Automation transforms manufacturing by streamlining repetitive tasks with fully autonomous machines, boosting efficiency and consistency on the production line. Cobots, or collaborative robots, work alongside human operators, enhancing flexibility and safety while enabling complex, precision tasks that require human oversight. Integrating cobots into automated systems combines the strengths of both, driving innovation and optimizing productivity in modern manufacturing environments.
Table of Comparison
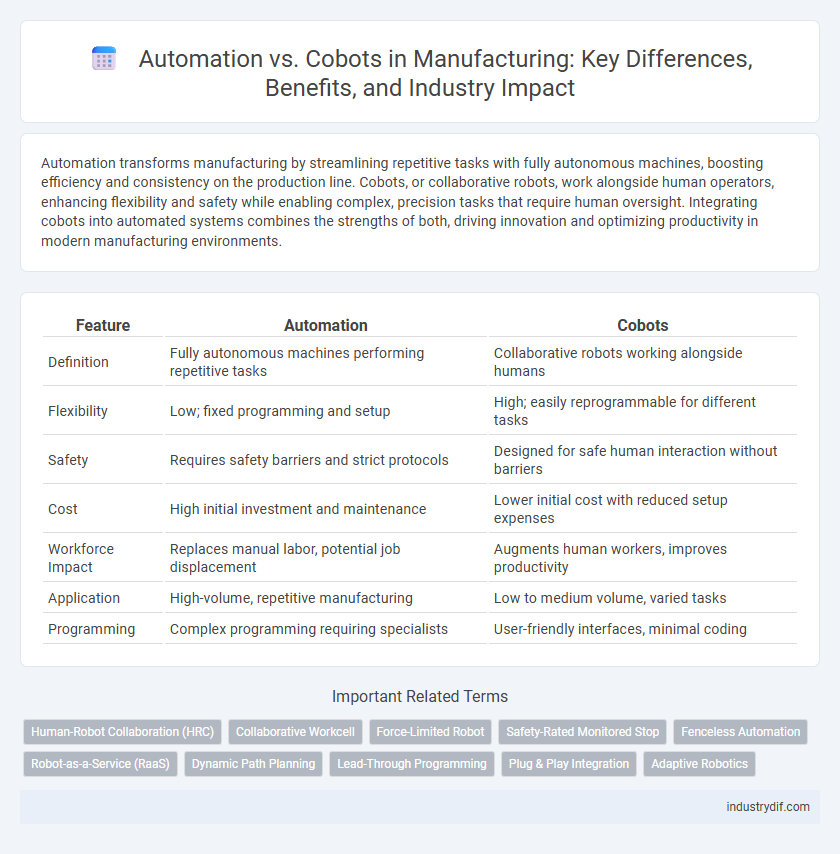
| Feature | Automation | Cobots |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully autonomous machines performing repetitive tasks | Collaborative robots working alongside humans |
| Flexibility | Low; fixed programming and setup | High; easily reprogrammable for different tasks |
| Safety | Requires safety barriers and strict protocols | Designed for safe human interaction without barriers |
| Cost | High initial investment and maintenance | Lower initial cost with reduced setup expenses |
| Workforce Impact | Replaces manual labor, potential job displacement | Augments human workers, improves productivity |
| Application | High-volume, repetitive manufacturing | Low to medium volume, varied tasks |
| Programming | Complex programming requiring specialists | User-friendly interfaces, minimal coding |
Defining Automation and Cobots in Modern Manufacturing
Automation in modern manufacturing refers to the use of advanced machinery, control systems, and software to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Cobots, or collaborative robots, are designed to work safely alongside human operators, augmenting manual processes by providing precision and repetitive task support without replacing the human workforce. Both automation and cobots drive innovation by optimizing production workflows and reducing operational costs in smart factories.
Key Differences Between Traditional Automation and Cobots
Traditional automation relies on fixed, programmed machinery designed for repetitive, high-volume tasks with minimal human interaction, optimizing speed and precision but lacking flexibility. Cobots, or collaborative robots, are engineered to safely work alongside humans, offering adaptability and ease of programming for varied and complex manufacturing processes. Key differences include safety features, ease of integration, and operational flexibility, with cobots enhancing human-robot collaboration to improve productivity and reduce downtime.
Advantages of Automation Systems in Manufacturing
Automation systems in manufacturing significantly increase production speed and consistency, reducing human error and operational costs. These systems enable continuous 24/7 operation, enhancing throughput and optimizing resource utilization. Integration of advanced robotics and machine learning further improves precision, quality control, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Unique Benefits of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots (cobots) offer unique benefits in manufacturing, such as enhanced safety features that enable direct human-robot interaction without protective barriers. Cobots provide exceptional flexibility, easily programmable for diverse tasks and adaptable to varying production needs, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime. Their compact design and lower cost of integration make cobots ideal for small and medium-sized enterprises seeking scalable automation solutions.
Implementation Challenges: Automation vs Cobots
Automation systems often face challenges related to high initial costs, complex integration with existing processes, and the need for specialized technical expertise during implementation. Cobots present fewer barriers due to their user-friendly programming, collaborative design, and adaptability to work alongside human operators without extensive retooling. However, cobots may have limitations in payload capacity and speed compared to traditional automation, impacting their suitability for certain high-volume manufacturing tasks.
