The factory floor represents the physical space where manufacturing processes occur, involving machinery, human labor, and real-time operations. A digital twin creates a virtual replica of the factory floor, enabling simulation, monitoring, and optimization of production systems without disrupting actual workflows. Integrating digital twins with the factory floor enhances predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
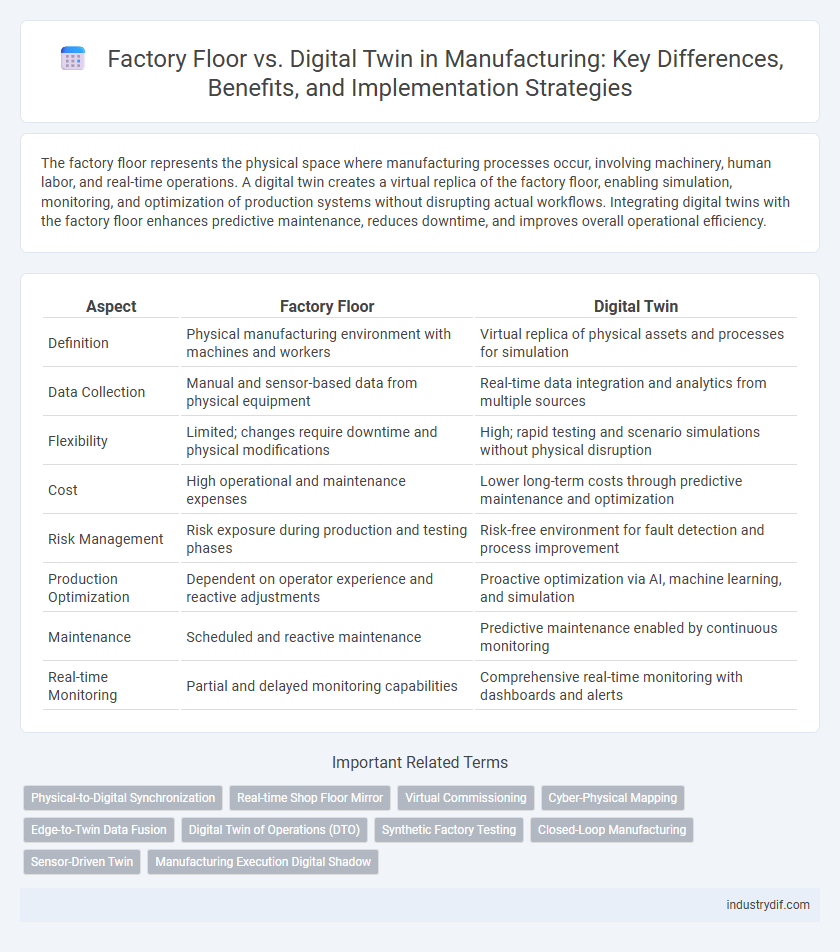
| Aspect | Factory Floor | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical manufacturing environment with machines and workers | Virtual replica of physical assets and processes for simulation |
| Data Collection | Manual and sensor-based data from physical equipment | Real-time data integration and analytics from multiple sources |
| Flexibility | Limited; changes require downtime and physical modifications | High; rapid testing and scenario simulations without physical disruption |
| Cost | High operational and maintenance expenses | Lower long-term costs through predictive maintenance and optimization |
| Risk Management | Risk exposure during production and testing phases | Risk-free environment for fault detection and process improvement |
| Production Optimization | Dependent on operator experience and reactive adjustments | Proactive optimization via AI, machine learning, and simulation |
| Maintenance | Scheduled and reactive maintenance | Predictive maintenance enabled by continuous monitoring |
| Real-time Monitoring | Partial and delayed monitoring capabilities | Comprehensive real-time monitoring with dashboards and alerts |
Defining the Factory Floor: Traditional Manufacturing Operations
The factory floor embodies traditional manufacturing operations where physical machinery, manual labor, and real-time processes converge to produce goods. It operates through direct interaction with equipment, relying on human supervision and physical workflow management. This environment contrasts with digital twin technology, which virtualizes factory floor activities for enhanced monitoring, simulation, and optimization.
Introduction to Digital Twin Technology in Manufacturing
Digital twin technology in manufacturing creates a virtual replica of the factory floor, enabling real-time monitoring and simulation of production processes. This innovation enhances predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and optimizes resource allocation by providing accurate data analytics from connected sensors and IoT devices. Integrating digital twins with factory floor operations drives smarter decision-making and accelerates Industry 4.0 transformation through increased efficiency and flexibility.
Key Differences Between Factory Floor and Digital Twin Systems
Factory floor systems involve physical production environments where machinery, equipment, and workers operate in real-time, while digital twin systems create virtual replicas of these environments to simulate, monitor, and optimize manufacturing processes. Key differences include real-time interaction on the factory floor versus predictive analytics and scenario testing in digital twins, with the latter enabling data-driven decision-making to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime. Digital twins integrate IoT sensors and AI algorithms, providing a dynamic model that reflects current conditions and forecasts future performance, unlike static factory floor setups.
Real-time Data: Physical Processes vs Virtual Models
Factory floors generate real-time data through sensors and machinery, capturing precise physical processes such as equipment status, production rates, and environmental conditions. Digital twins utilize this real-time data to create dynamic virtual models that simulate factory operations, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and scenario testing without interrupting actual production. The integration of physical real-time data with virtual twin models enhances manufacturing efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports informed decision-making.
