Lean Manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance for improved operational efficiency. Combining Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin capabilities accelerates process optimization and drives data-driven decision-making in production environments.
Table of Comparison
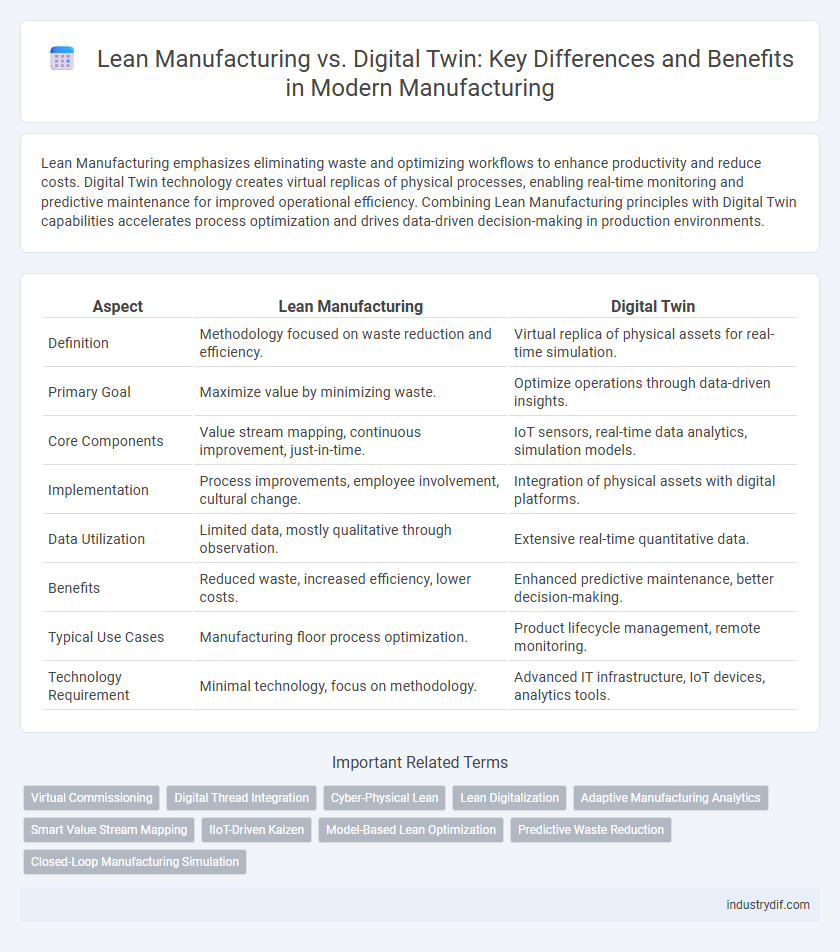
| Aspect | Lean Manufacturing | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Methodology focused on waste reduction and efficiency. | Virtual replica of physical assets for real-time simulation. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize value by minimizing waste. | Optimize operations through data-driven insights. |
| Core Components | Value stream mapping, continuous improvement, just-in-time. | IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, simulation models. |
| Implementation | Process improvements, employee involvement, cultural change. | Integration of physical assets with digital platforms. |
| Data Utilization | Limited data, mostly qualitative through observation. | Extensive real-time quantitative data. |
| Benefits | Reduced waste, increased efficiency, lower costs. | Enhanced predictive maintenance, better decision-making. |
| Typical Use Cases | Manufacturing floor process optimization. | Product lifecycle management, remote monitoring. |
| Technology Requirement | Minimal technology, focus on methodology. | Advanced IT infrastructure, IoT devices, analytics tools. |
Introduction to Lean Manufacturing and Digital Twin
Lean Manufacturing streamlines production processes by eliminating waste, reducing lead times, and enhancing operational efficiency to boost overall productivity. Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance. Integrating Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin insights drives smarter decision-making, reduces downtime, and optimizes resource utilization.
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing centers on eliminating waste, optimizing workflows, and enhancing value through continuous improvement and respect for people. Core principles include identifying value from the customer's perspective, mapping value streams to highlight inefficiencies, and creating smooth, uninterrupted production flow. While Digital Twin technology uses virtual models to simulate and analyze processes, Lean Manufacturing emphasizes foundational practices such as just-in-time production, pull systems, and built-in quality to drive operational excellence.
Digital Twin Technology: An Overview
Digital Twin technology in manufacturing creates virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems to enable real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization. This approach enhances predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves production efficiency by providing actionable insights through data integration from IoT sensors and advanced analytics. Digital Twins drive smart factory initiatives by facilitating digital transformation and enabling more responsive and flexible manufacturing operations.
Comparing Efficiency: Lean vs. Digital Twin
Lean manufacturing streamlines production by eliminating waste and improving process flow, achieving efficiency through standardization and continuous improvement. Digital Twin technology enhances efficiency by creating real-time virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing operations through data-driven insights. While Lean excels in simplifying workflows and reducing non-value-added activities, Digital Twin offers dynamic simulation and precise monitoring, driving efficiency via real-time adjustments and predictive analytics.
Implementation Challenges in Manufacturing
Implementing Lean Manufacturing often encounters challenges such as employee resistance to process changes and the difficulty of sustaining continuous improvement culture. Digital Twin technology faces obstacles including high initial costs, data integration complexities, and the need for skilled personnel to manage virtual simulations effectively. Combining both approaches requires overcoming interoperability issues between lean processes and digital models to fully optimize manufacturing efficiency.
