Static pricing in insurance offers fixed premiums based on generalized risk factors, providing predictability but often lacking personalization. Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data and behavioral insights to adjust premiums continuously, enhancing accuracy and fairness in risk assessment. Insurers adopting dynamic pricing can better align costs with individual risk profiles, improving customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Table of Comparison
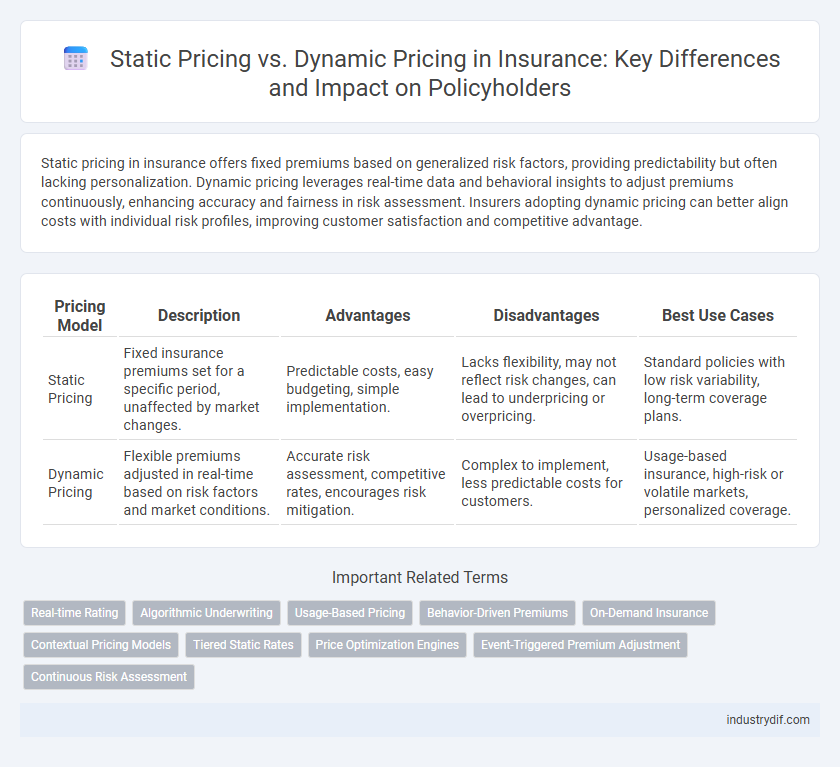
| Pricing Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Pricing | Fixed insurance premiums set for a specific period, unaffected by market changes. | Predictable costs, easy budgeting, simple implementation. | Lacks flexibility, may not reflect risk changes, can lead to underpricing or overpricing. | Standard policies with low risk variability, long-term coverage plans. |
| Dynamic Pricing | Flexible premiums adjusted in real-time based on risk factors and market conditions. | Accurate risk assessment, competitive rates, encourages risk mitigation. | Complex to implement, less predictable costs for customers. | Usage-based insurance, high-risk or volatile markets, personalized coverage. |
Introduction to Pricing Strategies in Insurance
Static pricing in insurance maintains fixed premiums based on historical data and risk assessments, providing predictability for both insurers and policyholders. Dynamic pricing adjusts premiums in real-time using algorithms that analyze evolving customer behavior, market trends, and risk factors, enabling personalized coverage and competitive advantage. Understanding these pricing strategies is crucial for insurers aiming to balance risk, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Defining Static Pricing in Insurance
Static pricing in insurance refers to a fixed premium model where rates remain constant over a specific policy period, regardless of changes in risk factors or market conditions. This pricing approach simplifies premium calculation by using predetermined criteria such as age, coverage amount, and historical claims data. Insurers relying on static pricing maintain stability and predictability but may lack responsiveness to real-time risk variations.
Understanding Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing models in insurance leverage real-time data, such as customer behavior, market demand, and risk factors, to adjust premiums continuously. These models utilize machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics to offer personalized pricing, improving risk assessment accuracy and competitiveness. Unlike static pricing, dynamic pricing enhances flexibility by responding to external trends and individual policyholder profiles in near real-time.
Key Differences: Static vs Dynamic Pricing
Static pricing in insurance involves fixed premium rates that remain constant over a policy period, providing predictability but lacking responsiveness to real-time risk changes. Dynamic pricing leverages data analytics and real-time information, adjusting premiums based on factors like driving behavior, weather conditions, or claim history, enhancing risk accuracy and customer personalization. Key differences include adaptability to risk variations, pricing transparency, and the potential impact on customer retention and profitability for insurers.
Advantages of Static Pricing for Insurers
Static pricing offers insurers stability and predictability in revenue streams by setting fixed premiums that do not fluctuate frequently. This approach simplifies underwriting processes and administrative tasks, reducing operational costs associated with frequent price adjustments. Insurers benefit from enhanced customer trust and loyalty, as policyholders appreciate consistent pricing without unexpected changes.
