Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency through standardized workflows and continuous improvement. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and responsiveness to market changes by adopting modular processes and rapid product development. Integrating lean principles with agile strategies enhances productivity while maintaining adaptability in dynamic production environments.
Table of Comparison
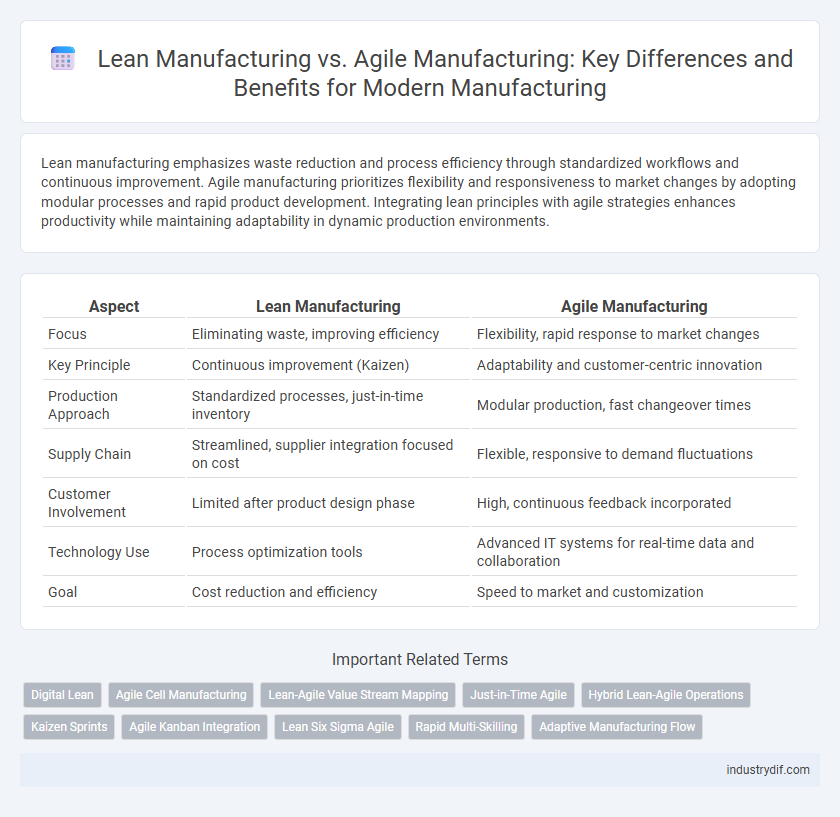
| Aspect | Lean Manufacturing | Agile Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Eliminating waste, improving efficiency | Flexibility, rapid response to market changes |
| Key Principle | Continuous improvement (Kaizen) | Adaptability and customer-centric innovation |
| Production Approach | Standardized processes, just-in-time inventory | Modular production, fast changeover times |
| Supply Chain | Streamlined, supplier integration focused on cost | Flexible, responsive to demand fluctuations |
| Customer Involvement | Limited after product design phase | High, continuous feedback incorporated |
| Technology Use | Process optimization tools | Advanced IT systems for real-time data and collaboration |
| Goal | Cost reduction and efficiency | Speed to market and customization |
Introduction to Lean and Agile Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and efficient resource utilization to enhance productivity and minimize operational costs. Agile Manufacturing prioritizes flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and customization to meet diverse customer demands in dynamic environments. Both methodologies aim to optimize manufacturing processes but differ in focus: Lean targets efficiency and stability, while Agile focuses on adaptability and speed.
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing centers on eliminating waste through continuous improvement and optimizing value streams to enhance operational efficiency. Core principles include defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping value streams to identify non-value-added activities, establishing flow by streamlining processes, implementing pull systems to reduce inventory, and striving for perfection via incremental improvements. These principles drive cost reduction, faster delivery, and higher quality in production environments.
Core Principles of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing centers on flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and customer-centric customization, contrasting with lean manufacturing's emphasis on waste reduction and process efficiency. Core principles of agile manufacturing include modular product design, cross-functional teamwork, and the integration of advanced information technologies to enable quick reconfiguration of production systems. This approach allows manufacturers to swiftly adapt to evolving consumer demands and volatile market conditions, enhancing competitiveness and innovation.
Key Differences Between Lean and Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency through standardized workflows and continuous improvement, focusing on predictable demand and minimizing inventory. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid responsiveness to changing market demands by utilizing modular processes and quick reconfiguration capabilities. The key differences lie in lean's pursuit of cost efficiency and stability versus agile's adaptability and customer-centric customization.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing enhances operational efficiency by minimizing waste and streamlining production processes, resulting in reduced costs and improved product quality. It promotes continuous improvement through techniques like Just-In-Time inventory and Kaizen, leading to faster turnaround times and increased customer satisfaction. Companies adopting Lean Manufacturing benefit from greater resource utilization and a more responsive supply chain, driving sustainable competitive advantage.
Advantages of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing enhances responsiveness to market fluctuations by enabling rapid product customization and scale adjustments. This approach reduces lead times and increases customer satisfaction through flexible resource allocation and cross-functional collaboration. Companies adopting agile practices often experience improved innovation cycles and stronger competitive positioning in dynamic industries.
