Indemnity insurance provides financial protection by compensating policyholders for losses according to the terms of their contract with a traditional insurer. Peer-to-peer insurance operates on a shared risk model where members contribute premiums to a collective pool used to pay claims, often leading to lower costs and increased transparency. This innovative approach fosters community trust while maintaining the financial security associated with indemnity coverage.
Table of Comparison
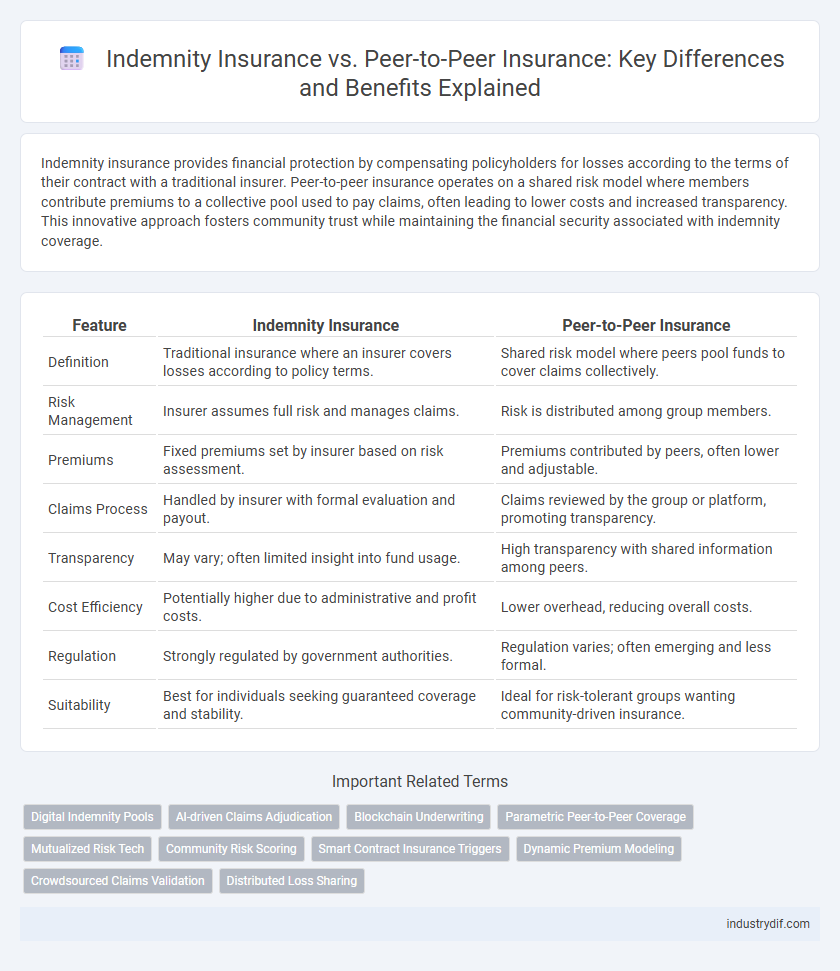
| Feature | Indemnity Insurance | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional insurance where an insurer covers losses according to policy terms. | Shared risk model where peers pool funds to cover claims collectively. |
| Risk Management | Insurer assumes full risk and manages claims. | Risk is distributed among group members. |
| Premiums | Fixed premiums set by insurer based on risk assessment. | Premiums contributed by peers, often lower and adjustable. |
| Claims Process | Handled by insurer with formal evaluation and payout. | Claims reviewed by the group or platform, promoting transparency. |
| Transparency | May vary; often limited insight into fund usage. | High transparency with shared information among peers. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher due to administrative and profit costs. | Lower overhead, reducing overall costs. |
| Regulation | Strongly regulated by government authorities. | Regulation varies; often emerging and less formal. |
| Suitability | Best for individuals seeking guaranteed coverage and stability. | Ideal for risk-tolerant groups wanting community-driven insurance. |
Understanding Indemnity Insurance
Indemnity insurance reimburses policyholders for actual losses incurred, ensuring financial protection by restoring their pre-loss financial position. This type of insurance typically involves contracts with traditional insurers who assess and settle claims based on verified damages. Understanding indemnity insurance is essential for risk management, as it offers precise compensation rather than fixed benefits or group-funded payouts characteristic of peer-to-peer insurance models.
What Is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance?
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance is a decentralized approach where individuals pool their premiums to insure against risks collectively, reducing reliance on traditional insurance companies. This model promotes transparency and cost-efficiency by refunding unused premiums back to policyholders, enhancing trust and reducing fraud. P2P Insurance leverages technology platforms to connect members, improve claims processing, and foster a community-driven risk management system.
Key Differences Between Indemnity and P2P Insurance
Indemnity insurance reimburses policyholders for actual losses up to the coverage limit, operating through traditional insurers that manage risk and claims. Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance pools premiums from a group of individuals who share similar risks, enabling direct risk sharing without a traditional insurer's involvement. Key differences include claim processing methods, risk pooling models, and the potential for premium refunds or lower costs in P2P structures versus fixed premiums and indemnity limits in traditional indemnity insurance.
How Indemnity Insurance Works
Indemnity insurance compensates policyholders for actual financial losses incurred, reimbursing costs up to the coverage limit rather than providing predetermined benefits. Claims are assessed based on verified damages or losses, ensuring that payouts correspond directly to the insured event's impact. This model contrasts with peer-to-peer insurance, which pools member contributions and may use collective funds to cover claims.
How Peer-to-Peer Insurance Operates
Peer-to-peer insurance operates by pooling premiums from a group of individuals with similar risk profiles to collectively cover claims, reducing reliance on traditional insurance companies. This model leverages blockchain or digital platforms to enhance transparency and distribute claims payments directly among members. The structure incentivizes risk mitigation and cost savings by returning unused premiums back to the insured group.
