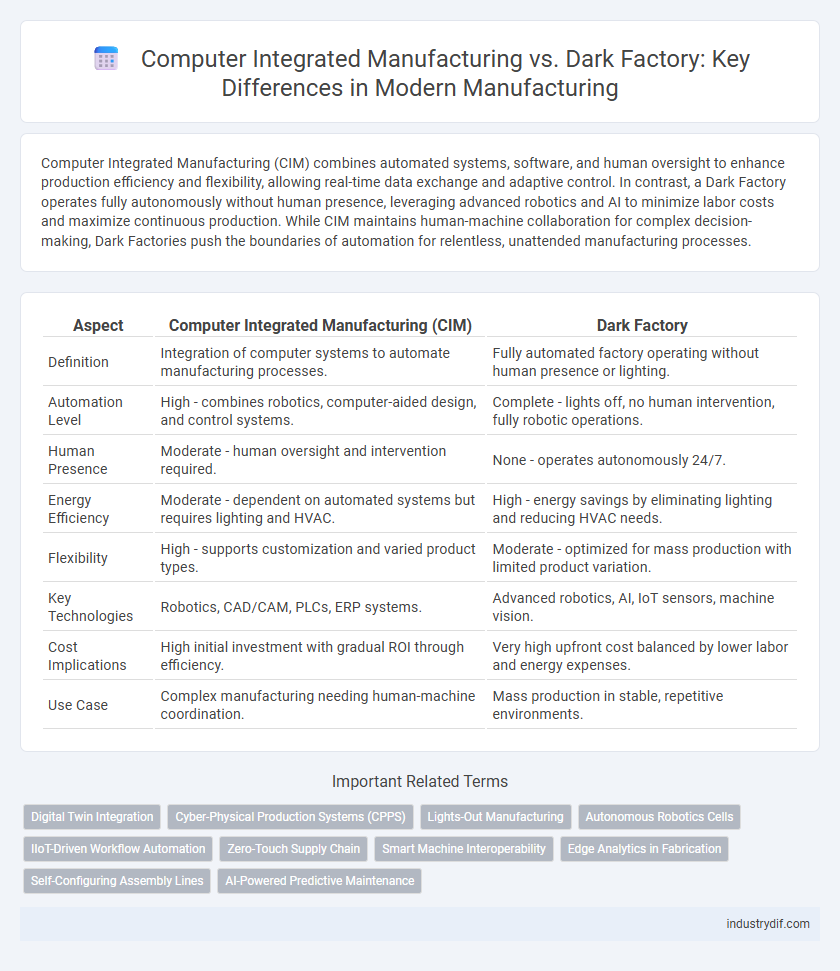
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) combines automated systems, software, and human oversight to enhance production efficiency and flexibility, allowing real-time data exchange and adaptive control. In contrast, a Dark Factory operates fully autonomously without human presence, leveraging advanced robotics and AI to minimize labor costs and maximize continuous production. While CIM maintains human-machine collaboration for complex decision-making, Dark Factories push the boundaries of automation for relentless, unattended manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) | Dark Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of computer systems to automate manufacturing processes. | Fully automated factory operating without human presence or lighting. |
| Automation Level | High - combines robotics, computer-aided design, and control systems. | Complete - lights off, no human intervention, fully robotic operations. |
| Human Presence | Moderate - human oversight and intervention required. | None - operates autonomously 24/7. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate - dependent on automated systems but requires lighting and HVAC. | High - energy savings by eliminating lighting and reducing HVAC needs. |
| Flexibility | High - supports customization and varied product types. | Moderate - optimized for mass production with limited product variation. |
| Key Technologies | Robotics, CAD/CAM, PLCs, ERP systems. | Advanced robotics, AI, IoT sensors, machine vision. |
| Cost Implications | High initial investment with gradual ROI through efficiency. | Very high upfront cost balanced by lower labor and energy expenses. |
| Use Case | Complex manufacturing needing human-machine coordination. | Mass production in stable, repetitive environments. |
Introduction to Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) seamlessly integrates computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), robotics, and automated material handling to optimize production efficiency and flexibility. CIM systems enhance real-time data exchange, enabling precise control over manufacturing processes and reducing human intervention, which contrasts with Dark Factories that operate fully autonomously without human presence. Implementing CIM improves product quality, shortens lead times, and lowers operational costs through synchronized, digital workflows within smart factory environments.
Defining the Dark Factory Concept
The Dark Factory concept refers to fully automated manufacturing facilities operating without human presence, relying on advanced robotics, AI, and IoT technologies for continuous production. Unlike traditional Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) systems that integrate human operators with automated machines and software, Dark Factories minimize human intervention to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and enable 24/7 operation. This shift leverages sensor networks, autonomous robots, and machine learning algorithms to monitor and control every aspect of production environments in real-time.
Key Technologies in CIM and Dark Factories
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) relies on advanced technologies such as robotics, computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and automated material handling systems to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Dark Factories utilize fully autonomous robotic systems, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to enable continuous, lights-out manufacturing with minimal human intervention. Both systems integrate real-time data analytics and digital twin technology to optimize production processes and ensure high-quality output.
Automation Levels: Human Involvement vs Full Autonomy
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) combines human involvement with automated machinery, facilitating greater flexibility and real-time decision-making on the production line. Dark Factories operate at the highest automation levels, achieving full autonomy with minimal or no human presence, relying entirely on robotics and AI for manufacturing processes. The distinct difference lies in CIM's hybrid approach versus Dark Factory's fully automated environment, impacting efficiency, error rates, and operational costs.
