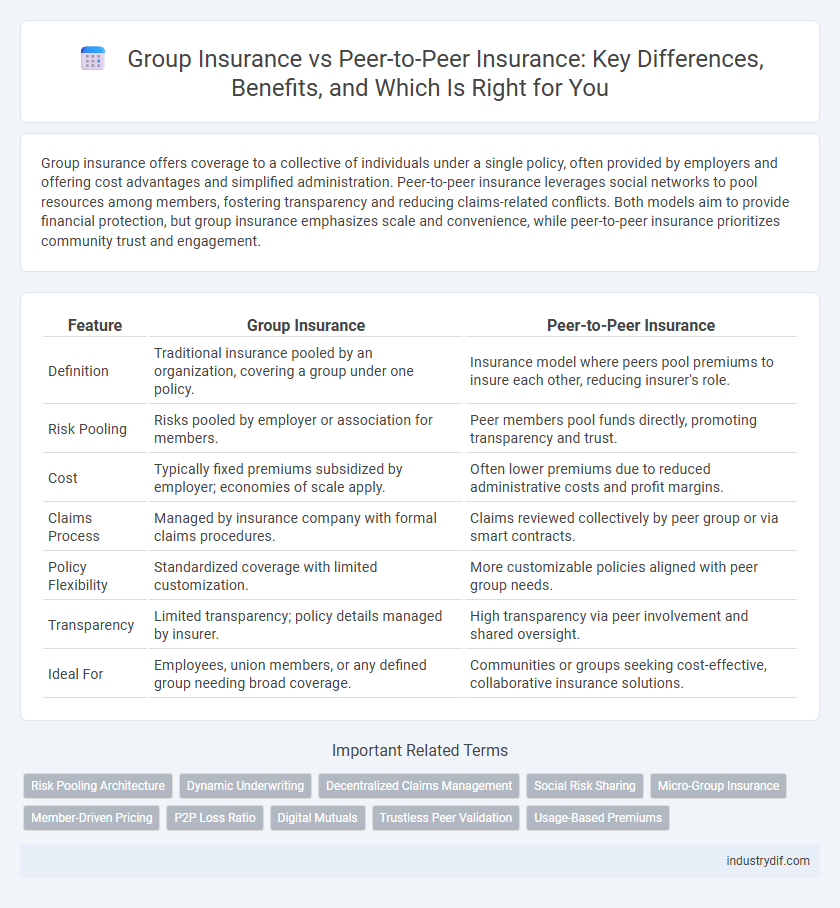
Group insurance offers coverage to a collective of individuals under a single policy, often provided by employers and offering cost advantages and simplified administration. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages social networks to pool resources among members, fostering transparency and reducing claims-related conflicts. Both models aim to provide financial protection, but group insurance emphasizes scale and convenience, while peer-to-peer insurance prioritizes community trust and engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Group Insurance | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional insurance pooled by an organization, covering a group under one policy. | Insurance model where peers pool premiums to insure each other, reducing insurer's role. |
| Risk Pooling | Risks pooled by employer or association for members. | Peer members pool funds directly, promoting transparency and trust. |
| Cost | Typically fixed premiums subsidized by employer; economies of scale apply. | Often lower premiums due to reduced administrative costs and profit margins. |
| Claims Process | Managed by insurance company with formal claims procedures. | Claims reviewed collectively by peer group or via smart contracts. |
| Policy Flexibility | Standardized coverage with limited customization. | More customizable policies aligned with peer group needs. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; policy details managed by insurer. | High transparency via peer involvement and shared oversight. |
| Ideal For | Employees, union members, or any defined group needing broad coverage. | Communities or groups seeking cost-effective, collaborative insurance solutions. |
Introduction to Group Insurance
Group insurance provides coverage to a collective of individuals under a single policy, often sponsored by an employer or organization. This type of insurance typically offers cost-effective premiums, standardized benefits, and streamlined administration compared to individual policies. It reduces individual risk exposure by pooling members together, enhancing access to health, life, or disability insurance options.
Understanding Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance is a decentralized insurance model where members pool their premiums to insure against shared risks, reducing reliance on traditional insurers. This approach enhances transparency, lowers administrative costs, and can result in premium savings by returning unused funds to members. By leveraging technology and social networks, P2P insurance fosters community trust and customized coverage options distinct from conventional group insurance plans.
Key Features of Group Insurance
Group insurance offers collective coverage for a defined group, typically employees within a company or members of an organization, providing cost-effective premiums through risk pooling. Key features include uniform policy terms, employer-paid or subsidized premiums, and comprehensive benefits such as health, dental, and life insurance tailored to meet the group's needs. This model ensures simplified administration, guaranteed issue without individual underwriting, and enhances employee retention by offering valuable protection.
Core Principles of P2P Insurance
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance operates on the core principle of risk-sharing within a trusted community, contrasting traditional group insurance where a central insurer manages risk pools. In P2P models, members contribute premiums into a shared fund that covers claims collectively, promoting transparency and reducing administrative costs. This decentralized approach aligns incentives between members and minimizes conflicts of interest inherent in conventional insurance structures.
Coverage and Policy Structure Comparison
Group insurance offers comprehensive coverage through a single policy underwritten for an entire group, typically providing standardized benefits and easier administration. Peer-to-peer insurance relies on a decentralized model where members pool premiums to cover claims, often resulting in more customizable coverage but variable risk distribution. The policy structure in group insurance ensures consistent coverage terms for all members, whereas peer-to-peer insurance policies may vary based on the group's dynamics and claim patterns.
