Just-in-Time manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by producing goods only as needed, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Lights-Out manufacturing leverages automated systems to operate production facilities without human intervention, enabling continuous operation and lower labor expenses. Combining Just-in-Time principles with Lights-Out automation can dramatically improve manufacturing responsiveness and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
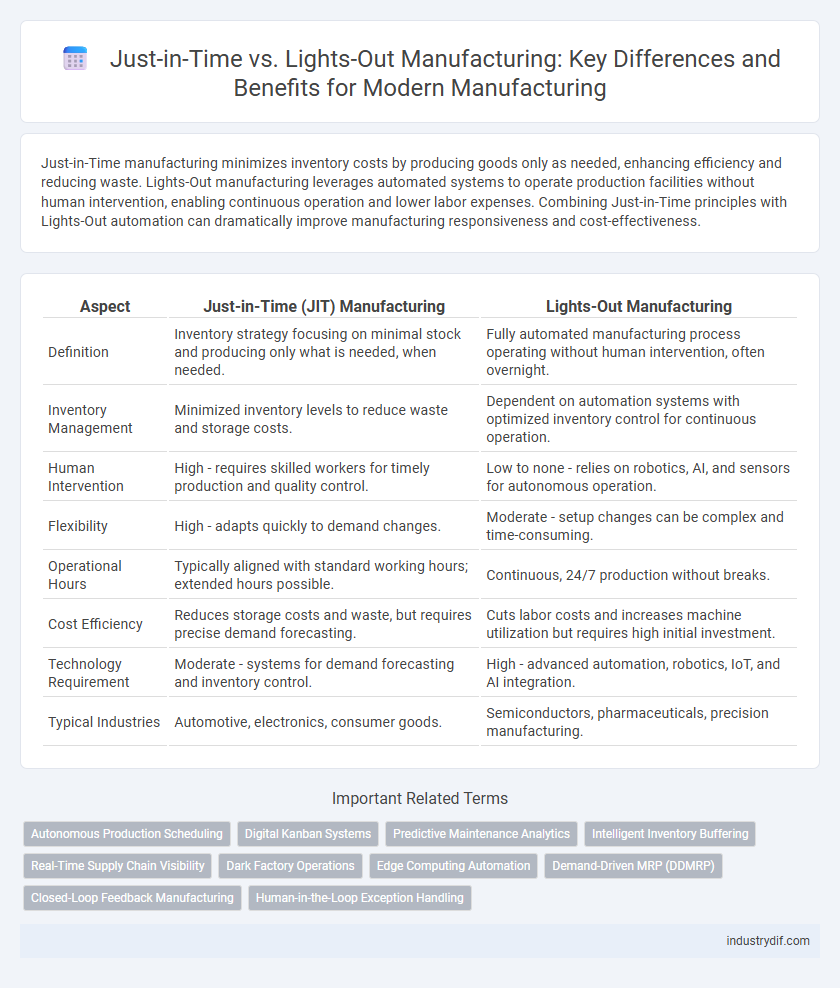
| Aspect | Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing | Lights-Out Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory strategy focusing on minimal stock and producing only what is needed, when needed. | Fully automated manufacturing process operating without human intervention, often overnight. |
| Inventory Management | Minimized inventory levels to reduce waste and storage costs. | Dependent on automation systems with optimized inventory control for continuous operation. |
| Human Intervention | High - requires skilled workers for timely production and quality control. | Low to none - relies on robotics, AI, and sensors for autonomous operation. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts quickly to demand changes. | Moderate - setup changes can be complex and time-consuming. |
| Operational Hours | Typically aligned with standard working hours; extended hours possible. | Continuous, 24/7 production without breaks. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces storage costs and waste, but requires precise demand forecasting. | Cuts labor costs and increases machine utilization but requires high initial investment. |
| Technology Requirement | Moderate - systems for demand forecasting and inventory control. | High - advanced automation, robotics, IoT, and AI integration. |
| Typical Industries | Automotive, electronics, consumer goods. | Semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, precision manufacturing. |
Introduction to Just-in-Time and Lights-Out Manufacturing
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by synchronizing production schedules with customer demand, ensuring materials arrive precisely when needed. Lights-Out manufacturing leverages full automation, allowing production to operate continuously without human intervention, optimizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Both methodologies aim to streamline manufacturing processes but differ significantly in technology reliance and operational strategies.
