Reinsurance involves traditional insurance companies transferring portions of their risk portfolios to other insurers to reduce potential losses, ensuring financial stability. Peer-to-peer insurance, on the other hand, allows groups of individuals to pool premiums to cover claims collectively, promoting transparency and potentially lower costs by cutting out intermediaries. Both models aim to manage risk but differ in structure, capital requirements, and regulatory oversight.
Table of Comparison
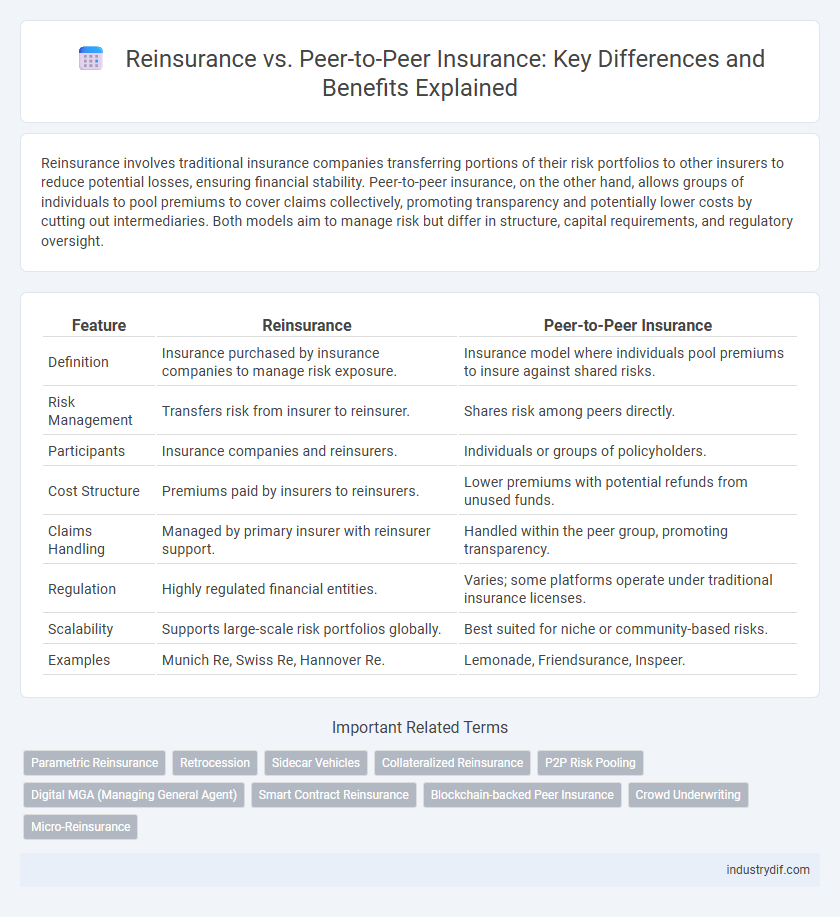
| Feature | Reinsurance | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance purchased by insurance companies to manage risk exposure. | Insurance model where individuals pool premiums to insure against shared risks. |
| Risk Management | Transfers risk from insurer to reinsurer. | Shares risk among peers directly. |
| Participants | Insurance companies and reinsurers. | Individuals or groups of policyholders. |
| Cost Structure | Premiums paid by insurers to reinsurers. | Lower premiums with potential refunds from unused funds. |
| Claims Handling | Managed by primary insurer with reinsurer support. | Handled within the peer group, promoting transparency. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated financial entities. | Varies; some platforms operate under traditional insurance licenses. |
| Scalability | Supports large-scale risk portfolios globally. | Best suited for niche or community-based risks. |
| Examples | Munich Re, Swiss Re, Hannover Re. | Lemonade, Friendsurance, Inspeer. |
Definition of Reinsurance
Reinsurance is a risk management practice where an insurance company transfers a portion of its risk portfolio to another insurer, known as the reinsurer, to reduce the potential financial impact of large claims. This mechanism enhances the primary insurer's solvency and stability by spreading the risk across multiple entities. Unlike peer-to-peer insurance, which involves individuals sharing risks directly, reinsurance operates strictly between professional insurance companies.
Definition of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance is a decentralized insurance model where policyholders pool their premiums to cover collective risks, bypassing traditional insurers. This approach fosters transparency, reduces administrative costs, and aligns interests by allowing members to share claims and potentially receive rebates if losses are minimal. Unlike reinsurance, which involves transferring risk from insurers to other insurance companies, peer-to-peer insurance directly connects participants, emphasizing community-based risk management.
Historical Evolution: Reinsurance and P2P Insurance
Reinsurance has evolved since the 14th century as a risk management tool where insurance companies transfer portions of risk to other insurers, enabling financial stability and capacity enhancement. Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance, emerging in the 21st century driven by digital platforms, facilitates direct risk-sharing among individuals without traditional insurers, promoting transparency and cost reduction. The historical shift from centralized reinsurance markets to decentralized P2P models reflects advancements in technology and changing consumer trust dynamics in the insurance industry.
Key Differences Between Reinsurance and Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Reinsurance involves insurance companies transferring portions of risk portfolios to other insurers to reduce exposure, whereas peer-to-peer insurance pools individual participants' premiums to cover claims within the group. Reinsurance operates between institutions and typically manages large-scale risk, while peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes community-based risk sharing and transparency. Key differences include the level of risk dispersion, regulatory frameworks, and the involvement of traditional insurance intermediaries.