Benefits of Indemnity Insurance
Indemnity insurance offers precise financial protection by reimbursing actual losses, ensuring policyholders recover the exact amount of their damages without overpayment or underpayment risks. This type of insurance provides clear contractual obligations and regulatory oversight, enhancing reliability and trust for individuals and businesses. The standardized claims process in indemnity insurance also facilitates quicker settlements and reduces disputes compared to alternative models like peer-to-peer insurance.
Advantages of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance offers reduced costs by eliminating traditional intermediaries and focusing on group risk-sharing among policyholders, leading to lower premiums. Enhanced transparency and increased trust emerge as members collaboratively manage claims and policies through digital platforms. The model promotes community-driven accountability, resulting in fewer fraudulent claims and more efficient claim processing.
Common Use Cases for Each Model
Indemnity insurance commonly serves individuals and businesses seeking coverage for property, health, and liability risks, offering defined compensation based on the extent of loss or damage. Peer-to-peer insurance is often utilized in communities or groups aiming to reduce premiums through shared risk pools, typically in niche markets like car insurance or renters' coverage. Both models address specific needs: indemnity insurance prioritizes guaranteed compensation, while peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes cost efficiency and community participation.
Cost Comparisons: Indemnity vs Peer-to-Peer
Indemnity insurance typically involves fixed premiums set by traditional insurers, often resulting in higher administrative costs and profit margins embedded in the pricing structure. Peer-to-peer insurance, by pooling members and reducing overhead, can offer lower premiums and potential refunds when claims are below expectations. Cost efficiency in peer-to-peer models stems from reduced intermediary involvement, enhancing affordability compared to conventional indemnity insurance policies.
Choosing the Right Insurance for Your Needs
Indemnity insurance provides financial compensation to policyholders for actual losses incurred, ensuring coverage tailored to specific risks like health, property, or liability claims. Peer-to-peer insurance operates through a community pooling funds to cover claims, often resulting in lower premiums and increased transparency, ideal for those seeking collaborative risk management. Choosing the right insurance depends on factors such as risk tolerance, coverage needs, premium budget, and preference for traditional insurer guarantees versus community-based models.
Related Important Terms
Digital Indemnity Pools
Digital indemnity pools in peer-to-peer insurance leverage blockchain technology to create transparent, decentralized fund management systems that enhance trust and reduce administrative costs compared to traditional indemnity insurance models. This digital approach enables members to contribute to and claim from a shared pool, aligning incentives and minimizing the involvement of intermediaries while maintaining indemnity principles.
AI-driven Claims Adjudication
AI-driven claims adjudication enhances indemnity insurance by automating damage assessment and fraud detection, resulting in faster, more accurate claim settlements. In peer-to-peer insurance, AI facilitates transparent and efficient claims processing by analyzing member data and optimizing risk-sharing among participants.
Blockchain Underwriting
Blockchain underwriting in indemnity insurance enhances transparency and reduces fraud by securely recording claims and policy details, ensuring accurate and timely compensation. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain to facilitate decentralized risk sharing, lowering costs and fostering trust among policyholders through automated smart contracts.
Parametric Peer-to-Peer Coverage
Parametric Peer-to-Peer Insurance leverages blockchain technology to automate claims processing by triggering payments based on predefined parameters like weather data or natural disaster indices, contrasting with traditional indemnity insurance that reimburses actual losses after claim verification. This model enhances transparency, reduces administrative costs, and provides faster payouts within decentralized communities sharing risk collectively.
Mutualized Risk Tech
Mutualized risk technology in indemnity insurance pools premiums to compensate policyholders based on individual loss assessments, ensuring financial protection through traditional underwriting. Peer-to-peer insurance utilizes blockchain and smart contracts for transparent risk-sharing among members, reducing middlemen and enabling more efficient claims processing within a decentralized network.
Community Risk Scoring
Indemnity insurance relies on traditional actuarial models for risk assessment, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages community risk scoring to evaluate collective risk profiles, enhancing transparency and fairness in premium calculation. Community risk scoring uses aggregated member data to identify risk patterns, fostering stronger member alignment and potentially reducing fraud through shared accountability.
Smart Contract Insurance Triggers
Indemnity insurance relies on traditional claim assessments while peer-to-peer insurance integrates smart contract insurance triggers to automate payouts based on predefined conditions recorded on a blockchain. Smart contract triggers enhance transparency and reduce fraud by instantly verifying events such as natural disasters or accidents, streamlining the claims process in peer-to-peer models.
Dynamic Premium Modeling
Indemnity insurance relies on fixed premium models based on risk assessments and past claims data, whereas peer-to-peer insurance employs dynamic premium modeling that adjusts contributions in real-time according to collective claim patterns and individual member behavior. This adaptive pricing mechanism in peer-to-peer insurance enhances cost efficiency and incentivizes risk reduction among participants.
Crowdsourced Claims Validation
Indemnity insurance relies on traditional underwriting and claims assessment by insurers, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages crowdsourced claims validation, enabling policyholders to collectively verify and approve claims, reducing fraud and administrative costs. This decentralized approach enhances transparency and trust by involving the insured community in the claims process, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Distributed Loss Sharing
Indemnity insurance operates on traditional risk transfer principles where an insurer compensates the insured for covered losses, while peer-to-peer insurance utilizes distributed loss sharing by pooling premiums among members to collectively cover claims, enhancing transparency and reducing costs. Distributed loss sharing in peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain or smart contract technology to automate claim payments, aligning incentives for risk management within the community.
Indemnity Insurance vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com