Outsourcing manufacturing can reduce costs and provide access to specialized expertise, but often comes with risks such as quality control issues and longer supply chains. Reshoring brings production closer to home, improving responsiveness, reducing lead times, and enhancing quality oversight. Companies must weigh cost savings against operational agility and supply chain resilience when choosing between outsourcing and reshoring strategies.
Table of Comparison
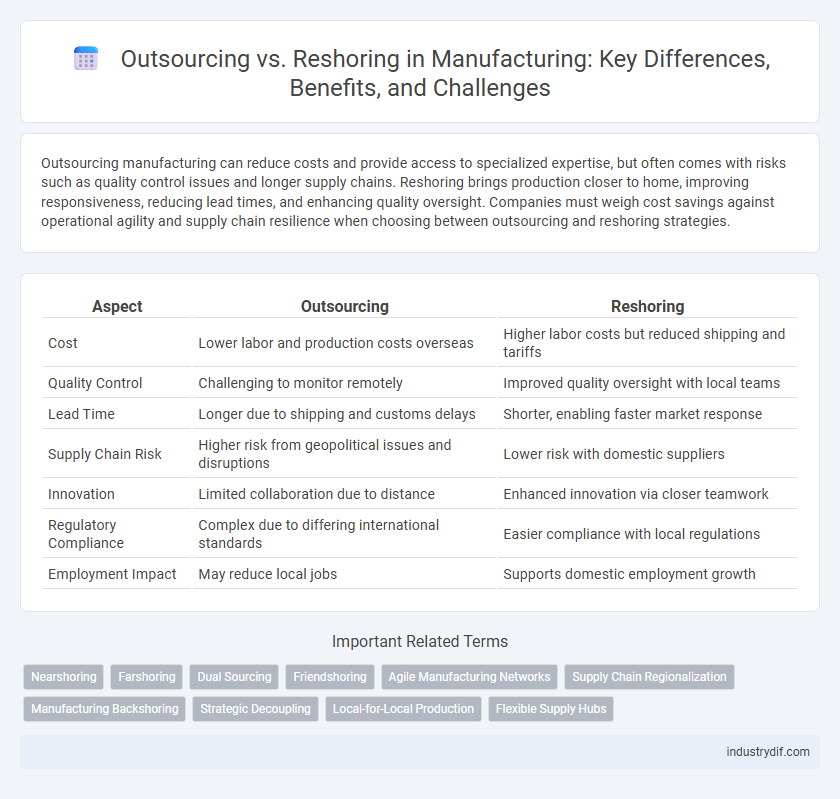
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Reshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower labor and production costs overseas | Higher labor costs but reduced shipping and tariffs |
| Quality Control | Challenging to monitor remotely | Improved quality oversight with local teams |
| Lead Time | Longer due to shipping and customs delays | Shorter, enabling faster market response |
| Supply Chain Risk | Higher risk from geopolitical issues and disruptions | Lower risk with domestic suppliers |
| Innovation | Limited collaboration due to distance | Enhanced innovation via closer teamwork |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex due to differing international standards | Easier compliance with local regulations |
| Employment Impact | May reduce local jobs | Supports domestic employment growth |
Introduction to Outsourcing and Reshoring in Manufacturing
Outsourcing in manufacturing involves contracting external suppliers to handle production processes, reducing costs and increasing flexibility. Reshoring refers to the strategic decision to bring manufacturing activities back to the company's home country, driven by factors like supply chain resilience and rising labor costs abroad. Companies evaluate outsourcing and reshoring by analyzing cost efficiency, quality control, and geopolitical risks.
Key Drivers of Outsourcing in the Manufacturing Sector
Key drivers of outsourcing in the manufacturing sector include cost reduction through lower labor and operational expenses, access to specialized expertise and advanced technology, and scalability to meet fluctuating demand without significant capital investment. Companies often seek outsourcing to improve supply chain efficiency and focus on core competencies while leveraging global supplier networks. Risk mitigation related to market volatility and regulatory compliance also plays a crucial role in the decision to outsource production processes.
Understanding Reshoring: Benefits and Challenges
Reshoring manufacturing brings benefits such as improved supply chain control, enhanced product quality, and quicker response times to market changes. Companies face challenges including higher labor costs, the need for advanced technology investments, and potential skill shortages in the domestic workforce. Strategic reshoring decisions depend on balancing these factors with long-term operational and financial goals.
Cost Implications: Outsourcing vs Reshoring
Outsourcing manufacturing often reduces labor and operational costs by leveraging lower wages and established supply chains in foreign countries, but it may incur hidden expenses such as shipping fees, tariffs, and quality control issues. Reshoring increases direct labor costs but can reduce transportation costs, improve supply chain reliability, and minimize inventory risks, resulting in potential long-term savings and enhanced quality control. Evaluating cost implications requires analyzing total cost of ownership, including wage differentials, logistics, tariffs, and risk management.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Outsourcing manufacturing to low-cost regions can enhance supply chain efficiency by reducing production expenses and leveraging specialized expertise, but it may introduce risks such as longer lead times and increased complexity in logistics. Reshoring production closer to the end market often improves supply chain agility, reduces transportation costs, and enhances responsiveness to demand fluctuations. Balancing these strategies depends on factors like supply chain visibility, risk tolerance, and the importance of speed-to-market in the manufacturing sector.
