Supply Chain Management focuses on optimizing the flow of materials and information from suppliers to the end customer to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. Circular Supply Chains prioritize reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials to minimize waste and promote sustainability throughout the product lifecycle. Integrating circular principles within traditional supply chain management enhances resource efficiency and supports environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
Table of Comparison
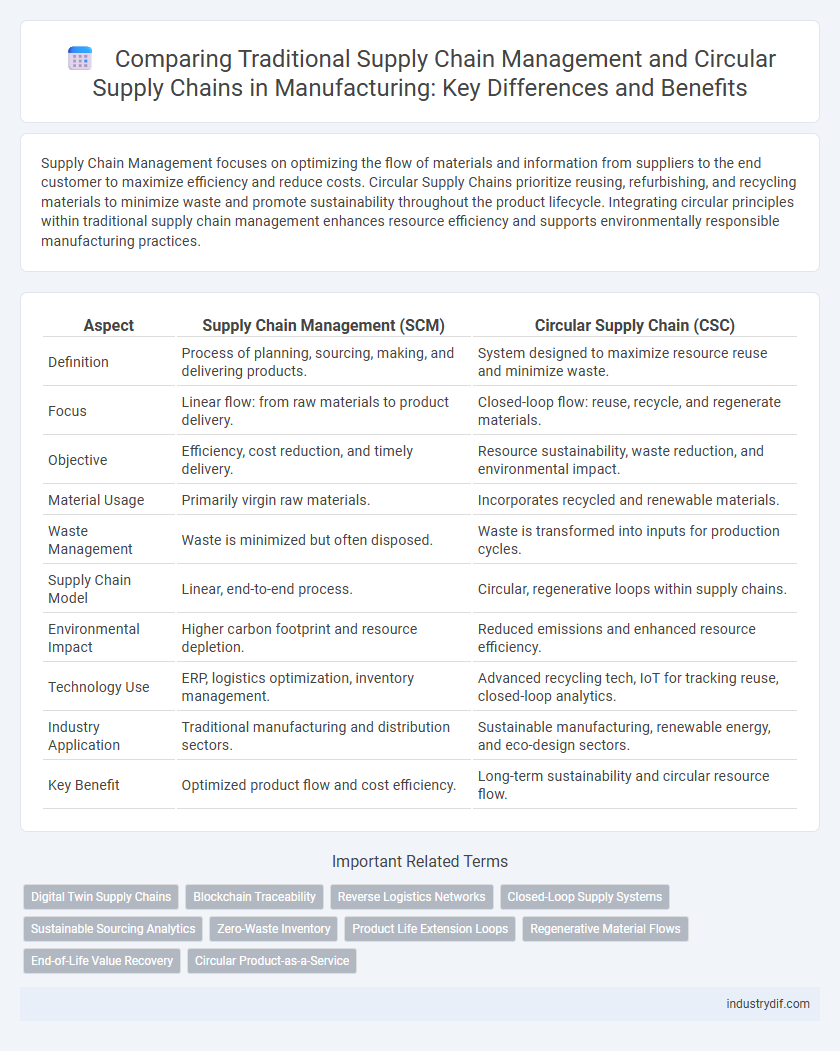
| Aspect | Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Circular Supply Chain (CSC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of planning, sourcing, making, and delivering products. | System designed to maximize resource reuse and minimize waste. |
| Focus | Linear flow: from raw materials to product delivery. | Closed-loop flow: reuse, recycle, and regenerate materials. |
| Objective | Efficiency, cost reduction, and timely delivery. | Resource sustainability, waste reduction, and environmental impact. |
| Material Usage | Primarily virgin raw materials. | Incorporates recycled and renewable materials. |
| Waste Management | Waste is minimized but often disposed. | Waste is transformed into inputs for production cycles. |
| Supply Chain Model | Linear, end-to-end process. | Circular, regenerative loops within supply chains. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint and resource depletion. | Reduced emissions and enhanced resource efficiency. |
| Technology Use | ERP, logistics optimization, inventory management. | Advanced recycling tech, IoT for tracking reuse, closed-loop analytics. |
| Industry Application | Traditional manufacturing and distribution sectors. | Sustainable manufacturing, renewable energy, and eco-design sectors. |
| Key Benefit | Optimized product flow and cost efficiency. | Long-term sustainability and circular resource flow. |
Understanding Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional Supply Chain Management focuses on the linear flow of materials from suppliers through manufacturing to end consumers, emphasizing efficiency, cost reduction, and timely delivery. It relies heavily on demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics coordination to optimize production and distribution processes. This approach often leads to resource depletion and waste, prompting the evolution toward more sustainable models like circular supply chains.
