Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes employee involvement and proactive equipment care to maximize overall production efficiency and minimize downtime. Predictive Maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling targeted interventions. Both strategies aim to enhance machinery reliability, but TPM focuses on holistic, team-driven maintenance while Predictive Maintenance relies heavily on technology and condition monitoring.
Table of Comparison
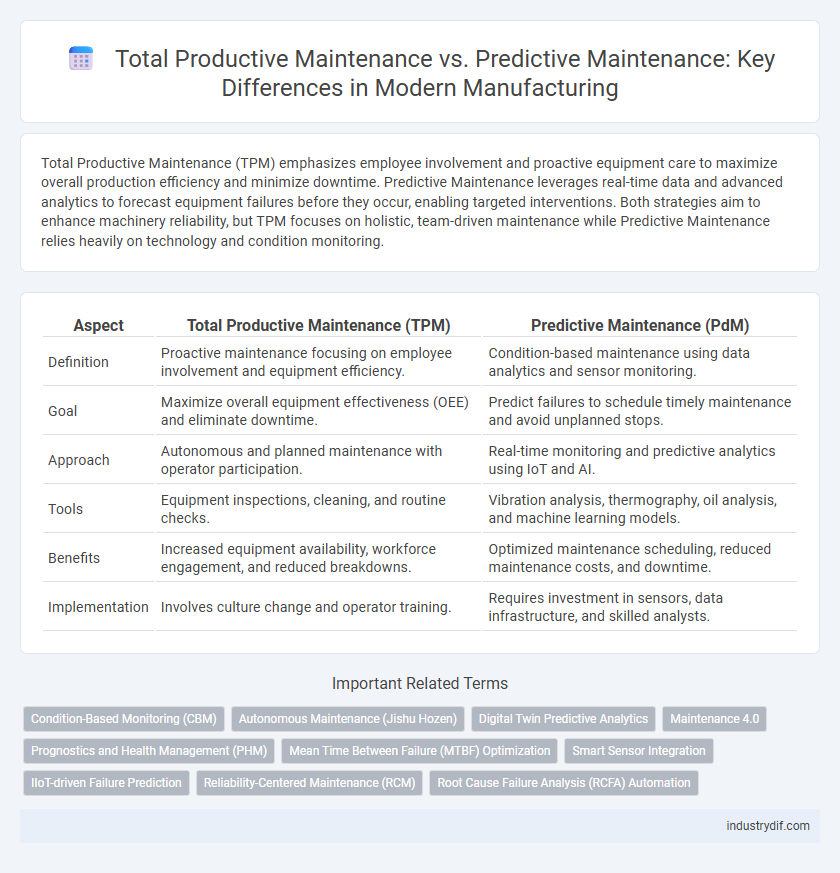
| Aspect | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive maintenance focusing on employee involvement and equipment efficiency. | Condition-based maintenance using data analytics and sensor monitoring. |
| Goal | Maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and eliminate downtime. | Predict failures to schedule timely maintenance and avoid unplanned stops. |
| Approach | Autonomous and planned maintenance with operator participation. | Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics using IoT and AI. |
| Tools | Equipment inspections, cleaning, and routine checks. | Vibration analysis, thermography, oil analysis, and machine learning models. |
| Benefits | Increased equipment availability, workforce engagement, and reduced breakdowns. | Optimized maintenance scheduling, reduced maintenance costs, and downtime. |
| Implementation | Involves culture change and operator training. | Requires investment in sensors, data infrastructure, and skilled analysts. |
Understanding Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach in manufacturing that aims to maximize equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive maintenance activities. TPM emphasizes autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and continuous improvement to reduce downtime and enhance production efficiency. Unlike Predictive Maintenance, which relies on condition-monitoring technologies to predict failures, TPM fosters a culture of shared responsibility and holistic equipment management.
What is Predictive Maintenance (PdM)?
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) uses real-time data and advanced analytics to monitor equipment conditions and predict potential failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned downtime. Leveraging sensors, IoT technology, and machine learning algorithms, PdM enables targeted maintenance only when necessary, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. Unlike Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), PdM focuses on condition-based interventions rather than scheduled preventive tasks.
Key Objectives of TPM and PdM
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) aims to maximize equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive and preventive maintenance activities to reduce downtime and improve overall productivity. Predictive Maintenance (PdM) focuses on using real-time data and advanced analytics, such as vibration analysis and sensor monitoring, to predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned outages. TPM emphasizes continuous improvement and operator autonomy, while PdM prioritizes condition-based interventions to optimize maintenance schedules and extend asset life.
Core Principles of Total Productive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) centers on maximizing equipment effectiveness through proactive operator involvement, cross-functional teamwork, and continuous improvement activities aimed at eliminating losses across availability, performance, and quality metrics. Core principles include autonomous maintenance, where operators perform routine maintenance to enhance equipment reliability, and planned maintenance, which schedules preventive tasks based on historical data to reduce unplanned downtime. TPM fosters a culture of shared responsibility and holistic asset management, contrasting with Predictive Maintenance that primarily relies on condition-monitoring technologies to predict failures before they occur.
Technologies Enabling Predictive Maintenance
Technologies enabling predictive maintenance include the integration of IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analytics, which collectively monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur. Unlike total productive maintenance, which emphasizes routine and preventive strategies, predictive maintenance leverages advanced diagnostics such as vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and AI-driven pattern recognition to optimize maintenance schedules. These technologies reduce unplanned downtime, improve asset efficiency, and lower operational costs by addressing issues precisely when needed.