Integrating Lean Concepts with Digital Twins
Integrating Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin technology enhances process optimization by providing real-time data visualization and predictive analytics, enabling continuous waste reduction and efficiency improvements. Digital Twins simulate production lines and workflows, allowing Lean teams to identify bottlenecks, test changes virtually, and implement just-in-time production strategies more effectively. This synergy drives operational excellence by combining Lean's focus on value stream mapping with Digital Twin's dynamic modeling capabilities.
Impact on Production Quality and Waste Reduction
Lean Manufacturing enhances production quality and waste reduction by streamlining processes, eliminating non-value-added activities, and fostering continuous improvement through principles like Kaizen and Just-In-Time production. Digital Twin technology boosts these outcomes by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and rapid identification of defects, which minimizes downtime and material waste. Combining Lean methodologies with Digital Twin analytics significantly improves product consistency and operational efficiency, driving substantial reductions in scrap and rework rates.
Real-Time Data Analytics in Digital Twin Systems
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency through continuous improvement methodologies, whereas Digital Twin systems leverage real-time data analytics to create dynamic, virtual replicas of physical manufacturing processes. Real-time data in Digital Twins enables precise monitoring, predictive maintenance, and rapid response to operational changes, significantly enhancing manufacturing agility and decision-making accuracy. Integrating Digital Twin technology with Lean principles optimizes production workflows by combining data-driven insights with streamlined process management.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Lean Manufacturing reduces operational costs by eliminating waste and improving process efficiency, resulting in faster ROI due to immediate savings in labor and materials. Digital Twin technology involves higher upfront investment but enables predictive maintenance and real-time optimization, leading to substantial long-term cost reductions and enhanced asset utilization. Integrating both approaches can maximize ROI by combining Lean's cost-efficient processes with Digital Twin's advanced data-driven insights.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Lean and Digital Twins
Lean manufacturing principles streamline production by minimizing waste and enhancing operational efficiency, while digital twins offer real-time, data-driven simulations of manufacturing processes. The future of manufacturing lies in the convergence of these methodologies, where digital twins enable continuous improvement cycles by providing precise performance feedback aligned with lean strategies. This integration drives predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and accelerated innovation within smart factories.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Commissioning
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process optimization to enhance operational efficiency, while Digital Twin technology enables virtual commissioning by creating real-time digital replicas of physical assets for simulation and performance testing. Virtual commissioning accelerates production line validation, reduces downtime, and improves accuracy by allowing manufacturers to identify and resolve issues in the digital environment before physical implementation.
Digital Thread Integration
Digital Twin technology enhances Lean Manufacturing by enabling real-time Digital Thread integration that connects product lifecycle data across design, production, and supply chain stages, facilitating continuous process optimization and waste reduction. This seamless data flow improves decision-making accuracy, accelerates identifying inefficiencies, and supports predictive maintenance to maximize manufacturing agility and quality.
Cyber-Physical Lean
Cyber-Physical Lean integrates Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin technology to create real-time, data-driven feedback loops that optimize production efficiency and minimize waste. By synchronizing physical processes with virtual models, manufacturers achieve enhanced decision-making, predictive maintenance, and continuous process improvement.
Lean Digitalization
Lean digitalization integrates Lean Manufacturing principles with digital twin technology to optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance real-time decision-making. Digital twins provide a virtual replica of manufacturing processes, enabling continuous improvement by simulating and analyzing workflows aligned with Lean strategies.
Adaptive Manufacturing Analytics
Lean Manufacturing streamlines production by minimizing waste and optimizing workflow efficiency, while Digital Twin technology enables real-time simulation and monitoring of manufacturing processes. Adaptive Manufacturing Analytics leverages data from Digital Twins to dynamically adjust operations, enhancing decision-making and driving continuous process improvements beyond traditional Lean methodologies.
Smart Value Stream Mapping
Smart Value Stream Mapping integrates Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin technology by creating real-time, data-driven simulations of production processes, enabling precise identification of waste and bottlenecks. This synergy enhances decision-making efficiency, reduces lead times, and optimizes resource allocation through continuous, dynamic process visualization and analysis.
IIoT-Driven Kaizen
Lean Manufacturing streamlines production by minimizing waste and optimizing workflow, while Digital Twin technology leverages IIoT data to create real-time virtual models that enable continuous Kaizen improvements. Integrating IIoT-driven Digital Twins with Lean principles enhances predictive maintenance, process transparency, and adaptive manufacturing, driving efficiency and agile decision-making on the shop floor.
Model-Based Lean Optimization
Model-Based Lean Optimization integrates Lean Manufacturing principles with Digital Twin technology to enhance process efficiency by simulating real-time production scenarios and identifying waste reduction opportunities. This approach leverages virtual models to optimize workflows, improve resource allocation, and accelerate decision-making in manufacturing environments.
Predictive Waste Reduction
Lean Manufacturing minimizes waste through continuous process improvements and value stream mapping, targeting inefficiencies in production workflows. Digital Twin technology enhances predictive waste reduction by utilizing real-time data simulations to foresee potential defects and equipment failures before they occur.
Closed-Loop Manufacturing Simulation
Lean Manufacturing minimizes waste and enhances efficiency by streamlining production processes, while Digital Twin technology enables closed-loop manufacturing simulation by creating real-time virtual replicas of physical systems for continuous monitoring and optimization. Integrating Lean principles with Digital Twin simulations accelerates decision-making, improves quality control, and reduces downtime through predictive analytics and feedback-driven process adjustments.
Lean Manufacturing vs Digital Twin Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com