Traditional supply chains often face challenges such as lack of transparency, delays, and counterfeit risks throughout the manufacturing process. Blockchain supply solutions enhance traceability and security by providing a decentralized ledger that records every transaction and movement of materials in real-time. This technology minimizes errors, reduces costs, and improves trust among manufacturers, suppliers, and customers.
Table of Comparison
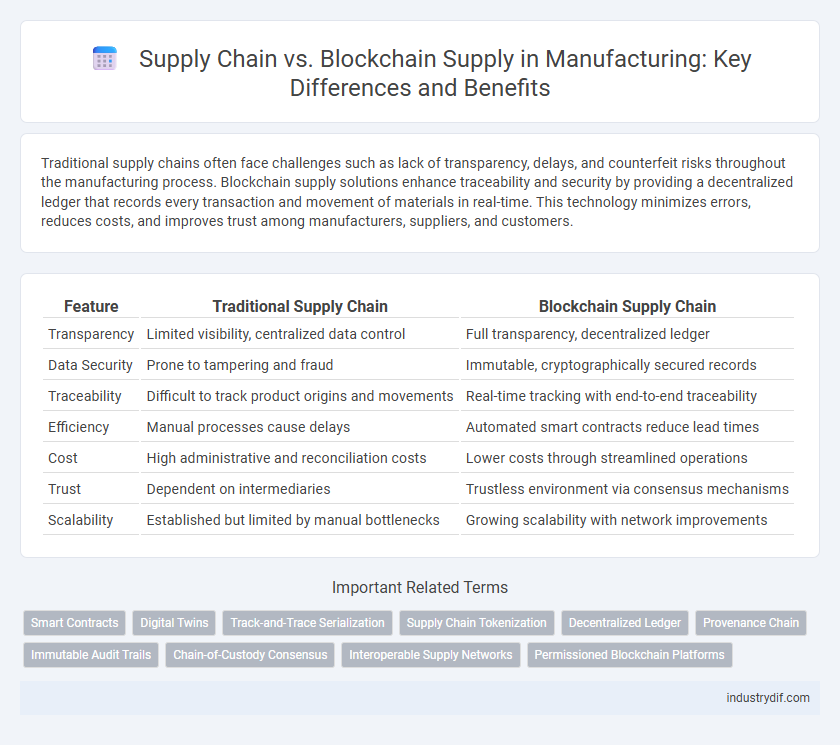
| Feature | Traditional Supply Chain | Blockchain Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Limited visibility, centralized data control | Full transparency, decentralized ledger |
| Data Security | Prone to tampering and fraud | Immutable, cryptographically secured records |
| Traceability | Difficult to track product origins and movements | Real-time tracking with end-to-end traceability |
| Efficiency | Manual processes cause delays | Automated smart contracts reduce lead times |
| Cost | High administrative and reconciliation costs | Lower costs through streamlined operations |
| Trust | Dependent on intermediaries | Trustless environment via consensus mechanisms |
| Scalability | Established but limited by manual bottlenecks | Growing scalability with network improvements |
Understanding Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional supply chain management involves coordinating suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and retailers to ensure efficient production and distribution of goods. It relies heavily on centralized databases and manual processes, which can lead to delays, errors, and limited transparency. This system often struggles with tracking product provenance and real-time data sharing across multiple stakeholders.
Key Challenges in Conventional Supply Chains
Conventional supply chains face key challenges such as lack of transparency, delayed information flow, and vulnerability to fraud and errors, leading to inefficiencies and increased operational costs. Complex logistics and multiple intermediaries hinder real-time tracking and accountability across production, inventory, and delivery stages. Limited data interoperability and manual record-keeping contribute to inaccurate demand forecasting and reduced responsiveness in global manufacturing networks.
Introduction to Blockchain Supply Solutions
Blockchain supply solutions introduce decentralized ledger technology to optimize manufacturing supply chains by enhancing transparency, traceability, and security of transactions. Unlike traditional supply chains relying on centralized databases, blockchain provides immutable records accessible to all stakeholders, reducing fraud, errors, and delays. This innovation streamlines operations, improves inventory management, and strengthens trust among suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Supply Chain: Core Differences
Blockchain supply chain integrates decentralized ledger technology, enhancing transparency, traceability, and security compared to traditional supply chains reliant on centralized databases. Traditional supply chains often face challenges like data discrepancies, delays in information sharing, and susceptibility to fraud, while blockchain provides real-time, immutable records accessible to all stakeholders. Smart contracts in blockchain automate and verify transactions, reducing intermediaries and operational costs, thus optimizing manufacturing supply chain efficiency.
Enhanced Transparency with Blockchain Supply Systems
Blockchain supply systems provide enhanced transparency by creating immutable, time-stamped records of every transaction and movement within the manufacturing supply chain. This decentralized ledger enables manufacturers to track raw materials, monitor production stages, and verify product authenticity in real time. Increased visibility reduces fraud, minimizes delays, and improves regulatory compliance, driving efficiency and trust across the entire supply network.
Real-Time Tracking and Data Integrity
Real-time tracking in traditional supply chains often faces delays and data discrepancies due to centralized data management and limited visibility. Blockchain supply chains utilize decentralized ledgers to provide immutable, transparent records, enhancing data integrity and enabling instantaneous tracking across all stakeholders. This technology reduces errors, prevents fraud, and improves efficiency by ensuring all parties access synchronized and verified supply chain information in real time.