Quality Control and Compliance Considerations
Outsourcing manufacturing can introduce variability in quality control due to differences in regulatory standards and oversight across countries, increasing the risk of non-compliance with industry-specific certifications such as ISO 9001 or FDA regulations. Reshoring manufacturing operations enhances direct oversight of production processes, allowing companies to maintain stricter adherence to quality standards and regulatory compliance, reducing defects and product recalls. Strategic decisions between outsourcing and reshoring must weigh the benefits of cost savings against the critical importance of preserving quality assurance and alignment with compliance frameworks.
Risk Management: Geopolitical, Economic, and Operational Factors
Outsourcing manufacturing presents risks such as geopolitical instability, fluctuating economic conditions, and supply chain disruptions that can impact operational continuity. Reshoring mitigates these risks by bringing production closer to home, enhancing control over quality, compliance, and responsiveness to market changes. Companies assessing risk management weigh factors like trade policies, labor costs, and proximity to key markets to determine the optimal manufacturing strategy.
Labor Market Dynamics and Workforce Availability
Outsourcing often leverages lower labor costs and abundant skilled workers in emerging markets, optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational expenses. Reshoring addresses challenges such as rising overseas wages and supply chain disruptions, tapping into a domestic workforce with evolving technical skills and increased automation integration. Labor market dynamics, including demographic shifts and regional talent pools, significantly influence decisions between outsourcing and reshoring in manufacturing sectors.
Technology, Automation, and Their Role in Decision-Making
Technology advancements and automation significantly influence outsourcing and reshoring decisions in manufacturing by enhancing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Reshoring becomes more viable as automation mitigates labor shortages and improves quality control, allowing firms to maintain operations domestically while minimizing expenses. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies facilitates real-time data analytics, enabling manufacturers to optimize supply chains and respond swiftly to market demands.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Outsourcing and Reshoring
Future trends in manufacturing reveal a growing balance between outsourcing and reshoring driven by advancements in automation, supply chain resilience, and geopolitical factors. Companies increasingly adopt hybrid models that combine offshore cost advantages with local production agility to mitigate risks and reduce lead times. Emerging technologies like AI-driven analytics and Industry 4.0 are transforming decision-making processes, enabling smarter choices between outsourcing and reshoring to optimize efficiency and sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Nearshoring
Nearshoring in manufacturing offers strategic advantages by relocating production closer to home markets, reducing lead times and transportation costs while enhancing supply chain resilience. This approach balances cost-efficiency and quality control, addressing challenges associated with traditional outsourcing and reshoring by leveraging regional trade agreements and skilled local labor pools.
Farshoring
Farshoring in manufacturing involves relocating production to distant countries with competitive labor costs and advanced infrastructure, offering a balance between cost savings and quality control compared to traditional offshoring. This strategy mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions, while enhancing access to emerging markets and technological expertise.
Dual Sourcing
Dual sourcing in manufacturing strategically balances outsourcing and reshoring to mitigate supply chain risks while enhancing cost efficiency and flexibility. By sourcing components both domestically and internationally, companies improve resilience against disruptions and capitalize on competitive advantages in labor, materials, and logistics.
Friendshoring
Friendshoring in manufacturing leverages trusted geopolitical partnerships to enhance supply chain resilience while reducing the risks associated with traditional outsourcing to volatile regions. This strategic shift supports reshoring efforts by aligning production closer to home within allied countries, optimizing cost efficiency and security in global manufacturing networks.
Agile Manufacturing Networks
Agile manufacturing networks leverage both outsourcing and reshoring strategies to enhance flexibility, reduce lead times, and optimize supply chain responsiveness. Integrating localized reshoring initiatives with strategic global outsourcing enables manufacturers to quickly adapt to market fluctuations and demand variability, driving operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Supply Chain Regionalization
Outsourcing often extends supply chains globally, increasing lead times and risk exposure, while reshoring promotes supply chain regionalization by shortening distances and enhancing responsiveness. Regionalized supply chains improve inventory management, reduce transportation costs, and increase resilience against disruptions.
Manufacturing Backshoring
Manufacturing backshoring involves relocating production processes from foreign countries back to the company's home country to improve supply chain resilience, reduce lead times, and enhance quality control. This strategic shift often results in higher labor costs but can lead to long-term savings through decreased transportation expenses and improved responsiveness to market demands.
Strategic Decoupling
Strategic decoupling in manufacturing involves separating global supply chains to enhance resilience by reshoring critical processes while outsourcing non-core activities to cost-effective regions. This approach reduces dependency on single markets, mitigates risks from geopolitical disruptions, and optimizes operational flexibility.
Local-for-Local Production
Local-for-local production in manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience by minimizing lead times and reducing transportation costs compared to outsourcing. Reshoring supports regional economies with job creation and aligns production closely with local market demands, improving customization and responsiveness.
Flexible Supply Hubs
Flexible supply hubs enhance manufacturing agility by enabling companies to strategically outsource specific processes while maintaining core production capabilities in reshored facilities. This hybrid approach optimizes cost efficiency, reduces lead times, and mitigates risks associated with global supply chain disruptions.
Outsourcing vs Reshoring Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com