What Are Circular Supply Chains?
Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency by designing processes that prioritize reuse, recycling, and sustainable sourcing throughout the product lifecycle. Unlike traditional linear supply chains, circular models emphasize closed-loop systems where materials are continuously cycled back into production to reduce environmental impact. Industries implementing circular supply chains benefit from reduced raw material costs, enhanced sustainability credentials, and compliance with increasing regulatory demands for eco-friendly practices.
Key Differences: Linear vs. Circular Models
Supply Chain Management traditionally follows a linear model focused on a sequential flow of materials from raw resources to end consumers, often resulting in waste and resource depletion. Circular Supply Chains emphasize closed-loop processes by integrating product reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing to minimize waste and extend material lifecycle. Key differences lie in resource efficiency, environmental impact, and system design, where circular models prioritize sustainability and continuous material flow in contrast to the one-way throughput of linear supply chains.
Environmental Impact of Each Approach
Traditional Supply Chain Management often prioritizes cost-efficiency and speed, leading to significant waste generation and higher carbon emissions. Circular Supply Chains emphasize resource recovery and product lifecycle extension, substantially reducing environmental impact through minimized raw material extraction and waste. Studies show circular models can lower greenhouse gas emissions by up to 40%, highlighting their role in sustainable manufacturing.
Operational Efficiency in Manufacturing
Supply Chain Management in manufacturing prioritizes streamlined processes, cost reduction, and timely delivery to enhance operational efficiency. Circular Supply Chains emphasize resource recovery, waste minimization, and product lifecycle extension, driving sustainable efficiency improvements. Integrating circular principles with traditional supply chains optimizes material flows and reduces environmental impacts, boosting overall manufacturing performance.
Role of Technology in Supply Chain Transformation
Technology drives supply chain transformation by integrating advanced analytics, IoT, and blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and real-time decision-making in both traditional Supply Chain Management and Circular Supply Chains. In circular supply chains, technology enables efficient resource tracking, waste reduction, and product lifecycle management, promoting sustainability and closed-loop processes. Digital platforms and automation streamline procurement, inventory control, and reverse logistics, accelerating the shift from linear to circular supply chain models.
Cost Implications: Traditional vs. Circular Supply Chains
Traditional supply chain management often incurs higher costs due to linear processes involving raw material extraction, production, and disposal, leading to increased waste and resource depletion. Circular supply chains reduce these expenses by integrating reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing, enhancing resource efficiency and minimizing waste management costs. Cost savings in circular models also arise from extended product lifecycles and decreased reliance on virgin materials, improving long-term financial sustainability in manufacturing operations.
Challenges in Adopting Circular Supply Chains
Adopting circular supply chains in manufacturing faces significant challenges such as redesigning production processes to enable material reuse and establishing reverse logistics systems for efficient product return and recycling. Companies must overcome supply chain complexity, including securing reliable sources of recycled materials and ensuring quality standards consistent with linear supply chains. Limited technological infrastructure and regulatory ambiguities further hinder large-scale implementation, slowing the transition from traditional supply chain management to circular models.