When to Implement Lean vs Agile Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is most effective in stable production environments where minimizing waste and optimizing efficiency are critical, especially in high-volume, repetitive processes. Agile Manufacturing excels in dynamic markets requiring rapid adaptation to changing customer demands, product customization, and short lead times. Implement Lean when process stability and cost reduction are priorities; choose Agile when flexibility and responsiveness drive competitive advantage.
Challenges in Adopting Lean and Agile Methods
Challenges in adopting Lean manufacturing include resistance to cultural change, difficulties in sustaining continuous improvement, and the need for precise waste identification and elimination. Agile manufacturing faces obstacles such as integrating flexible systems with existing processes, managing supply chain variability, and ensuring rapid response without compromising quality. Both methods demand significant training, investment in technology, and alignment across teams to overcome implementation barriers.
Case Studies: Lean vs Agile Success Stories
Case studies reveal Lean Manufacturing significantly reduces waste and improves efficiency in automotive and electronics industries by streamlining production processes and standardizing workflows. Agile Manufacturing demonstrates superior adaptability in fashion and consumer electronics sectors, responding rapidly to market changes through flexible production schedules and modular workstations. Success stories highlight Lean's strength in cost minimization while Agile excels in innovation and speed to market, offering complementary strategies depending on manufacturing goals.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Methodologies
Future trends in manufacturing methodologies emphasize the integration of Lean Manufacturing's waste reduction principles with Agile Manufacturing's flexibility to respond quickly to market changes. Advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics enable seamless adaptation and continuous improvement in production processes. Embracing hybrid models allows manufacturers to optimize efficiency, enhance customization, and accelerate innovation in highly competitive global markets.
Related Important Terms
Digital Lean
Digital Lean Manufacturing integrates IoT, real-time data analytics, and automation to streamline production processes, reduce waste, and enhance operational efficiency compared to traditional Lean frameworks. Agile Manufacturing emphasizes flexibility and rapid response to market changes, leveraging digital technologies to adapt workflows and optimize resource allocation dynamically.
Agile Cell Manufacturing
Agile Cell Manufacturing enhances Lean Manufacturing principles by organizing production into flexible, self-contained units that rapidly adapt to market changes, reducing lead times and increasing customization capabilities. This approach emphasizes cross-functional teams, real-time problem-solving, and modular equipment, driving efficiency and responsiveness in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Lean-Agile Value Stream Mapping
Lean-Agile Value Stream Mapping integrates Lean Manufacturing's waste reduction principles with Agile Manufacturing's flexibility to enhance production efficiency and responsiveness. This hybrid approach enables real-time workflow visualization, accelerates decision-making, and optimizes resource allocation across the value stream for continuous improvement.
Just-in-Time Agile
Just-in-Time Agile manufacturing combines the principles of lean manufacturing's waste reduction with agile methods' flexibility, enabling rapid response to market changes while minimizing inventory costs. This hybrid approach improves production efficiency by synchronizing supply chain processes and accelerating product delivery cycles through adaptive planning and real-time feedback.
Hybrid Lean-Agile Operations
Hybrid Lean-Agile operations combine Lean Manufacturing's waste reduction and process efficiency with Agile Manufacturing's flexibility and rapid response to market changes, enhancing overall production adaptability. This integrated approach results in improved product quality, faster time-to-market, and optimized resource utilization in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Kaizen Sprints
Kaizen Sprints enhance Lean Manufacturing by driving continuous, incremental improvements through focused, time-boxed events that eliminate waste and boost efficiency. Agile Manufacturing incorporates Kaizen Sprints to rapidly adapt processes, promoting flexibility and quick responses to market changes while sustaining operational excellence.
Agile Kanban Integration
Agile manufacturing integrates Kanban systems to enhance workflow flexibility and reduce inventory waste by signaling real-time production needs. This approach enables rapid response to market changes, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction compared to traditional lean manufacturing methods focused primarily on waste elimination.
Lean Six Sigma Agile
Lean Six Sigma Agile integrates Lean Manufacturing's waste reduction with Six Sigma's quality control and Agile Manufacturing's flexibility, optimizing production efficiency and responsiveness to market changes. This hybrid approach enhances process improvement, reduces defects, and accelerates time-to-market in complex manufacturing environments.
Rapid Multi-Skilling
Rapid multi-skilling enhances Lean Manufacturing by reducing waste and increasing efficiency through cross-trained employees capable of performing various tasks within standardized workflows. In Agile Manufacturing, rapid multi-skilling supports flexibility and quick adaptation to market changes by enabling workers to switch roles seamlessly, accelerating production responsiveness and customization.
Adaptive Manufacturing Flow
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and streamlined processes to optimize production efficiency, while Agile Manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid response to market changes. Adaptive Manufacturing Flow integrates principles from both, enabling dynamic adjustments in operations to meet fluctuating customer demands without sacrificing efficiency.
Lean Manufacturing vs Agile Manufacturing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com