Safety Considerations: Automated Machines vs Collaborative Robots
Automated machines in manufacturing typically operate within safety cages or designated zones to prevent human contact, reducing the risk of accidents but limiting flexibility. Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed with advanced sensors and force-limiting features to ensure safe interaction alongside human workers, enhancing operational efficiency in shared workspaces. Safety standards such as ISO 10218 and ISO/TS 15066 provide guidelines for assessing and implementing risk mitigation measures for both automated systems and cobots.
Cost Implications: Long-term ROI of Automation and Cobots
Automation systems often require a significant upfront investment but deliver substantial long-term cost savings through increased production speed and reduced labor expenses. Cobots, or collaborative robots, involve lower initial costs and flexible deployment, enabling manufacturers to scale operations with minimal disruption and optimize labor efficiency. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance, integration, and productivity gains, reveals that cobots offer faster ROI for small to mid-sized production, while full automation yields greater savings in high-volume, repetitive manufacturing.
Workforce Impact: Job Transformation in Automated Environments
Automation and cobots drive significant workforce transformation by reallocating human roles towards oversight, maintenance, and programming of machines instead of repetitive manual tasks. Cobots enhance collaboration, enabling workers to focus on higher-value activities while ensuring safety and efficiency on the manufacturing floor. This shift promotes upskilling, reduces physical strain, and fosters innovation within industrial environments.
Flexibility and Scalability: Automation vs Cobots Solutions
Cobots offer unmatched flexibility in manufacturing environments, easily adapting to various tasks without extensive reprogramming, which significantly shortens deployment times. Automation systems provide high scalability for large-scale production, delivering consistent performance and efficiency in repetitive, high-volume processes. Integrating cobots with traditional automation enhances overall system flexibility and scalability, allowing manufacturers to optimize resource allocation and respond swiftly to market changes.
Future Trends: Integration of AI with Automation and Cobots
The future of manufacturing revolves around the integration of AI with automation and cobots, enabling smarter, more adaptive production lines that enhance efficiency and precision. AI-driven analytics empower cobots to learn from real-time data, optimize workflows, and collaborate safely with human workers. This convergence accelerates innovation, reducing downtime and operational costs while enabling mass customization.
Related Important Terms
Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC)
Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) in manufacturing enhances productivity by integrating collaborative robots (cobots) with traditional automation systems, allowing workers to safely share tasks with robots. Cobots adapt to dynamic environments and provide flexibility that rigid automation lacks, improving efficiency and reducing ergonomic risks in complex assembly and quality control processes.
Collaborative Workcell
Collaborative workcells integrating cobots enhance manufacturing automation by enabling safe, flexible human-robot interaction that boosts productivity and reduces downtime. Unlike traditional automation, cobots adapt to dynamic tasks and optimize workflow efficiency within shared workspaces.
Force-Limited Robot
Force-limited robots in manufacturing enhance safety by using sensors to precisely control applied force, reducing risk during human-robot interaction compared to traditional automation systems. Cobots equipped with force-limited capabilities provide flexible, collaborative solutions optimizing efficiency without compromising worker protection.
Safety-Rated Monitored Stop
Safety-rated monitored stop technology in automation ensures machines halt immediately when a human enters a hazardous zone, significantly reducing injury risks compared to traditional systems. While cobots are designed for direct human-robot interaction with integrated safety features, the monitored stop enhances safety in both fully automated and collaborative environments by preventing unintended movements during human intervention.
Fenceless Automation
Fenceless automation leverages advanced sensors and AI technology to enable collaborative robots (cobots) and automated systems to operate safely in shared workspaces without physical barriers, enhancing flexibility and productivity in manufacturing environments. This approach contrasts traditional fenced automation, reducing costs and improving human-robot interaction while maintaining strict safety compliance.
Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) transforms manufacturing automation by providing flexible, subscription-based access to advanced robots and cobots without the need for hefty upfront investment. This model enables manufacturers to rapidly scale production and integrate collaborative robots that enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize labor costs in dynamic industrial environments.
Dynamic Path Planning
Dynamic path planning in automation leverages advanced algorithms and sensor data to enable autonomous robots to adapt trajectories in real-time for optimized manufacturing efficiency. Collaborative robots (cobots) integrate dynamic path planning with human interaction capabilities, allowing flexible, safe adjustments to workflows while maintaining precision and reducing cycle times.
Lead-Through Programming
Lead-through programming enables both automation systems and collaborative robots (cobots) to be intuitively guided by human operators, reducing setup time and complexity in manufacturing processes. Cobots leverage lead-through programming to easily adapt to variable tasks and environments, enhancing flexibility compared to traditional automation that often relies on rigid, pre-programmed routines.
Plug & Play Integration
Automation systems offer scalable solutions with high precision and speed, but often require complex programming and setup, whereas cobots provide plug & play integration that enhances flexibility and rapid deployment on manufacturing lines. Collaborative robots can seamlessly work alongside human operators, minimizing downtime with intuitive interfaces and simplified installation processes.
Adaptive Robotics
Adaptive robotics enhance manufacturing efficiency by integrating both automation and collaborative robots (cobots), enabling real-time adjustments to dynamic production environments. This synergy reduces downtime and increases precision, surpassing traditional automation's limitations.
Automation vs Cobots Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com