UBI) models that assess risk through real-time driving behavior and patterns. This granular data improves premium accuracy, reduces fraud, and encourages safer driving habits by providing personalized feedback and incentives. Consequently, insurers leverage telematics to enhance customer engagement and optimize claims processing efficiency.
Privacy Concerns in Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based insurance (UBI) collects extensive personal driving data through telematics devices, raising significant privacy concerns among policyholders. Unlike traditional policies that rely on general risk factors, UBI tracks real-time location, speed, and driving behavior, potentially exposing sensitive information to insurers and third parties. Ensuring data security and transparent usage policies is critical to maintaining consumer trust in usage-based insurance models.
Risk Assessment and Claims Management
Traditional insurance policies rely on demographic data and historical loss statistics for risk assessment, often resulting in generalized premium pricing. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics data and real-time driving behavior analysis to provide personalized risk profiles, enhancing accuracy in premium calculation. Claims management in usage-based insurance benefits from precise event data, allowing faster verification and more efficient claim processing compared to the conventional assessment methods used in traditional policies.
Cost Savings and Incentives for Customers
Traditional insurance policies often involve fixed premiums that may not reflect individual driving behavior, leading to potentially higher costs for low-risk drivers. Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics data to assess driving habits, enabling personalized pricing and significant cost savings by rewarding safe driving with lower premiums. Incentives in UBI programs commonly include discounts, cashback offers, and tailored safety recommendations, enhancing customer engagement and promoting risk reduction.
Future Trends in Auto Insurance Industry
Traditional auto insurance policies rely on fixed premiums based on demographic data and historical risk assessments, while usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics to offer dynamic pricing tied to actual driving behavior. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards UBI models enhanced by AI and IoT technologies, enabling more personalized, real-time risk evaluation and fraud detection. This transformation drives cost efficiency, encourages safer driving habits, and supports the growth of smart, connected vehicles within the insurance ecosystem.
Related Important Terms
Telematics-based Underwriting
Telematics-based underwriting leverages real-time data on driving behavior, location, and vehicle usage to create personalized insurance premiums, making usage-based insurance more accurate and fair compared to traditional policies that rely on static factors like age and driving history. This approach reduces risk for insurers by enabling dynamic pricing and encourages safer driving habits, ultimately benefiting both policyholders and providers.
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD)
Traditional insurance policies typically charge fixed premiums based on estimated risk factors, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), particularly Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD), calculates premiums according to actual mileage driven and driving behavior, promoting cost-effectiveness and personalized coverage. PAYD leverages telematics data to adjust rates in real-time, encouraging safer driving habits and potentially lowering insurance expenses for low-mileage drivers.
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD)
Traditional insurance policies charge fixed premiums based on general risk factors, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), particularly Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD) models, calculate premiums dynamically using real-time driving data such as distance, speed, and braking patterns. PHYD policies leverage telematics technology to reward safe driving behavior with lower premiums, enhancing personalized risk assessment and cost savings.
On-Demand Coverage
Traditional insurance policies offer fixed premiums and coverage limits regardless of actual usage, leading to potentially higher costs for infrequent drivers. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics and real-time data to provide on-demand coverage with dynamic pricing, allowing policyholders to pay precisely for the miles driven and driving behavior, optimizing cost efficiency and risk assessment.
Embedded Insurance
Traditional insurance policies offer fixed premiums based on general risk factors, while usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics and real-time data to tailor premiums according to actual driving behavior and mileage. Embedded insurance seamlessly integrates UBI into digital platforms, enabling customers to purchase personalized coverage at the point of sale, enhancing convenience and reducing underwriting complexity.
Dynamic Premium Adjustment
Traditional insurance policies use fixed premiums based on generalized risk factors, resulting in static pricing that may not reflect actual driver behavior. Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics data to enable dynamic premium adjustment, rewarding safe driving habits with lower costs and providing more personalized coverage.
Parametric Insurance
Traditional insurance policies typically involve claims adjustments based on loss assessments, whereas parametric insurance offers predefined payouts triggered by specific parameters such as weather events or natural disasters, enabling faster and more transparent claims processing. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics data to personalize premiums, but parametric insurance uniquely reduces indemnity delays by using objective, verifiable triggers rather than subjective damage evaluations.
Behavioral Analytics
Traditional insurance policies rely on fixed premiums determined by demographic factors and historical data, often failing to accurately reflect individual risk behavior. Usage-based insurance leverages behavioral analytics through telematics and real-time data monitoring to personalize premiums based on actual driving habits, enhancing risk assessment and promoting safer driving patterns.
Micro-duration Policy
Traditional insurance policies typically involve fixed premiums based on broad risk assessments and long-term coverage periods, whereas micro-duration policies in usage-based insurance offer flexible, short-term coverage tailored to specific usage intervals. This approach leverages telematics data to provide customized premiums, enhancing affordability and responsiveness for low-frequency or sporadic drivers.
Policyholder Data Monetization
Traditional insurance policies rely on aggregated historical data and generalized risk profiles, limiting policyholder data monetization potential. Usage-based insurance leverages real-time telematics and behavioral data, enabling insurers to create personalized premiums and unlock continuous data-driven revenue streams from policyholders.
Traditional policy vs Usage-based insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com