Core Principles of Just-in-Time Manufacturing
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing centers on reducing inventory waste by producing goods precisely when needed, emphasizing continuous flow and pull-based production systems. Its core principles include eliminating excess inventory, minimizing lead times, and enhancing quality through systematic problem-solving alongside strong supplier relationships. These practices optimize resource utilization and responsiveness, contrasting with Lights-Out manufacturing's focus on fully automated, unattended operations.
Fundamental Concepts of Lights-Out Manufacturing
Lights-Out Manufacturing operates with fully automated production processes running without human intervention, maximizing efficiency by reducing labor costs and minimizing downtime. This approach relies heavily on advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven systems to monitor and control manufacturing workflows in real-time. Compared to Just-in-Time manufacturing, which emphasizes inventory reduction and timely supply chain coordination, Lights-Out Manufacturing prioritizes continuous operation and precision automation to achieve higher throughput and quality consistency.
Key Differences Between Just-in-Time and Lights-Out Approaches
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing emphasizes minimizing inventory by producing goods only as needed, relying heavily on synchronized supply chains and human labor. Lights-Out manufacturing operates with fully automated, unattended production systems, enabling continuous operation without human intervention. The key difference lies in JIT's dependency on precise timing and human coordination versus Lights-Out's focus on automation and 24/7 efficiency.
Technological Requirements for Each Manufacturing Model
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing demands advanced inventory management systems, real-time data analytics, and seamless supplier integration to minimize waste and ensure timely production. Lights-Out manufacturing relies heavily on automation technologies, including robotics, machine learning, and IoT sensors, to enable unattended operations and maximize efficiency. Both models require robust software solutions, but Lights-Out manufacturing places greater emphasis on reliability and autonomous decision-making capabilities.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing minimizes inventory levels and reduces waste by synchronizing production with demand, enhancing supply chain responsiveness but increasing vulnerability to disruptions. Lights-Out manufacturing automates production facilities to operate without human intervention, improving efficiency and consistency while requiring robust supply chain coordination to maintain continuous operations. The integration of these approaches demands advanced real-time data analytics and resilient supplier networks to optimize inventory flow and minimize downtime.
Efficiency and Cost Considerations
Just-in-Time manufacturing enhances efficiency by minimizing inventory levels and reducing waste, leading to lower storage costs and faster response to market demand. Lights-Out manufacturing maximizes cost savings through fully automated, unattended operations that operate continuously, cutting labor expenses and increasing production uptime. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing the agility of supply chains with the capital investment in automation technology and maintenance.
Challenges and Risks in Implementation
Just-in-Time manufacturing faces challenges such as supply chain disruptions, inventory shortages, and demand variability, increasing the risk of production delays and increased costs. Lights-Out manufacturing demands significant upfront investments in automation technology and robust maintenance systems to prevent unexpected downtimes that can halt fully automated operations. Both methodologies require rigorous planning, skilled workforce management, and adaptive risk mitigation strategies to ensure seamless production flow and minimize operational hazards.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing is widely used in the automotive and electronics industries to minimize inventory costs and improve production efficiency, exemplified by Toyota's production system. Lights-Out Manufacturing, leveraging fully automated factories like FANUC's unmanned facility in Japan, is ideal for high-precision industries requiring 24/7 operations without human intervention. Case studies reveal JIT's success in reducing waste and lead times, while Lights-Out manufacturing excels in environments demanding continuous, error-free production with minimal labor costs.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Automation
Future trends in manufacturing automation emphasize seamless integration of Just-in-Time (JIT) and Lights-Out manufacturing technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Advances in AI-driven robotics, IoT connectivity, and predictive analytics enable real-time adaptive production schedules and unmanned facilities, supporting zero-defect manufacturing with minimal human intervention. This convergence accelerates digital transformation, driving smart factories toward fully autonomous, flexible manufacturing ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Autonomous Production Scheduling
Just-in-Time manufacturing relies on precise, real-time inventory control to minimize waste, while Lights-Out manufacturing leverages fully autonomous production scheduling systems to operate continuous, unmanned production lines. Advanced algorithms in Lights-Out setups optimize machine utilization and workflow efficiency, reducing downtime and enhancing throughput without human intervention.