Risk Management Approaches
Reinsurance employs a traditional risk transfer model where insurance companies cede portions of their risk portfolios to reinsurers, enhancing financial stability and mitigating losses from large claims. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages a community-based model, pooling premiums from participants to cover claims within a defined group, promoting transparency and reducing overhead costs. Both risk management approaches aim to optimize capital efficiency and claim payouts but differ in structure, with reinsurance providing external risk absorption and peer-to-peer focusing on collective risk sharing.
Operational Models Compared
Reinsurance operates through traditional risk transfer agreements between insurance companies and reinsurers, relying on large-scale underwriting and capital reserves to spread risk. Peer-to-peer insurance employs a decentralized model where policyholders pool funds collaboratively, supported by digital platforms that enhance transparency and reduce administrative costs. Both models differ in risk management, with reinsurance emphasizing institutional backing and peer-to-peer focusing on community-driven mechanisms.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Reinsurance operates under well-established regulatory frameworks that mandate capital requirements, risk assessments, and solvency standards to ensure financial stability and policyholder protection. Peer-to-peer insurance faces evolving regulatory challenges as it blends traditional insurance principles with decentralized risk-sharing models, often requiring tailored compliance strategies to address transparency, consumer protection, and anti-money laundering standards. Understanding these distinct regulatory landscapes is crucial for insurers and policyholders to navigate compliance risks and leverage the benefits of each model effectively.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Reinsurance
Reinsurance offers insurers financial protection by spreading risk, which enhances stability and capacity to underwrite large policies while mitigating potential losses from catastrophic events. However, it involves additional costs and complex contractual arrangements that may reduce overall profitability and introduce counterparty risk. Unlike peer-to-peer insurance, reinsurance maintains traditional risk transfer mechanisms but with less transparency and lower customer engagement.
Advantages and Limitations of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance offers greater transparency and lower costs by eliminating traditional intermediaries, fostering a community-driven approach to risk sharing. It enables policyholders to have more control over claims and premiums, often resulting in higher customer satisfaction and reduced fraud. However, limitations include potentially lower risk diversification compared to traditional reinsurance, and challenges in scalability and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends in Risk Sharing Mechanisms
Reinsurance continues to evolve with increased integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology to enhance risk assessment and transparency. Peer-to-peer insurance platforms are gaining traction by leveraging decentralized networks and smart contracts, promoting community-based risk sharing and reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining the scalability of reinsurance with the agility and personalization of peer-to-peer models.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Reinsurance
Parametric reinsurance offers insurers a streamlined risk transfer solution by triggering payouts based on predefined event parameters rather than loss assessments, enhancing speed and transparency compared to traditional indemnity-based coverage. Peer-to-peer insurance models emphasize community risk-sharing and direct member engagement but often lack the parametric triggers that enable objective, rapid claims settlements found in parametric reinsurance contracts.
Retrocession
Retrocession in reinsurance involves transferring portions of risk from one reinsurer to another, providing diversified risk management and enhanced capital efficiency. Peer-to-peer insurance bypasses traditional retrocession by distributing risk directly within a member group, relying on mutual trust rather than external risk transfer mechanisms.
Sidecar Vehicles
Sidecar vehicles in reinsurance offer insurers a mechanism to cede specific risk segments to third-party investors, enhancing capital efficiency and risk diversification. In contrast, peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized pools of policyholders to share risk directly, bypassing traditional reinsurers and often reducing dependency on sidecar structures for capital management.
Collateralized Reinsurance
Collateralized reinsurance provides insurers with secured risk transfer by requiring collateral assets, enhancing financial stability compared to traditional reinsurance. Peer-to-peer insurance decentralizes risk sharing among participants but lacks the robust capital backing inherent in collateralized reinsurance structures, making the latter more reliable for large-scale risk management.
P2P Risk Pooling
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance utilizes risk pooling by grouping policyholders to share premiums and claims directly within the network, reducing reliance on traditional reinsurance structures. This model enhances transparency and cost efficiency, allowing members to benefit from collective risk management without intermediary reinsurers.
Digital MGA (Managing General Agent)
Digital MGAs leverage advanced data analytics and automation to efficiently manage reinsurance agreements, offering scalable risk transfer solutions, while peer-to-peer insurance platforms utilize decentralized pooling of premiums to reduce costs and enhance transparency for policyholders. The integration of digital MGAs in reinsurance optimizes underwriting accuracy and claims processing speed, positioning them as pivotal intermediaries in modern risk management ecosystems.
Smart Contract Reinsurance
Smart contract reinsurance leverages blockchain technology to automate claim verification and payout processes, reducing administrative costs and enhancing transparency compared to traditional reinsurance models. Peer-to-peer insurance, while fostering community risk sharing, lacks the scalability and contractual certainty that smart contract reinsurance provides through secure, self-executing agreements.
Blockchain-backed Peer Insurance
Blockchain-backed peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized ledgers to increase transparency, reduce administrative costs, and directly connect policyholders, contrasting traditional reinsurance which relies on centralized risk transfer mechanisms between insurers. This innovative model enhances trust and efficiency by enabling real-time claims processing and automated smart contracts, disrupting conventional reinsurance paradigms.
Crowd Underwriting
Crowd underwriting in peer-to-peer insurance leverages collective risk assessment by pooling individual members to share premiums and claims, contrasting with reinsurance where large institutions assume the risk from primary insurers to stabilize losses. This decentralized approach enhances transparency and potentially lowers costs by directly involving insured parties in risk evaluation and decision-making processes.
Micro-Reinsurance
Micro-reinsurance offers targeted risk transfer solutions for small-scale insurers, enhancing capital efficiency and enabling access to global reinsurance markets compared to traditional peer-to-peer insurance models. It facilitates scalable coverage for microinsurance providers by mitigating aggregated losses with professional risk management frameworks.
Reinsurance vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com