Physical loss insurance covers tangible damage to property caused by events such as fire, theft, or natural disasters, providing financial protection for rebuilding and replacing physical assets. Cyber risk insurance specifically addresses intangible threats like data breaches, ransomware attacks, and cyber fraud, offering coverage for data restoration, business interruption, and legal liabilities. Distinguishing between these two types of insurance is crucial for businesses to ensure comprehensive risk management in both physical and digital domains.
Table of Comparison
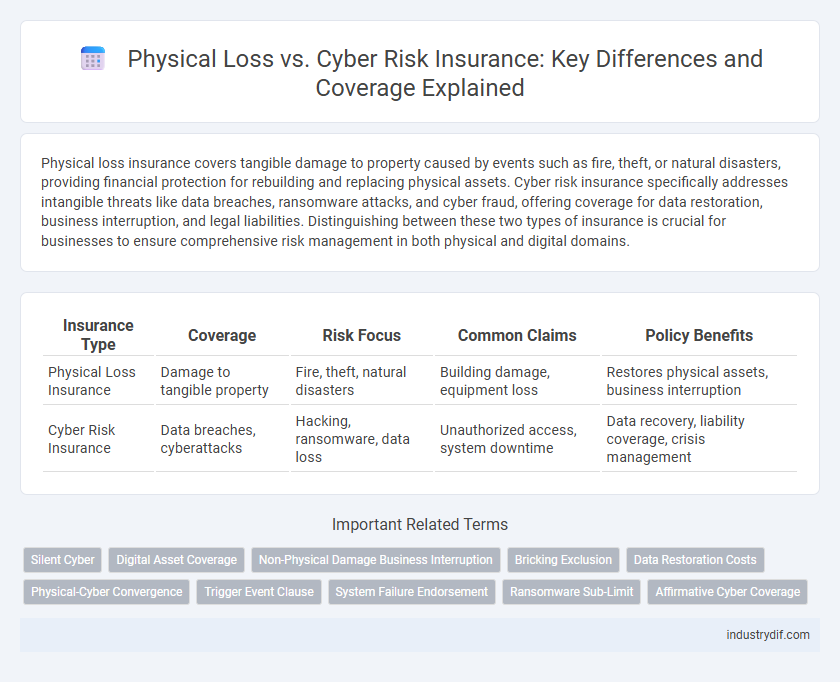
| Insurance Type | Coverage | Risk Focus | Common Claims | Policy Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Loss Insurance | Damage to tangible property | Fire, theft, natural disasters | Building damage, equipment loss | Restores physical assets, business interruption |
| Cyber Risk Insurance | Data breaches, cyberattacks | Hacking, ransomware, data loss | Unauthorized access, system downtime | Data recovery, liability coverage, crisis management |
Defining Physical Loss in Insurance
Physical loss in insurance refers to tangible damage or destruction of property caused by events such as fire, theft, or natural disasters, resulting in measurable impairment to insured assets. Unlike cyber risk insurance, which covers intangible losses like data breaches and network interruptions, physical loss requires demonstrable alteration or harm to physical objects. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately assessing coverage scope and claim eligibility in property insurance policies.
Understanding Cyber Risk Insurance
Cyber Risk Insurance provides coverage for financial losses resulting from data breaches, cyberattacks, and network disruptions, addressing threats unique to digital environments. Unlike Physical Loss Insurance that protects tangible assets against damage or theft, Cyber Risk Insurance safeguards intangible assets such as sensitive customer data and proprietary information. Businesses adopting cloud services and remote work policies increasingly require Cyber Risk Insurance to mitigate evolving cyber threats and regulatory compliance risks.
Key Policy Coverage Differences
Physical loss insurance covers tangible damage to property caused by events such as fire, theft, or natural disasters, providing compensation for repair or replacement costs. Cyber risk insurance addresses data breaches, cyberattacks, and network interruptions, offering coverage for business interruption, data recovery, and liability from cyber incidents. Key policy differences include coverage scope--physical loss policies focus on material damage, whereas cyber risk policies emphasize digital asset protection, privacy liability, and regulatory fines.
Common Exclusions in Physical Loss Policies
Physical loss insurance commonly excludes damages caused by cyber incidents such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and network failures. These policies often do not cover intangible assets or losses resulting from cyber-related business interruptions. Cyber risk insurance specifically addresses these gaps, providing coverage for cyberattacks, data restoration, and liability associated with digital threats.
Cyber Threat Landscape and Emerging Risks
Cyber risk insurance addresses the evolving cyber threat landscape characterized by ransomware, data breaches, and sophisticated phishing attacks that target digital assets and critical infrastructure. Emerging risks include vulnerabilities from increased remote work, cloud service dependencies, and the rise of IoT devices, which amplify exposure to cyber incidents. Unlike traditional physical loss insurance that covers tangible property damage, cyber insurance specifically protects against financial losses from cyberattacks and data compromise, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Claims Process: Physical Loss vs Cyber Incidents
Claims process for physical loss insurance typically involves on-site damage assessment, documentation of tangible property damage, and valuation based on repair or replacement costs. Cyber risk insurance claims require detailed forensic analysis of digital breaches, identification of data compromised, and assessment of business interruption or liability resulting from cyber incidents. Timely notification and collaboration with cybersecurity experts are crucial for validating cyber claims, whereas physical loss claims often rely on traditional adjusters and contractors.