Cost and Premium Differences
Group insurance typically offers lower premiums due to risk pooling across a large member base, reducing individual cost exposure. Peer-to-peer insurance can result in cost savings through diminished administrative fees and profit margins, often allowing premiums to reflect the actual claim experience of the smaller community. Premium structures in group insurance are more standardized, while peer-to-peer models provide dynamic pricing that can adapt based on the claim behavior of the members involved.
Risk Sharing Models
Group insurance pools risk across a large number of policyholders through a centralized entity, typically an employer or association, offering predictable premiums and broader coverage. Peer-to-peer insurance distributes risk within smaller, self-selected groups, promoting transparency and often lower costs by reducing administrative overhead and aligning incentives for loss prevention. Both models leverage collective risk sharing but differ in structure, scale, and control over underwriting practices.
Claims Process: Group vs P2P
The claims process in group insurance typically involves a centralized administrator who reviews and approves claims based on predefined policy terms, ensuring standardized handling and quicker payouts. In peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance, claims are often reviewed collectively by members within the peer group, promoting transparency and potential cost savings but possibly extending processing times. Group insurance offers reliability through established procedures, whereas P2P insurance enhances trust via member involvement in claims adjudication.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Model
Group insurance offers broad risk pooling and cost efficiency, providing members with predictable premiums and comprehensive coverage, but it often lacks customization and may include non-transparent administrative fees. Peer-to-peer insurance enhances transparency and member control by allowing participants to share risks directly, reducing conflicts of interest and potentially lowering costs, yet it faces challenges in scalability, regulatory compliance, and risk concentration. Evaluating the balance between collective risk management efficiency in group insurance and the innovative, community-driven approach in peer-to-peer models is essential for choosing the appropriate coverage framework.
Choosing the Best Insurance Solution
Choosing the best insurance solution depends on individual needs, risk tolerance, and cost considerations between group insurance and peer-to-peer insurance. Group insurance offers collective coverage with potentially lower premiums through employer or association plans, providing stability and broad risk pooling. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages community-based risk sharing, often resulting in increased transparency, potential refunds on claims, and more personalized coverage options.
Related Important Terms
Risk Pooling Architecture
Group insurance relies on a centralized risk pooling architecture where premiums from a large collective are aggregated to cover claims, enabling diversified risk and cost stability. Peer-to-peer insurance employs a decentralized risk pool, connecting smaller groups of peers who share risk directly, often enhancing transparency and aligning incentives to reduce fraudulent claims.
Dynamic Underwriting
Dynamic underwriting in group insurance leverages aggregated risk data to adjust premiums periodically, ensuring more accurate risk assessments for large member pools. Peer-to-peer insurance utilizes real-time behavioral data and social trust metrics to dynamically underwrite individual policies, promoting personalized risk management and potential premium discounts.
Decentralized Claims Management
Decentralized claims management in peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain technology to enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and expedite payouts by allowing policyholders to validate claims collaboratively. Group insurance typically relies on centralized administrative bodies, which may introduce delays and less transparency in claims processing compared to the decentralized peer-to-peer model.
Social Risk Sharing
Group insurance pools premiums from multiple members under a single policy, offering collective risk coverage and reduced individual costs through economies of scale. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages social risk sharing by connecting individuals directly, enabling more transparent claims handling and fostering trust within smaller, self-governed risk pools.
Micro-Group Insurance
Micro-group insurance offers tailored coverage for small, closely-knit groups, enhancing risk pooling and cost efficiency compared to traditional group insurance plans. Unlike peer-to-peer insurance, which relies on decentralized member claims management, micro-group insurance maintains structured underwriting and administration while fostering community-based support within limited member pools.
Member-Driven Pricing
Group insurance typically offers member-driven pricing based on collective risk assessments and employer contributions, resulting in more stable premiums aligned with the overall group's demographics. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages member-driven pricing by pooling risk among smaller, self-selected groups, often incorporating real-time data and transparency to adjust premiums dynamically and potentially reduce costs.
P2P Loss Ratio
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance typically achieves lower loss ratios compared to traditional group insurance by pooling risk among a smaller, more transparent community, which reduces fraud and administrative costs. This model aligns incentives between members, improving claim management efficiency and enhancing overall cost-effectiveness in loss ratio performance.
Digital Mutuals
Group insurance pools risk among a defined member base, typically managed by a centralized insurer, offering standardized coverage and collective bargaining advantages. Digital mutuals in peer-to-peer insurance leverage blockchain and smart contracts to enable decentralized risk sharing, increased transparency, and reduced administrative costs, empowering members to directly influence policy terms and claims management.
Trustless Peer Validation
Trustless peer validation in peer-to-peer insurance eliminates the need for a centralized authority by leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts to verify claims transparently and securely. Unlike traditional group insurance, this decentralized approach enhances trust among participants through automated consensus mechanisms and immutable transaction records.
Usage-Based Premiums
Group insurance typically calculates premiums based on aggregated risk factors of the entire group, offering stable yet less personalized rates. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages usage-based premiums driven by individual behavior data, enabling more accurate pricing and potential cost savings for low-risk policyholders.
Group Insurance vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com