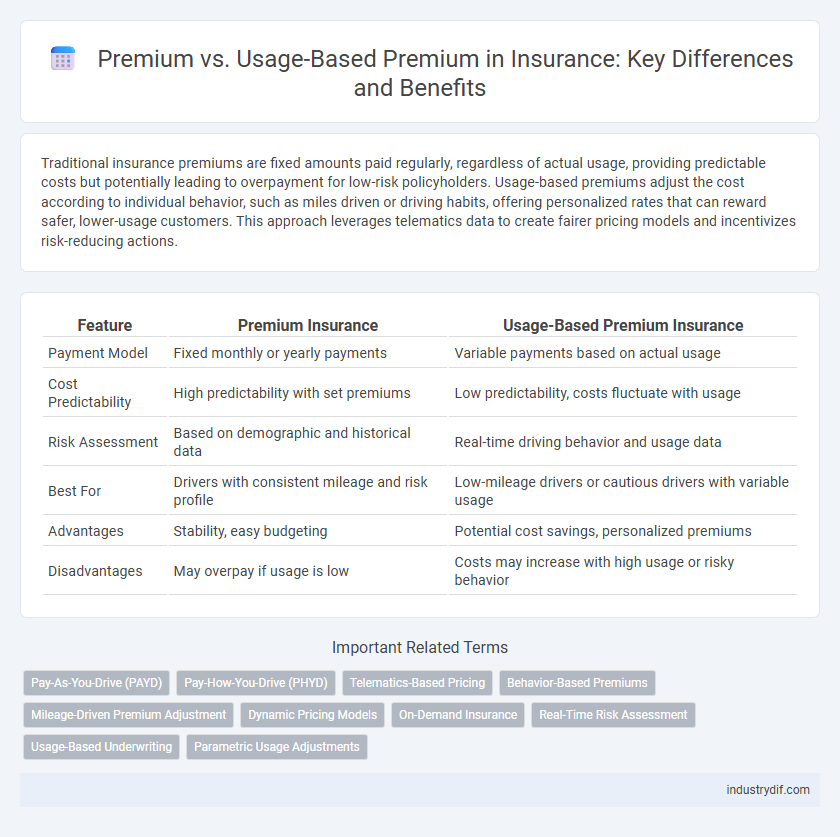
Traditional insurance premiums are fixed amounts paid regularly, regardless of actual usage, providing predictable costs but potentially leading to overpayment for low-risk policyholders. Usage-based premiums adjust the cost according to individual behavior, such as miles driven or driving habits, offering personalized rates that can reward safer, lower-usage customers. This approach leverages telematics data to create fairer pricing models and incentivizes risk-reducing actions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Premium Insurance | Usage-Based Premium Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Model | Fixed monthly or yearly payments | Variable payments based on actual usage |
| Cost Predictability | High predictability with set premiums | Low predictability, costs fluctuate with usage |
| Risk Assessment | Based on demographic and historical data | Real-time driving behavior and usage data |
| Best For | Drivers with consistent mileage and risk profile | Low-mileage drivers or cautious drivers with variable usage |
| Advantages | Stability, easy budgeting | Potential cost savings, personalized premiums |
| Disadvantages | May overpay if usage is low | Costs may increase with high usage or risky behavior |
Overview of Premium Models in Insurance
Insurance premium models primarily include traditional fixed premiums and usage-based premiums, each offering distinct risk assessment approaches. Fixed premiums rely on generalized factors such as age, location, and vehicle type, providing stable, predictable payments regardless of actual usage. Usage-based premiums leverage telematics and real-time data on driving behavior or usage patterns, enabling personalized pricing that reflects individual risk more accurately.
Defining Traditional Premiums
Traditional insurance premiums are fixed amounts paid periodically by policyholders, calculated based on factors such as age, location, and coverage limits. These premiums remain constant regardless of the insured's actual usage or behavior, providing predictable payment structures for both insurers and clients. The static nature of traditional premiums often contrasts with usage-based models, which adjust costs dynamically according to real-time risk assessments.
Understanding Usage-Based Premiums
Usage-based premiums calculate insurance costs based on actual driving behavior and mileage tracked through telematics devices or mobile apps. This model offers personalized rates by evaluating factors like speed, acceleration, braking patterns, and total distance driven, promoting safer driving habits and potential cost savings. Insurers benefit from more accurate risk assessment, while policyholders gain transparency and control over their premium expenses.
Key Differences Between Premium and Usage-Based Premium
Premium insurance refers to a fixed payment made regularly to maintain coverage regardless of actual usage, while usage-based premium varies depending on individual driving behavior, distance traveled, or specific risk factors. Traditional premiums rely on general risk assessments such as age, location, and vehicle type, whereas usage-based premiums use telematics data to tailor rates dynamically. This fundamental difference allows usage-based premiums to offer personalized pricing, often resulting in lower costs for safe or infrequent drivers compared to fixed standard premiums.
Advantages of Traditional Premiums
Traditional insurance premiums offer predictable and stable payments, making budgeting simpler for policyholders. These fixed premiums do not fluctuate with short-term changes in behavior, providing financial security and ease of planning. Established underwriting methods also support risk assessment accuracy, benefiting both insurers and insureds.