Benefits of Dynamic Pricing for Policyholders
Dynamic pricing in insurance offers policyholders personalized premiums based on real-time risk assessment, leading to fairer rates that reflect individual behavior and circumstances. It enhances affordability by rewarding safe actions and enabling adjustments as risk profiles change, promoting proactive risk management. This approach increases transparency and competitiveness, empowering policyholders to make informed decisions and access optimal coverage.
Challenges in Implementing Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing in insurance faces challenges such as data privacy concerns and regulatory compliance, limiting access to real-time customer data essential for accurate rate adjustments. The complexity of integrating advanced algorithms with legacy insurance systems often leads to implementation delays and increased operational costs. Furthermore, customer trust issues arise when premium fluctuations are perceived as unfair or unpredictable, impacting retention and satisfaction.
The Role of Technology in Pricing Evolution
Technology drives the evolution of insurance pricing by enabling dynamic models that analyze real-time data such as driver behavior, weather patterns, and claim history. Advanced algorithms and machine learning enhance risk assessment accuracy compared to traditional static pricing, which relies on fixed rates and historical averages. Insurers utilizing telematics and big data platforms can personalize premiums, improve competitiveness, and adapt to market changes rapidly.
Regulatory Considerations in Insurance Pricing
Regulatory considerations in insurance pricing mandate that both static and dynamic pricing models comply with fairness, transparency, and non-discrimination standards to protect consumers. Static pricing offers stability and predictability, meeting regulatory demands for consistent premium rates, while dynamic pricing must ensure real-time adjustments do not result in unfair discrimination or violate state-specific insurance laws. Insurers must document pricing algorithms and justify rate changes to regulators to maintain compliance and avoid potential sanctions.
Future Trends: The Shift Toward Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing in insurance leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to adjust premiums based on individual risk profiles and market conditions, offering more personalized and accurate rates. The future of insurance pricing trends emphasizes a shift from static, one-size-fits-all pricing models to dynamic frameworks that incorporate telematics, behavioral data, and predictive analytics. This evolution enables carriers to improve risk assessment, enhance customer engagement, and maintain competitive advantage in a rapidly changing industry landscape.
Related Important Terms
Real-time Rating
Static pricing in insurance relies on fixed premiums determined by historical data and risk assessments, often leading to less personalized coverage. Real-time rating within dynamic pricing leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to adjust premiums instantly, improving risk accuracy and customer segmentation.
Algorithmic Underwriting
Algorithmic underwriting leverages dynamic pricing by analyzing real-time data and risk factors, enabling insurers to offer personalized premiums instead of static, one-size-fits-all rates. This approach improves risk assessment accuracy, enhances competitive positioning, and optimizes profitability through continuous price adjustments based on evolving customer information.
Usage-Based Pricing
Usage-based pricing in insurance leverages real-time data from telematics devices to adjust premiums based on actual driving behavior, promoting fairness and cost efficiency. This dynamic pricing model contrasts with static pricing by offering personalized rates that reflect individual risk profiles rather than broad demographic averages.
Behavior-Driven Premiums
Behavior-driven premiums utilize dynamic pricing models that adjust insurance rates based on real-time customer data, such as driving habits or health metrics, enhancing risk assessment accuracy. Static pricing relies on fixed premiums determined by generalized risk factors, often leading to less personalized and potentially less fair insurance costs.
On-Demand Insurance
On-demand insurance leverages dynamic pricing models that adjust premiums in real-time based on user behavior, risk exposure, and market conditions, offering personalized coverage at competitive rates. Static pricing, by contrast, relies on fixed premiums set periodically, which can lead to less flexible and potentially less cost-effective insurance for short-term or usage-based needs.
Contextual Pricing Models
Contextual pricing models in insurance leverage real-time data such as driver behavior, location, and weather conditions to dynamically adjust premiums, offering more personalized and accurate risk assessments. Static pricing models rely on fixed rates based on historical data and broad risk categories, often resulting in less precise pricing and reduced competitiveness.
Tiered Static Rates
Tiered static rates in insurance categorize risk groups with fixed premium levels, providing predictable costs and simplified policy management. This approach contrasts with dynamic pricing by maintaining consistent rates over time despite changes in individual risk factors or market conditions.
Price Optimization Engines
Price optimization engines leverage dynamic pricing models in insurance to analyze real-time data, customer behavior, and risk factors, enabling insurers to set personalized premiums that maximize profitability and competitiveness. Static pricing relies on fixed rates based on historical data, limiting responsiveness to market fluctuations and individual risk profiles.
Event-Triggered Premium Adjustment
Event-triggered premium adjustment in insurance leverages dynamic pricing to modify rates based on specific occurrences such as natural disasters or claims history, enhancing risk alignment and financial sustainability. Static pricing, however, maintains fixed premiums regardless of events, potentially leading to mispriced risk and less responsive policyholder costs.
Continuous Risk Assessment
Continuous risk assessment enables dynamic pricing in insurance by regularly updating premiums based on real-time data such as driving behavior, health metrics, or claim history. Unlike static pricing, which relies on fixed rates determined during policy issuance, dynamic pricing adapts to ongoing risk factors, improving pricing accuracy and risk management efficiency.
Static Pricing vs Dynamic Pricing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com