Data Integration and Digital Connectivity
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) emphasizes seamless data integration across design, production, and quality control systems, enabling real-time decision-making and enhanced operational efficiency. Dark Factories leverage advanced digital connectivity through IoT sensors and AI-driven automation to operate without human intervention, optimizing continuous production and minimizing downtime. Both approaches rely heavily on robust data integration frameworks to synchronize digital workflows and drive smart manufacturing outcomes.
Operational Efficiency and Production Speed
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) enhances operational efficiency by seamlessly integrating design, production, and control processes through advanced software and automation, enabling real-time monitoring and rapid adjustments. Dark Factory leverages fully automated, human-free production environments to maximize production speed and reduce errors, relying heavily on robotics and AI-driven systems. While CIM improves coordination and reduces cycle times, Dark Factory pushes the boundaries of speed and consistency by eliminating human-related delays and variability.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) streamlines production processes through automation and real-time data exchange, significantly reducing labor costs and minimizing material waste, which enhances overall cost efficiency. Dark Factory operations, characterized by fully automated, unmanned facilities, further cut labor expenses and enable 24/7 production, accelerating return on investment through higher throughput and reduced downtime. While CIM requires substantial upfront infrastructure and software integration investments, Dark Factories demand higher capital expenditure on robotics and AI systems but offer superior long-term cost savings and faster ROI due to continuous, autonomous operations.
Scalability and Flexibility in Both Systems
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) offers high scalability through automated system integration, enabling seamless expansion across production lines while maintaining flexibility in customizing workflows. Dark Factories leverage autonomous operations and AI-driven machinery to enhance scalability by minimizing human intervention, though flexibility may be limited by fixed robotic programming. Both systems improve production efficiency, but CIM accommodates variable product designs better, whereas Dark Factories excel in consistent, high-volume output with optimized resource allocation.
Challenges and Limitations of CIM and Dark Factories
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, complex system integration, and reliance on skilled personnel for maintenance and troubleshooting. Dark Factories, while offering full automation with minimal human intervention, are limited by current technology constraints in handling unexpected errors and adapting to varying production requirements. Both systems encounter difficulties in scalability, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and maintaining flexibility in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Future Trends in Smart Manufacturing
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) integrates advanced computer systems with production processes to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility in manufacturing operations. Dark Factories represent the evolution of CIM by utilizing autonomous robots and AI-driven systems to operate without human presence, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing operational continuity. Future trends in smart manufacturing emphasize the fusion of IoT, machine learning, and real-time data analytics to create fully autonomous, self-optimizing production environments that maximize productivity and sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Integration
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) leverages Digital Twin Integration to create real-time virtual replicas of physical production systems, enabling precise monitoring and adaptive process optimization. In contrast, Dark Factory environments fully automate operations with minimal human intervention, relying on advanced Digital Twin models to synchronize and control autonomous machinery, maximizing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Cyber-Physical Production Systems (CPPS)
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) leverages Cyber-Physical Production Systems (CPPS) to seamlessly connect digital design, automated machinery, and real-time data analytics, optimizing production efficiency and flexibility. Dark Factories extend CPPS by enabling fully autonomous operations without human intervention or lighting, maximizing energy savings and operational precision through advanced robotics and AI-driven control systems.
Lights-Out Manufacturing
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) streamlines production through automation and real-time data integration, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Lights-Out Manufacturing, exemplified by Dark Factories, eliminates the need for on-site human presence by utilizing fully automated systems, enabling continuous, 24/7 operation and significant cost savings.
Autonomous Robotics Cells
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) leverages Autonomous Robotics Cells to enhance production efficiency, enabling real-time data integration and adaptive process control. In contrast, Dark Factories utilize these autonomous cells in completely unmanned environments, maximizing operation continuity and minimizing human intervention for 24/7 manufacturing.
IIoT-Driven Workflow Automation
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) leverages IIoT-driven workflow automation to seamlessly connect machinery, sensors, and control systems, enabling real-time data exchange and enhanced production efficiency. In contrast, Dark Factories operate fully automated, human-free environments where IIoT devices optimize operations continuously, reducing errors and maximizing uptime through autonomous decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Zero-Touch Supply Chain
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) enables seamless automation of production processes through real-time data integration, while Dark Factory emphasizes fully autonomous operations without human presence, optimizing efficiency and reducing errors. Zero-Touch Supply Chain leverages CIM and Dark Factory technologies to achieve end-to-end automation, minimizing manual interventions and accelerating order fulfillment in manufacturing.
Smart Machine Interoperability
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) enables smart machine interoperability by unifying diverse automated systems through centralized control protocols, enhancing real-time data exchange and operational efficiency. Dark Factories rely heavily on this advanced interoperability to operate autonomously without human intervention, optimizing production with seamless machine-to-machine communication and intelligent process coordination.
Edge Analytics in Fabrication
Computer Integrated Manufacturing leverages centralized systems for design-to-production workflows, while Dark Factories utilize fully automated, lights-out operations enhanced by Edge Analytics to monitor real-time sensor data and optimize fabrication processes on-site. Edge Analytics in these environments enables low-latency decision-making, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control, significantly improving production efficiency and reducing downtime in smart manufacturing.
Self-Configuring Assembly Lines
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) enhances production efficiency through automated data exchange and system integration, enabling self-configuring assembly lines that adapt in real-time to varying production demands. In contrast, dark factories leverage fully autonomous, sensor-driven self-configuring assembly lines operating without human intervention, maximizing operational continuity and reducing labor costs.
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) leverages AI-powered predictive maintenance to minimize downtime by analyzing real-time sensor data and forecasting equipment failures. Dark Factories enhance this approach with fully autonomous operations, enabling continuous monitoring and maintenance without human intervention, significantly boosting productivity and operational efficiency.
Computer Integrated Manufacturing vs Dark Factory Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com