Digital Kanban Systems
Digital Kanban systems enhance Just-in-Time manufacturing by providing real-time inventory visibility and seamless workflow automation, reducing waste and production delays. In Lights-Out manufacturing, these systems enable autonomous operations through precise demand forecasting and automated replenishment, ensuring uninterrupted production without human intervention.
Predictive Maintenance Analytics
Predictive maintenance analytics enhances Just-in-Time manufacturing by minimizing downtime through real-time equipment monitoring and data-driven fault detection, ensuring seamless production flow. In lights-out manufacturing, predictive maintenance leverages IoT sensors and AI algorithms to autonomously predict and address machine failures, maximizing operational efficiency without human intervention.
Intelligent Inventory Buffering
Intelligent inventory buffering enhances Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing by precisely matching material supply with production demand, reducing waste and minimizing holding costs. In contrast, Lights-Out manufacturing leverages automated systems and real-time data analytics to maintain optimal inventory levels without human intervention, ensuring continuous operation and improved efficiency.
Real-Time Supply Chain Visibility
Real-time supply chain visibility enhances Just-in-Time manufacturing by enabling precise inventory management and minimizing downtime through instantaneous data on material availability and production status. In Lights-Out manufacturing, this visibility supports autonomous operations by providing continuous monitoring and rapid response to supply chain disruptions without human intervention.
Dark Factory Operations
Dark factory operations utilize fully automated systems to enable continuous production with minimal human intervention, optimizing efficiency and reducing labor costs in comparison to traditional Just-in-Time manufacturing, which relies heavily on precise inventory timing and human coordination. Emphasizing predictive maintenance and real-time data analytics, dark factories enhance output consistency and decrease downtime, making them ideal for high-volume, low-variability manufacturing environments.
Edge Computing Automation
Edge computing automation enhances just-in-time manufacturing by enabling real-time data processing and immediate response on the factory floor, reducing latency and minimizing downtime. Lights-out manufacturing leverages edge computing to maintain fully autonomous operations, optimizing machine performance and predictive maintenance without human intervention.
Demand-Driven MRP (DDMRP)
Demand-Driven MRP (DDMRP) in Just-in-Time manufacturing optimizes inventory levels and production schedules by responding directly to customer demand signals, reducing lead times and minimizing waste. In contrast, Lights-Out Manufacturing leverages automation and DDMRP to enable unattended, continuous production lines that enhance efficiency and flexibility while maintaining precise demand-driven inventory control.
Closed-Loop Feedback Manufacturing
Closed-loop feedback manufacturing integrates real-time data monitoring and automated adjustments to enhance both Just-in-Time (JIT) and Lights-Out production processes, ensuring minimal inventory and maximizing operational efficiency. This system uses sensors and AI-driven analytics to continuously refine workflows, reduce downtime, and maintain precise quality control without human intervention.
Human-in-the-Loop Exception Handling
Just-in-Time manufacturing relies heavily on human-in-the-loop exception handling to address supply chain disruptions and machine malfunctions, ensuring minimal inventory waste. Lights-Out manufacturing minimizes human intervention, emphasizing automated exception detection and resolution to maintain continuous, unmanned production cycles.
Just-in-Time vs Lights-Out Manufacturing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com