Life insurance provides financial protection by offering a lump sum or regular payments to beneficiaries upon the policyholder's death, ensuring long-term security and peace of mind. Embedded insurance seamlessly integrates insurance coverage into the purchase of products or services, offering convenience and immediate protection without a separate policy. Choosing between life insurance and embedded insurance depends on whether comprehensive, standalone coverage or streamlined, product-linked protection best meets individual needs.
Table of Comparison
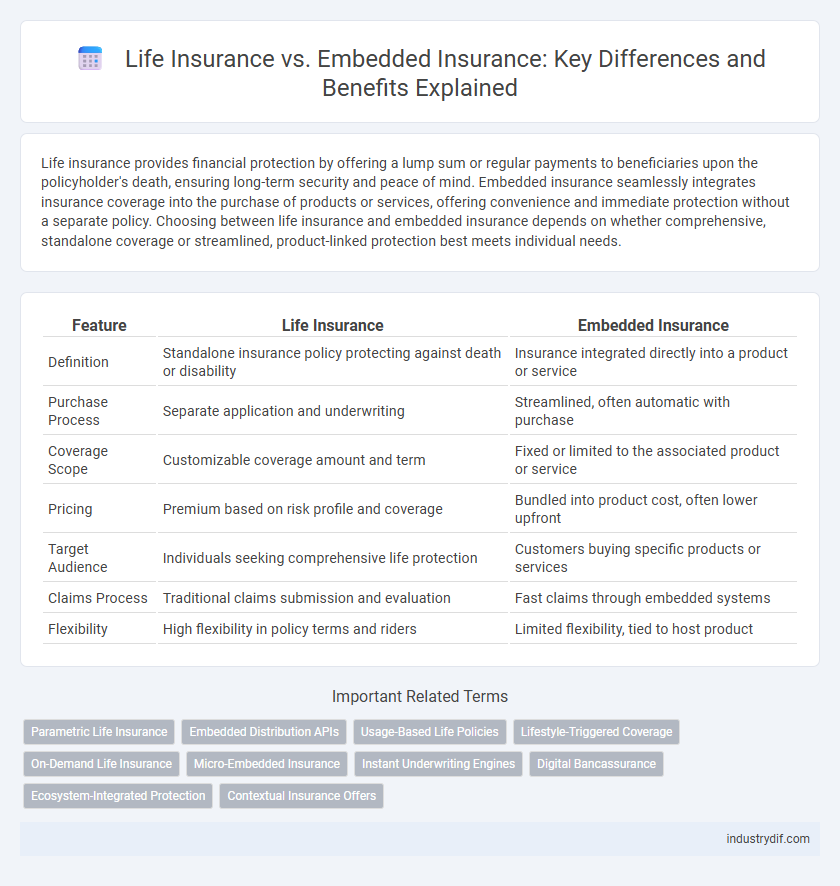
| Feature | Life Insurance | Embedded Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standalone insurance policy protecting against death or disability | Insurance integrated directly into a product or service |
| Purchase Process | Separate application and underwriting | Streamlined, often automatic with purchase |
| Coverage Scope | Customizable coverage amount and term | Fixed or limited to the associated product or service |
| Pricing | Premium based on risk profile and coverage | Bundled into product cost, often lower upfront |
| Target Audience | Individuals seeking comprehensive life protection | Customers buying specific products or services |
| Claims Process | Traditional claims submission and evaluation | Fast claims through embedded systems |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in policy terms and riders | Limited flexibility, tied to host product |
Understanding Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection by paying beneficiaries a lump sum or annuity upon the policyholder's death, ensuring income replacement and debt coverage. Embedded insurance integrates life insurance coverage directly into products or services such as loans, mortgages, or travel packages, offering seamless protection without requiring separate policies. Understanding life insurance involves recognizing policy types like term, whole, and universal life that vary in coverage duration, premiums, and cash value accumulation.
What Is Embedded Insurance?
Embedded insurance integrates life insurance coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, simplifying the acquisition process for consumers. This approach enhances customer convenience by bundling protection within transactions like loans, travel bookings, or retail purchases. By embedding life insurance, companies leverage transaction moments to offer seamless risk management without requiring separate policy underwriting.
Key Differences Between Life and Embedded Insurance
Life insurance provides a standalone policy that offers financial protection in the event of death, typically requiring separate purchase and underwriting. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase of a product or service, such as travel or electronics, offering seamless protection without separate contracts. Key differences include the purchase process, coverage scope, and risk assessment, with life insurance being more comprehensive and embedded insurance focusing on convenience and immediacy.
How Life Insurance Works
Life insurance provides a financial payout to beneficiaries upon the insured's death, offering economic security and covering expenses such as debts, funeral costs, and living expenses. Embedded insurance integrates life insurance coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, simplifying access and often bundling premiums with regular payments. Life insurance policies function through risk assessment, premium collection, and payout triggers tied to specific life events, primarily death.
How Embedded Insurance Operates
Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, allowing customers to buy insurance seamlessly alongside their primary transaction. This model leverages digital platforms and APIs to offer tailored protection without requiring separate insurance applications or underwriting processes. By embedding insurance within the customer journey, businesses enhance convenience, reduce friction, and increase policy adoption rates compared to traditional life insurance methods.