Future Trends Shaping Supply Chain Strategies
Future trends in supply chain management emphasize the integration of circular supply chains to enhance sustainability and resource efficiency. Technologies like blockchain and AI enable real-time tracking and optimization, reducing waste and promoting product lifecycle extension. Companies adopting circular supply chains can improve resilience and comply with increasing environmental regulations while meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Best Practices for Manufacturers Transitioning to Circularity
Manufacturers transitioning to circular supply chains should prioritize resource efficiency by integrating closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize material reuse throughout production processes. Collaboration with suppliers and stakeholders ensures transparency and traceability, enabling effective reverse logistics and sustainable sourcing strategies. Leveraging digital technologies like IoT and blockchain enhances inventory management and data analytics, supporting continuous improvement in circularity and compliance with environmental regulations.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Supply Chains
Digital Twin Supply Chains enhance traditional Supply Chain Management by creating real-time digital replicas of physical processes, enabling predictive analytics and seamless resource optimization. Circular Supply Chains leverage these digital twins to monitor product lifecycle, facilitate closed-loop recycling, and minimize waste through continuous data-driven feedback.
Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability enhances traditional supply chain management by providing immutable records of product origins and movements, fostering transparency and accountability in manufacturing processes. In circular supply chains, blockchain technology further enables efficient tracking of materials for reuse and recycling, optimizing resource recovery and minimizing waste.
Reverse Logistics Networks
Reverse logistics networks in circular supply chains emphasize product return, refurbishment, and recycling to extend asset lifecycle, contrasting traditional supply chain management that prioritizes forward flow efficiency. Implementing robust reverse logistics enhances sustainability, reduces waste, and supports closed-loop systems, driving circular economy goals within manufacturing operations.
Closed-Loop Supply Systems
Closed-loop supply systems in circular supply chains enhance sustainability by integrating product return, remanufacturing, and recycling processes, reducing raw material dependency and waste generation. Traditional supply chain management primarily focuses on linear resource flow, whereas circular models prioritize resource recovery and product lifecycle extension to optimize environmental and economic performance.
Sustainable Sourcing Analytics
Supply Chain Management integrates data-driven sustainable sourcing analytics to optimize procurement while minimizing environmental impact through efficient resource allocation and supplier performance tracking. Circular Supply Chains enhance sustainability by leveraging analytics to facilitate product lifecycle extension, waste reduction, and material reuse, promoting closed-loop systems and reducing dependency on virgin resources.
Zero-Waste Inventory
Traditional supply chain management emphasizes efficiency and cost reduction, often leading to excess inventory and waste, while circular supply chains prioritize zero-waste inventory by redesigning processes to reuse materials and minimize resource consumption. Implementing circular supply chain principles can significantly reduce environmental impact and operational costs through closed-loop systems and enhanced resource recovery.
Product Life Extension Loops
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes efficient resource flow from raw materials to end consumers, whereas Circular Supply Chains prioritize Product Life Extension Loops by redesigning processes to maximize the reuse, refurbishing, and remanufacturing of products. These loops reduce waste and resource consumption by extending product lifespan through strategies such as repair, remanufacturing, and product-as-a-service models, driving sustainable manufacturing practices.
Regenerative Material Flows
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes linear resource flows focused on efficiency and cost reduction, while Circular Supply Chains prioritize regenerative material flows that minimize waste and enable continuous reuse of resources. Implementing circular strategies enhances sustainability by closing material loops and fostering resource resilience within manufacturing operations.
End-of-Life Value Recovery
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes efficient product flow from raw materials to end-user delivery, often neglecting the potential value in end-of-life products, whereas Circular Supply Chains prioritize End-of-Life Value Recovery by reintegrating used materials through recycling, refurbishing, and remanufacturing processes. This approach reduces waste, lowers costs, and enhances sustainability by extending product lifecycles and capturing residual value from discarded assets.
Circular Product-as-a-Service
Circular Product-as-a-Service models in supply chain management prioritize product lifecycle extension, resource efficiency, and waste reduction by shifting ownership from consumers to producers who retain responsibility for product maintenance, reuse, and recycling. This approach contrasts traditional linear supply chains by integrating circularity principles, driving sustainable manufacturing while optimizing cost management and customer value through product-service systems.
Supply Chain Management vs Circular Supply Chains Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com