Policy insurance typically involves comprehensive coverage with higher premiums, suited for individuals seeking extensive protection against significant risks. Microinsurance provides affordable, limited coverage tailored to low-income populations, focusing on essential risks like health, agriculture, or property. Both options address different market needs by balancing coverage scope and cost.
Table of Comparison
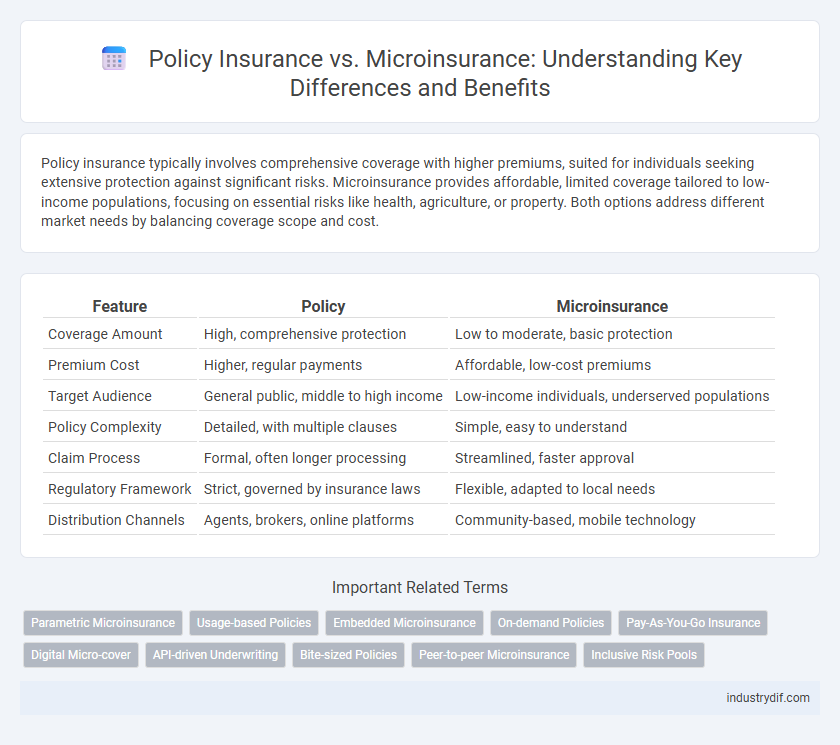
| Feature | Policy | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Amount | High, comprehensive protection | Low to moderate, basic protection |
| Premium Cost | Higher, regular payments | Affordable, low-cost premiums |
| Target Audience | General public, middle to high income | Low-income individuals, underserved populations |
| Policy Complexity | Detailed, with multiple clauses | Simple, easy to understand |
| Claim Process | Formal, often longer processing | Streamlined, faster approval |
| Regulatory Framework | Strict, governed by insurance laws | Flexible, adapted to local needs |
| Distribution Channels | Agents, brokers, online platforms | Community-based, mobile technology |
Understanding Traditional Insurance Policies
Traditional insurance policies typically involve comprehensive coverage with higher premiums and long-term contracts designed to protect against significant financial risks such as property damage, health emergencies, or life insurance claims. These policies often require detailed underwriting processes, including medical exams or property assessments, to determine risk levels and premium costs. In contrast, microinsurance targets low-income individuals by offering affordable, simplified coverage with lower premiums and shorter terms, focusing on basic protection against specific risks.
Defining Microinsurance: Key Characteristics
Microinsurance provides affordable coverage tailored for low-income individuals, offering protection against specific risks such as health, agriculture, or property loss with lower premiums and simplified underwriting compared to traditional insurance policies. Key characteristics include limited coverage amounts, easy enrollment processes, and flexible payment options often aligned with the insured's income schedule. Unlike conventional policies, microinsurance emphasizes accessibility, community-based distribution, and rapid claims settlement to support vulnerable populations.
Coverage Scope: Policy vs Microinsurance
Traditional insurance policies typically offer comprehensive coverage, including extensive protection against a wide range of risks such as health, property, liability, and life, often with higher coverage limits and customizable options. Microinsurance, by contrast, provides limited coverage tailored to low-income individuals, focusing on specific, high-impact risks like basic health emergencies, crop failure, or small asset damage, with lower premiums and simplified claim processes. The coverage scope of microinsurance is narrower and more targeted, designed to address the essential protection gaps often underserved by full-scale policy offerings.
Target Consumer Segments Comparison
Traditional insurance policies primarily target middle to high-income consumers seeking comprehensive coverage with higher premiums and extensive benefits. Microinsurance is designed for low-income and underserved populations, offering affordable, simplified coverage with lower premiums and limited benefits tailored to financial constraints. Both approaches focus on risk protection, but microinsurance emphasizes accessibility and inclusivity for vulnerable groups.
Premium Structures and Payment Flexibility
Policy premiums often require higher fixed payments, designed for comprehensive coverage with scheduled payment intervals, whereas microinsurance features lower, more affordable premiums tailored to low-income clients, often allowing flexible payment options such as daily or weekly installments. Microinsurance premium structures emphasize accessibility and simplicity to accommodate irregular income streams common in underserved populations. Payment flexibility in microinsurance enhances enrollment and retention rates by enabling participants to align premium payments with their cash flow patterns, contrasting with traditional insurance policies that may impose stricter payment schedules and penalties.