Benefits of Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance policies provide financial security by offering a death benefit that supports beneficiaries in covering expenses such as mortgages, education, and daily living costs. They often include options like cash value accumulation, which can serve as a savings or investment component over time. Life insurance policies also offer greater flexibility in customization compared to embedded insurance, allowing policyholders to select coverage levels and riders tailored to their individual needs.
Advantages of Embedded Insurance Solutions
Embedded insurance solutions offer seamless integration within the purchase journey, enhancing customer convenience and increasing conversion rates by providing immediate coverage without separate policy purchases. These solutions leverage real-time data to tailor personalized insurance products, improving risk assessment accuracy and customer satisfaction. Additionally, embedded insurance reduces administrative costs and accelerates claim processing through automated digital platforms.
Use Cases: Life Insurance vs Embedded Insurance
Life insurance primarily serves individuals seeking financial security for beneficiaries in case of death or critical illness, often purchased as standalone policies through insurers or brokers. Embedded insurance integrates life coverage seamlessly within products like mortgages, car loans, or retail purchases, offering convenience and tailored protection at the point of sale. Use cases for embedded insurance include insuring loans against borrower default or providing automatic life coverage with high-value purchases, enhancing customer experience and broadening access.
Choosing Between Life and Embedded Insurance
Choosing between life insurance and embedded insurance depends on individual financial goals and coverage needs. Life insurance provides dedicated, customizable protection against death and financial risk for beneficiaries, while embedded insurance integrates insurance coverage within product purchases, offering convenience and potentially lower upfront costs. Assessing factors such as coverage amount, policy flexibility, and cost helps determine the best option for comprehensive financial security.
Future Trends in Life and Embedded Insurance
Future trends in life insurance and embedded insurance emphasize increased integration of AI and IoT technologies to enhance personalized product offerings and risk assessment. Embedded insurance is expected to grow rapidly, driven by seamless inclusion within digital platforms and ecosystems, improving customer convenience and real-time coverage options. Life insurance will evolve through data-driven underwriting and automated claims processing, resulting in more tailored policies and faster service delivery.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Life Insurance
Parametric life insurance offers streamlined claims processing through predefined triggers such as health indices or biometric data, eliminating the need for traditional claim assessments and speeding up payout times. Embedded insurance integrates life coverage directly into products or services, enhancing customer experience and accessibility, but parametric models specifically optimize risk transfer with automated, data-driven settlement mechanisms.
Embedded Distribution APIs
Embedded insurance leverages APIs to seamlessly integrate life insurance products within third-party platforms, enhancing customer experience and streamlining policy issuance. This API-driven approach facilitates real-time underwriting and personalized coverage options, differentiating embedded insurance from traditional standalone life insurance models.
Usage-Based Life Policies
Usage-based life insurance policies leverage real-time data from wearable devices and health apps to tailor premiums according to individual behaviors and health metrics, enhancing risk assessment accuracy. Embedded insurance integrates these usage-based life policies directly into other services like fitness memberships or telehealth platforms, offering seamless protection without requiring separate insurance purchases.
Lifestyle-Triggered Coverage
Life insurance provides a fixed payout based on predetermined terms, while embedded insurance integrates lifestyle-triggered coverage directly into everyday products or services, activating protection when specific life events or behaviors occur. This approach enhances customer engagement by offering personalized, context-sensitive policies that automatically adjust to changes in a policyholder's lifestyle, such as travel, fitness activities, or health milestones.
On-Demand Life Insurance
On-demand life insurance offers flexible, short-term coverage activated as needed, contrasting with traditional embedded insurance integrated into products like loans or credit cards. This model allows policyholders to pay only for periods of actual risk, optimizing cost-efficiency and accessibility within the life insurance market.
Micro-Embedded Insurance
Micro-embedded insurance integrates small-scale life insurance coverage directly into everyday products and services, enhancing accessibility and affordability for low-income populations. This approach leverages digital platforms and seamless user experiences, driving higher adoption rates compared to traditional standalone life insurance policies.
Instant Underwriting Engines
Instant underwriting engines accelerate policy issuance by using real-time data analytics and AI algorithms to assess risk in life insurance and embedded insurance products. Embedded insurance integrates life coverage within other services, leveraging instant underwriting to provide seamless, automated protection without traditional delays.
Digital Bancassurance
Digital bancassurance integrates life insurance products directly into banking platforms, enhancing customer convenience and streamlining policy management through seamless digital channels. Embedded insurance leverages real-time data and APIs within banking services to offer tailored life insurance solutions at the point of need, driving higher engagement and improving risk assessment accuracy.
Ecosystem-Integrated Protection
Life insurance provides standalone financial security by paying a lump sum or annuity upon death, while embedded insurance seamlessly integrates coverage into everyday products and services within digital ecosystems, enhancing user convenience and proactive risk management. Ecosystem-integrated protection leverages data analytics and real-time monitoring to offer personalized, context-aware insurance solutions, driving higher customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Contextual Insurance Offers
Life insurance provides standalone coverage for individual policyholders, while embedded insurance integrates protection directly into the purchase of products or services, enabling contextual insurance offers tailored to specific consumer needs. Embedded insurance leverages real-time data and purchase behavior to deliver relevant, seamless coverage options that enhance customer experience and risk management.
Life Insurance vs Embedded Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com