Policy Triggers and Event Scenarios
Physical loss insurance policies typically activate coverage upon tangible damage or destruction to physical assets caused by events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. Cyber risk insurance policy triggers revolve around digital incidents such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, or network interruptions that compromise information security or business operations. Understanding the distinct event scenarios for each policy type is crucial for comprehensive risk management and selecting appropriate coverage limits.
Risk Assessment Methods in Both Domains
Physical loss insurance risk assessment methods emphasize tangible asset inspections, hazard identification, and historical claim analysis to evaluate potential property damage or theft. Cyber risk insurance relies on vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and continuous monitoring of network security to identify threats such as data breaches and ransomware attacks. Both domains integrate quantitative modeling and scenario analysis but differ significantly in handling dynamic cyber threats versus more static physical risks.
Regulatory Requirements for Insurance Coverage
Physical loss insurance typically meets strict regulatory requirements by covering tangible asset damage, ensuring compliance with property insurance statutes and risk assessments mandated by insurance regulators. Cyber risk insurance, governed by evolving cybersecurity laws and data protection regulations, must address coverage for data breaches, business interruption, and liability related to cyber incidents, aligning with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and state-specific mandates such as New York DFS Cybersecurity Regulation. Insurers offering cyber risk policies are often required to implement rigorous underwriting processes and maintain transparency on coverage limits and exclusions to comply with regulatory frameworks.
Best Practices for Comprehensive Risk Management
Physical loss insurance covers tangible assets and property damage caused by events like fire, theft, or natural disasters, while cyber risk insurance protects against digital threats such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and network downtime. Best practices for comprehensive risk management involve integrating both policies to address the full spectrum of risks, conducting regular risk assessments, and implementing robust cybersecurity protocols alongside physical security measures. Combining these approaches ensures businesses mitigate financial losses and maintain operational resilience in an increasingly interconnected risk landscape.
Related Important Terms
Silent Cyber
Silent cyber refers to cyber-related risks that are not explicitly covered or excluded in traditional physical loss insurance policies, creating potential coverage gaps for businesses facing cyber-attacks. Unlike cyber risk insurance, which specifically addresses data breaches, hacking, and other digital threats, physical loss insurance often unintentionally exposes insurers and policyholders to silent cyber risks through ambiguous policy language.
Digital Asset Coverage
Physical Loss insurance primarily covers tangible assets damaged or destroyed by events such as fire or theft, while Cyber Risk Insurance focuses on protecting digital assets, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and cyber extortion. Digital Asset Coverage under Cyber Risk Insurance safeguards intangible electronic resources, ensuring business continuity and financial recovery from cyber incidents.
Non-Physical Damage Business Interruption
Physical Loss insurance covers tangible property damage causing operational downtime, whereas Cyber Risk Insurance addresses Non-Physical Damage Business Interruption caused by cyberattacks, such as ransomware or data breaches that halt business activities without visible damage. Cyber Risk policies include coverage for lost income, extra expenses, and data restoration, highlighting the critical distinction from traditional physical loss claims.
Bricking Exclusion
Physical loss insurance typically covers tangible asset damage, whereas cyber risk insurance addresses digital threats and data breaches, with bricking exclusion specifically omitting coverage for devices rendered unusable due to software corruption or malware. This exclusion highlights the necessity for businesses to invest in specialized cyber insurance policies that explicitly cover cyber-induced physical damage or device disablement.
Data Restoration Costs
Physical loss insurance typically covers tangible property damage but often excludes data restoration costs, whereas cyber risk insurance specifically addresses expenses related to recovering and restoring compromised digital data after a cyber incident. Data restoration costs under cyber risk policies include expenses for forensic investigation, system repairs, and reinstallation of software and information, crucial for minimizing downtime and operational disruption.
Physical-Cyber Convergence
Physical loss insurance traditionally covers tangible property damage from events like fire or theft, while cyber risk insurance addresses digital threats such as data breaches and ransomware attacks. The emerging physical-cyber convergence highlights the necessity for integrated coverage solutions that protect against complex risks involving both physical assets and cyber vulnerabilities, driven by increased dependence on interconnected technologies.
Trigger Event Clause
Physical Loss insurance covers damage or destruction of tangible property caused by identifiable trigger event clauses like fire or theft, while Cyber Risk insurance addresses losses from intangible digital incidents such as data breaches or ransomware attacks, with trigger event clauses centered on cyber-related disruptions and unauthorized access. The differences in trigger event clauses define the scope and applicability of each policy, emphasizing physical damage versus cyber event-induced financial loss.
System Failure Endorsement
Physical Loss insurance typically covers tangible damages to property while Cyber Risk Insurance addresses data breaches, cyberattacks, and system failures. The System Failure Endorsement under Cyber Risk Insurance specifically offers coverage for losses resulting from unexpected system malfunctions, ensuring protection against operational disruptions that are not caused by physical damage.
Ransomware Sub-Limit
Physical loss insurance typically covers damages to tangible assets caused by events like fire or theft, whereas cyber risk insurance addresses digital threats including data breaches and ransomware attacks. Ransomware sub-limits within cyber policies restrict the maximum payout for ransom payments, highlighting the importance of evaluating these caps to ensure adequate coverage for costly ransomware incidents.
Affirmative Cyber Coverage
Affirmative Cyber Coverage specifically addresses losses from cyber incidents such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and network interruptions, providing clear protection distinct from traditional Physical Loss insurance that covers tangible property damage. This type of insurance ensures coverage for intangible cyber risks including business interruption, data restoration, and cyber extortion, filling gaps not covered under standard property policies.
Physical Loss vs Cyber Risk Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com