Claims Process: Policy versus Microinsurance
The claims process for traditional insurance policies often involves extensive documentation, longer approval times, and higher premiums reflective of comprehensive coverage. Microinsurance simplifies claims procedures by offering streamlined, digital claim submissions and faster payouts, catering specifically to low-income or underserved populations. This efficient claims handling reduces barriers and enhances accessibility while maintaining adequate protection for policyholders.
Distribution Channels and Accessibility
Policy insurance typically relies on traditional distribution channels such as agents, brokers, and bancassurance networks, which can limit accessibility for low-income or rural populations. Microinsurance leverages alternative channels including mobile platforms, community-based organizations, and direct outreach to improve accessibility and enrollment in underserved areas. These innovative distribution methods enhance convenience and affordability, effectively bridging the insurance gap for vulnerable groups.
Regulatory Frameworks for Policies and Microinsurance
Regulatory frameworks for insurance policies often involve stringent compliance requirements, risk assessment protocols, and capital reserve standards governed by national insurance commissions to protect policyholders. Microinsurance regulations are designed to be more flexible, enabling broader access for low-income populations by simplifying underwriting processes and reducing minimum capital thresholds. Both frameworks aim to balance consumer protection with market accessibility, ensuring sustainable growth within the insurance sector.
Advantages and Challenges of Microinsurance
Microinsurance offers affordable, accessible coverage tailored to low-income individuals who often lack traditional insurance options, providing protection against risks such as health emergencies, natural disasters, and crop failures. Its advantages include simplified application processes, lower premiums, and community-based risk pooling that enhances inclusivity. Challenges encompass limited coverage scope, potential for lower claim payouts, difficulties in regulatory compliance, and the need for greater consumer education to ensure understanding and trust.
Future Trends in Insurance: Standard Policy vs Microinsurance
Future trends in insurance show a growing shift towards microinsurance, driven by increasing demand for affordable, accessible coverage among low-income and underserved populations. Standard policies continue to dominate traditional markets with comprehensive coverage, but technological advancements like AI and mobile platforms enable microinsurance to expand rapidly. Data analytics and digital distribution channels will further optimize risk assessment and streamline claims processing, bridging gaps between conventional policies and microinsurance solutions.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers a streamlined alternative to traditional insurance policies by paying out fixed benefits based on predefined triggers such as weather events, enabling faster claims settlement and reduced administrative costs. This model enhances financial inclusion by providing affordable coverage tailored to low-income individuals vulnerable to specific risks, contrasting with conventional policies that rely on loss assessments and complex underwriting.
Usage-based Policies
Usage-based policies leverage telematics and real-time data to tailor premiums based on individual driving behavior, making them more dynamic and personalized compared to traditional insurance policies. Microinsurance targets low-income populations by offering affordable, limited-coverage plans, while usage-based policies emphasize risk-based pricing and engagement through continuous monitoring.
Embedded Microinsurance
Embedded microinsurance integrates insurance coverage directly into everyday products or services, offering affordable, accessible protection tailored to low-income consumers. Unlike traditional policies with formal underwriting and separate transactions, embedded microinsurance leverages digital platforms and partnerships to streamline enrollment and claims, enhancing financial inclusion.
On-demand Policies
On-demand policies offer flexible, pay-per-use insurance coverage tailored for short-term needs, contrasting with traditional policies that require long-term commitments and higher premiums. Microinsurance provides affordable, limited coverage to low-income individuals, often integrating on-demand features to increase accessibility and responsiveness.
Pay-As-You-Go Insurance
Pay-As-You-Go insurance enables policyholders to pay premiums based on actual usage or risk exposure, offering flexibility compared to traditional insurance policies that require fixed periodic payments. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, limited coverage, often integrating Pay-As-You-Go models to increase accessibility and reduce financial barriers.
Digital Micro-cover
Digital microinsurance provides affordable, tailored coverage through mobile platforms, enabling low-income populations to access essential protection with minimal premiums and simplified claims processes. Unlike traditional policies, digital micro-covers leverage technology to offer flexible, on-demand insurance solutions that bridge coverage gaps in underserved markets.
API-driven Underwriting
API-driven underwriting enhances efficiency and accuracy in both traditional insurance policies and microinsurance by enabling real-time data integration and automated risk assessment. This technology allows insurers to tailor coverage options quickly and cost-effectively, meeting the diverse needs of large-scale policyholders and underserved microinsurance markets.
Bite-sized Policies
Bite-sized policies in microinsurance offer affordable, customizable coverage options designed to meet the specific needs of low-income individuals, providing financial protection without the high premiums or complex terms of traditional insurance policies. These small-scale insurance plans enable policyholders to manage risks in manageable increments, enhancing accessibility and encouraging wider adoption in underserved markets.
Peer-to-peer Microinsurance
Peer-to-peer microinsurance leverages community-based risk sharing to offer affordable, tailored coverage for low-income individuals, contrasting traditional insurance policies that rely on centralized underwriting and complex bureaucracy. This model enhances transparency and trust by enabling participants to pool funds directly, reducing administrative costs and improving claim processing efficiency.
Inclusive Risk Pools
Traditional insurance policies often require higher premiums and extensive underwriting, limiting accessibility for low-income individuals, whereas microinsurance offers affordable, simplified coverage designed to include marginalized populations in risk pools. Inclusive risk pools in microinsurance enhance financial resilience by spreading risks across a broader base, promoting equitable access to protection against health, agricultural, and disaster-related losses.
Policy vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com