Improving Traceability in Manufacturing Supply Chains
Manufacturing supply chains benefit significantly from blockchain technology by enhancing traceability through immutable, decentralized ledgers that record every transaction and movement of materials in real-time. This improved traceability reduces errors, prevents counterfeiting, and ensures compliance with industry standards by providing transparent and verifiable data across all supply chain participants. In traditional supply chains, information silos and manual record-keeping often cause delays and inaccuracies, whereas blockchain enables seamless data sharing and auditing, fostering trust and efficiency.
Cost Efficiencies: Blockchain versus Legacy Supply Chains
Blockchain supply chains enhance cost efficiencies by reducing intermediaries and streamlining transactions through decentralized ledgers, resulting in lower administrative and reconciliation expenses. Legacy supply chains often incur higher costs due to manual processes, opaque data flows, and slower settlement times, which increase overhead and inventory holding costs. Implementing blockchain technology in manufacturing supply chains improves transparency and traceability, minimizing fraud and errors while fostering faster payment cycles and optimized inventory management.
Case Studies: Blockchain Implementation in Manufacturing
Case studies in manufacturing reveal that blockchain implementation enhances supply chain transparency, reduces counterfeit risks, and streamlines inventory management. Companies like BMW and Siemens utilize blockchain to track parts provenance and secure data sharing across global suppliers, improving efficiency and trust. This technology drives real-time visibility and traceability, crucial for minimizing disruptions and ensuring regulatory compliance in complex manufacturing supply chains.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Supply Chain with Blockchain
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by enhancing transparency, traceability, and security in global manufacturing networks. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of decentralized ledgers to streamline provenance tracking, reduce fraud, and optimize inventory management through smart contracts. Integration of blockchain with IoT and AI will drive real-time data synchronization, enabling predictive analytics and more efficient, automated supply chain operations.
Related Important Terms
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts in blockchain supply chains automate procurement and payment processes, increasing transparency and reducing human error compared to traditional supply chain systems. This technology ensures real-time tracking of goods and enforces contract terms without intermediaries, optimizing manufacturing operations and reducing costs.
Digital Twins
Supply Chain management integrates Digital Twins to create real-time, virtual replicas of physical assets, enhancing visibility and predictive analytics for inventory and logistics operations. Blockchain Supply leverages these Digital Twins within a decentralized ledger, ensuring tamper-proof data tracking, improved traceability, and secure collaboration across manufacturing stakeholders.
Track-and-Trace Serialization
Track-and-trace serialization in traditional supply chains relies on barcode scanning and manual data entry, often leading to errors and limited real-time visibility. Blockchain-enabled supply chain solutions provide immutable, decentralized records that enhance transparency, allow for precise tracking of serialized items, and reduce counterfeiting risks in manufacturing.
Supply Chain Tokenization
Supply Chain Tokenization leverages blockchain technology to create secure, immutable digital representations of physical assets, enhancing transparency and traceability across manufacturing supply chains. This innovation reduces fraud, optimizes inventory management, and enables real-time tracking, significantly improving efficiency compared to traditional supply chain systems.
Decentralized Ledger
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases vulnerable to single points of failure, whereas blockchain supply chains utilize decentralized ledgers that enhance transparency, security, and traceability of manufacturing processes. This immutable, distributed ledger technology ensures real-time access to verified data by all stakeholders, reducing fraud and improving efficiency across global manufacturing networks.
Provenance Chain
Traditional supply chains often suffer from transparency issues and data silos, leading to inefficiencies and vulnerabilities in product tracking. Blockchain-based Provenance Chains enhance manufacturing supply networks by providing immutable, decentralized records that ensure real-time visibility, traceability, and trust in the origin and journey of materials.
Immutable Audit Trails
Traditional supply chains often struggle with transparency and trust due to centralized data management, leading to vulnerabilities in audit trails. Blockchain supply chain systems create immutable audit trails by recording every transaction on a decentralized ledger, enhancing traceability, reducing fraud, and enabling real-time verification of product authenticity.
Chain-of-Custody Consensus
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized record-keeping systems prone to errors and fraud, whereas blockchain supply chains utilize decentralized, tamper-proof ledgers to enhance chain-of-custody consensus by providing real-time, immutable tracking of goods from origin to delivery. This blockchain-enabled transparency improves traceability, reduces disputes, and ensures authentic provenance throughout the manufacturing supply process.
Interoperable Supply Networks
Interoperable supply networks leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency, traceability, and data integrity across multiple stakeholders in manufacturing supply chains. Traditional supply chains lack real-time, decentralized data synchronization, whereas blockchain-enabled networks facilitate seamless collaboration, reduce fraud, and optimize inventory management through secure, tamper-proof ledgers.
Permissioned Blockchain Platforms
Permissioned blockchain platforms enhance traditional supply chain management by providing secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping accessible only to authorized participants, improving trust and traceability. This technology reduces fraud, streamlines compliance, and enables real-time tracking of goods, outperforming conventional centralized systems in efficiency and data integrity.
Supply Chain vs Blockchain Supply Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com