Benefits of Usage-Based Premiums
Usage-based premiums in insurance offer personalized pricing by leveraging real-time data such as driving behavior, mileage, and risk patterns, resulting in fairer rates compared to traditional flat premiums. This model incentivizes safer habits and can significantly lower costs for low-risk policyholders, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention. Insurers benefit from reduced claims frequency and improved risk assessment accuracy, optimizing underwriting efficiency and profitability.
Factors Influencing Premium Calculations
Premium calculations in traditional insurance rely heavily on demographic factors such as age, gender, location, and credit score, while usage-based premiums incorporate real-time driving behavior including mileage, speed, and braking patterns. Advanced telematics and IoT devices provide granular data that allows insurers to adjust premiums dynamically based on actual risk exposure rather than historical averages. Regulatory frameworks and data privacy laws also significantly influence how usage-based premiums are structured and implemented in various markets.
Technology’s Role in Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics, GPS, and IoT devices to monitor driving behavior and calculate premiums based on actual usage and risk profiles. This technology enables insurers to offer personalized premiums that reflect real-time data such as mileage, speed, and braking patterns, improving accuracy over traditional fixed premiums. Advanced data analytics and AI algorithms process vast amounts of driving data, enhancing risk assessment and fostering fairer, more cost-effective insurance models.
Considerations for Policyholders
Policyholders should evaluate the stability of their driving habits when choosing between traditional premiums and usage-based premiums, as usage-based premiums can offer cost savings for low-mileage or safe drivers by tracking real-time behavior. Privacy concerns arise since usage-based insurance relies on telematics data, potentially exposing sensitive personal information. Understanding potential fluctuations in monthly costs and reviewing policy terms carefully ensures informed decisions aligned with individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Future Trends in Insurance Premium Models
Usage-based premiums leverage telematics and real-time data to tailor insurance costs based on actual behavior, enhancing accuracy over traditional fixed premiums. Future trends point towards increased adoption of AI-driven analytics and IoT integration to refine risk assessment and personalize policies dynamically. This shift promotes transparency, incentivizes safer behavior, and transforms premium models into more flexible, customer-centric solutions.
Related Important Terms
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD)
Usage-based insurance models, such as Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD), calculate premiums based on actual driving behavior and mileage, offering personalized rates that reflect individual risk levels. Traditional fixed premiums often rely on static factors like demographics, whereas PAYD promotes cost efficiency and encourages safer driving habits through real-time data monitoring.
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD)
Premium in traditional insurance is a fixed amount based on risk factors such as age, location, and vehicle type, while Usage-Based Premium adapts to actual driving behavior through Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD) technology. PHYD leverages telematics data to monitor metrics like speed, braking, and mileage, enabling personalized premiums that reward safe drivers with lower costs and promote risk-aware driving habits.
Telematics-Based Pricing
Telematics-based pricing leverages real-time driving data to tailor insurance premiums, offering more accurate and personalized rates compared to traditional fixed premiums. Usage-based premiums dynamically adjust costs based on factors such as mileage, driving behavior, and time of use, leading to potential savings and incentivizing safer driving habits.
Behavior-Based Premiums
Behavior-based premiums in insurance leverage telematics and real-time data to adjust rates according to individual driving habits, rewarding safe drivers with lower costs. This model contrasts traditional fixed premiums, offering dynamic pricing that promotes risk-reducing behavior and personalized coverage.
Mileage-Driven Premium Adjustment
Mileage-driven premium adjustment in insurance recalculates policy costs based on the actual miles driven, reducing premiums for low-mileage drivers while increasing costs for high-mileage usage. This usage-based premium model leverages telematics data to tailor rates more accurately, promoting fair pricing aligned with individual driving behavior.
Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing models in insurance utilize real-time data and usage patterns to adjust premiums more accurately, reflecting the individual risk profile of policyholders. Usage-based premiums incentivize safer behavior by linking costs directly to actual usage and driving habits, enhancing fairness and affordability in insurance pricing.
On-Demand Insurance
On-demand insurance offers the flexibility of usage-based premiums, allowing policyholders to pay only for the coverage they need when they need it, resulting in cost efficiency compared to traditional fixed premiums. This model leverages real-time data and telematics to tailor insurance costs precisely to individual behavior and risk exposure.
Real-Time Risk Assessment
Usage-based premiums leverage real-time risk assessment by analyzing driving behavior through telematics, enabling insurers to adjust rates dynamically based on actual risk exposure. Traditional premiums rely on static data such as demographics and historical claims, which may not accurately reflect current risk levels.
Usage-Based Underwriting
Usage-based underwriting leverages telematics and real-time data to tailor insurance premiums based on individual driving behavior, resulting in more accurate risk assessment and potentially lower costs for safe drivers. This method contrasts with traditional premium models by shifting from static risk factors to dynamic, personalized evaluations that enhance pricing precision and customer engagement.
Parametric Usage Adjustments
Traditional insurance premiums are fixed amounts determined by risk factors assessed at policy inception, while usage-based premiums leverage real-time data to adjust costs according to actual behavior. Parametric usage adjustments streamline claims processing by triggering payouts based on predefined parameters, enhancing transparency and reducing settlement time.
Premium vs Usage-based Premium Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com