Integration of IoT Devices in Factory Floor and Digital Twins
Integration of IoT devices on the factory floor enables real-time data collection and machine monitoring, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Digital twins leverage this IoT-generated data to create dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets, facilitating simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes. Seamless connectivity between IoT sensors and digital twins drives smarter decision-making and reduces downtime by simulating scenarios before implementation.
Operational Efficiency: Traditional vs Digital Twin Approaches
Factory floor operations rely on manual monitoring and physical inspections, leading to slower response times and higher chances of human error. Digital twin technology leverages real-time data simulations and predictive analytics to optimize equipment performance and minimize downtime. This digital approach enhances operational efficiency by providing continuous insights and enabling proactive maintenance strategies.
Predictive Maintenance: Manual Methods vs Digital Twin Analytics
Manual predictive maintenance on the factory floor relies heavily on scheduled inspections and operator experience, often leading to reactive repairs and unexpected downtime. Digital twin analytics use real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures before they occur, enhancing maintenance accuracy and minimizing operational interruptions. Integrating digital twins enables continuous monitoring and data-driven decision-making, significantly improving asset reliability and production efficiency.
Cost Implications: Factory Floor Operations vs Digital Twin Adoption
Factory floor operations often involve substantial costs related to physical resources, labor, energy consumption, and equipment maintenance, leading to variable overhead expenses. Digital twin adoption incurs initial investment in advanced sensors, IoT integration, and software platforms, but yields long-term savings through predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and optimized resource allocation. Analyzing cost implications highlights that while factory floor operations have recurring operational expenses, digital twin technology drives efficiency that can significantly lower total cost of ownership over time.
Workforce Skills: Evolving Roles in Digital Twin Environments
Workforce skills in factory floor operations are rapidly evolving as digital twin technology integrates real-time data and virtual simulations, requiring employees to develop expertise in data analytics, IoT systems, and digital modeling. Digital twin environments demand a blend of traditional manufacturing knowledge with advanced software proficiency to optimize production processes and enable predictive maintenance. This shift enhances operational efficiency and empowers the workforce to respond proactively to system anomalies and workflow disruptions.
Future Trends: Convergence of Factory Floor and Digital Twin Solutions
The convergence of factory floor operations and digital twin solutions is reshaping manufacturing by enabling real-time data integration and predictive analytics, which optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime. Advanced IoT sensors and AI-driven digital twins simulate physical assets and processes, providing actionable insights for proactive maintenance and quality control. This integration fosters smart factories that enhance agility, sustainability, and scalability, aligning with Industry 4.0 future trends.
Related Important Terms
Physical-to-Digital Synchronization
Factory floor operations leverage real-time sensor data to create a digital twin, enabling precise physical-to-digital synchronization that enhances process monitoring and predictive maintenance. This continuous data loop between the physical machinery and its digital counterpart drives improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and informed decision-making in manufacturing environments.
Real-time Shop Floor Mirror
A digital twin acts as a real-time shop floor mirror by continuously replicating factory floor operations, enabling instant monitoring and rapid response to production anomalies. This synchronized virtual model enhances decision-making, optimizes workflows, and reduces downtime through accurate, live data integration from manufacturing equipment and sensors.
Virtual Commissioning
Virtual commissioning leverages digital twin technology to simulate and validate factory floor operations, allowing for efficient identification and resolution of system errors before physical deployment. This approach reduces downtime, enhances productivity, and accelerates the integration of manufacturing equipment through precise virtual testing and optimization.
Cyber-Physical Mapping
Cyber-physical mapping integrates real-time sensor data from the factory floor with digital twin models to enhance precision in monitoring and optimizing manufacturing processes. This seamless synchronization enables predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves operational efficiency through accurate virtual replication of physical assets.
Edge-to-Twin Data Fusion
Edge-to-twin data fusion integrates real-time sensor data from factory floor machines with digital twin models, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance. This fusion enhances operational efficiency by providing synchronized insights between physical assets and their virtual counterparts in manufacturing environments.
Digital Twin of Operations (DTO)
Digital Twin of Operations (DTO) integrates real-time data from the factory floor to create a dynamic, virtual model that enhances predictive maintenance, optimizes workflows, and improves overall operational efficiency. By simulating production processes, DTO enables manufacturers to identify bottlenecks and implement data-driven decisions without disrupting actual manufacturing activities.
Synthetic Factory Testing
Synthetic factory testing using digital twins enables manufacturers to simulate and optimize factory floor operations in a virtual environment, reducing downtime and minimizing physical errors. This digital replication of production lines accelerates troubleshooting, enhances predictive maintenance, and supports efficient resource allocation.
Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Factory floors rely on physical processes and real-time sensor data, while digital twins create virtual replicas that simulate operations for predictive insights and optimization. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates these environments by continuously synchronizing factory floor feedback with digital twin models, enabling dynamic adjustments and enhancing production efficiency.
Sensor-Driven Twin
Sensor-driven digital twins on the factory floor utilize real-time data from IoT sensors to create dynamic, precise virtual replicas of manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized production flows. These digital twins enhance operational efficiency by continuously synchronizing physical equipment conditions with their virtual models, allowing manufacturers to detect anomalies and reduce downtime proactively.
Manufacturing Execution Digital Shadow
Manufacturing Execution Digital Shadow integrates real-time factory floor data with digital twin technology, enabling precise monitoring and optimization of production processes. This seamless connection enhances decision-making by providing an accurate, up-to-date virtual representation of manufacturing operations.
Factory Floor vs Digital Twin Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com