Benefits of Implementing TPM
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) significantly enhances equipment availability and reliability by engaging all employees in proactive maintenance activities, reducing unexpected downtime and increasing overall production efficiency. TPM fosters a culture of continuous improvement and operator involvement, leading to higher maintenance quality and lower repair costs compared to Predictive Maintenance, which relies primarily on data analytics for equipment condition monitoring. Implementing TPM also improves safety standards and equipment lifespan, driving greater productivity and cost savings across manufacturing operations.
Advantages of Predictive Maintenance Solutions
Predictive Maintenance solutions leverage real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing unplanned downtime. This proactive approach optimizes maintenance schedules based on actual machine conditions, leading to improved asset utilization and cost savings. Compared to Total Productive Maintenance, Predictive Maintenance enhances operational efficiency by minimizing unnecessary preventive checks and extending the lifespan of critical manufacturing equipment.
TPM vs Predictive Maintenance: Key Differences
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness, while Predictive Maintenance relies on real-time data and advanced analytics to predict failures before they happen. TPM fosters a culture of continuous improvement and operator involvement, enhancing equipment reliability through scheduled inspections and autonomous maintenance. Predictive Maintenance leverages Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, machine learning algorithms, and condition monitoring tools to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce unscheduled downtime.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy for Your Facility
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes operator involvement and routine equipment checks to maximize overall equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Predictive Maintenance leverages real-time data, sensors, and machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures before they occur, enabling targeted interventions. Selecting the appropriate strategy depends on facility size, production complexity, budget constraints, and the availability of skilled personnel to support proactive or data-driven maintenance approaches.
Future Trends in Industrial Maintenance Approaches
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is evolving with the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, emphasizing employee involvement and continuous improvement to optimize equipment efficiency. Predictive Maintenance leverages advancements in IoT sensors, machine learning, and big data analytics to forecast equipment failures with higher accuracy and reduce unplanned downtime. Future trends indicate a convergence of TPM and Predictive Maintenance into hybrid models that combine human expertise with AI-driven insights for smarter, proactive maintenance strategies in manufacturing.
Related Important Terms
Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes operator involvement and proactive equipment upkeep to maximize overall equipment effectiveness, while Predictive Maintenance leverages real-time Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) through IoT sensors and data analytics to detect anomalies and predict failures before breakdowns occur. CBM enables precise maintenance scheduling by continuously tracking machine health metrics such as vibration, temperature, and oil quality, optimizing uptime and reducing unplanned maintenance costs.
Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen)
Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks, preventing equipment deterioration and extending machine life, contrasting with Predictive Maintenance that relies on data analytics and sensor monitoring to forecast failures. This hands-on approach fosters operator ownership and immediate issue detection, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and reducing downtime in manufacturing environments.
Digital Twin Predictive Analytics
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) integrates operator involvement and continuous improvement to maximize equipment effectiveness, while Predictive Maintenance leverages Digital Twin predictive analytics to simulate real-time asset behavior and forecast failures with high precision. Digital Twin technology enhances Predictive Maintenance by creating virtual replicas of manufacturing equipment, enabling data-driven decision-making and reducing unplanned downtime through advanced sensor data analysis.
Maintenance 4.0
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes operator involvement and autonomous maintenance to maximize equipment effectiveness, while Predictive Maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics through IoT and AI to forecast equipment failures. Maintenance 4.0 integrates TPM's proactive strategies with Predictive Maintenance's data-driven insights, enhancing overall equipment reliability and reducing unplanned downtime in smart manufacturing environments.
Prognostics and Health Management (PHM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive equipment care through operator involvement and routine inspections, while Predictive Maintenance leverages Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) technologies such as sensors and data analytics to forecast equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules. PHM integrates condition monitoring, failure prognostics, and diagnostic processes, enabling manufacturers to reduce downtime and improve asset reliability by predicting maintenance needs before breakdowns occur.
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) Optimization
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) by involving all employees in proactive equipment care and daily maintenance routines, reducing unexpected breakdowns. Predictive Maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate failures, optimizing MTBF by scheduling maintenance only when necessary and preventing downtime.
Smart Sensor Integration
Smart sensor integration in Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances equipment monitoring by collecting real-time data to minimize downtime and improve asset efficiency, while Predictive Maintenance leverages these sensors to analyze condition trends and predict failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules. The combination of TPM's holistic approach with predictive analytics enabled by smart sensors drives smarter decision-making and maximizes overall manufacturing productivity.
IIoT-driven Failure Prediction
IIoT-driven failure prediction enhances Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) by enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Predictive Maintenance leverages sensor data, machine learning algorithms, and cloud connectivity to anticipate malfunctions, while TPM integrates this insight into holistic operational strategies for continuous improvement and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes operator involvement and autonomous maintenance to minimize downtime, while Predictive Maintenance relies on real-time data and condition monitoring to anticipate equipment failures. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) integrates the proactive strategies of TPM and Predictive Maintenance by systematically analyzing equipment functions and failure modes to optimize maintenance tasks, enhancing overall asset reliability and operational efficiency.
Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA) Automation
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive operator involvement and continuous improvement to minimize equipment downtime, while Predictive Maintenance leverages sensor data and machine learning algorithms for real-time condition monitoring and failure prediction. Automation of Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA) in manufacturing integrates AI-driven diagnostics to rapidly identify underlying causes, enabling faster corrective actions and enhancing both TPM and Predictive Maintenance strategies.
Total Productive Maintenance vs Predictive Maintenance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com