Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to monitor equipment conditions and forecast potential failures, reducing downtime by scheduling timely interventions. Prescriptive maintenance goes beyond prediction by recommending specific actions to optimize repair processes and enhance operational efficiency. Implementing prescriptive maintenance enables manufacturers to not only anticipate issues but also to make informed decisions that minimize costs and improve asset longevity.
Table of Comparison
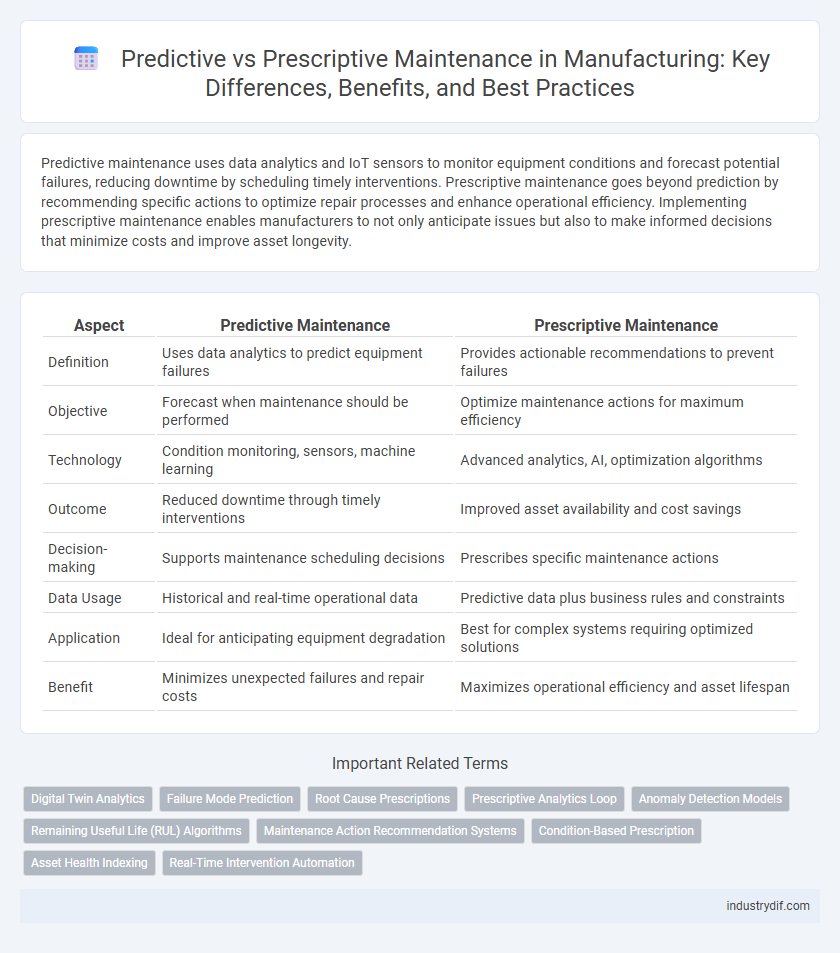
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Prescriptive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analytics to predict equipment failures | Provides actionable recommendations to prevent failures |
| Objective | Forecast when maintenance should be performed | Optimize maintenance actions for maximum efficiency |
| Technology | Condition monitoring, sensors, machine learning | Advanced analytics, AI, optimization algorithms |
| Outcome | Reduced downtime through timely interventions | Improved asset availability and cost savings |
| Decision-making | Supports maintenance scheduling decisions | Prescribes specific maintenance actions |
| Data Usage | Historical and real-time operational data | Predictive data plus business rules and constraints |
| Application | Ideal for anticipating equipment degradation | Best for complex systems requiring optimized solutions |
| Benefit | Minimizes unexpected failures and repair costs | Maximizes operational efficiency and asset lifespan |
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data from sensors and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules. By analyzing vibration, temperature, and acoustic signals, manufacturers can identify patterns indicative of wear or malfunction, allowing targeted interventions only when necessary. This approach enhances asset lifespan and operational efficiency while reducing maintenance costs compared to traditional reactive methods.
Defining Prescriptive Maintenance
Prescriptive Maintenance uses advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to recommend specific actions for equipment upkeep, going beyond the fault detection capabilities of Predictive Maintenance. It integrates real-time sensor data, historical maintenance records, and operational conditions to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce downtime. By providing actionable insights, Prescriptive Maintenance enhances decision-making, minimizes unexpected failures, and maximizes asset longevity in manufacturing environments.
Key Differences Between Predictive and Prescriptive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely intervention before breakdowns occur. Prescriptive maintenance builds on predictive insights by recommending specific actions to prevent failures and optimize operational efficiency based on data-driven decision models. Key differences include predictive maintenance focusing on failure prediction, while prescriptive maintenance emphasizes actionable recommendations for maintenance strategies.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance in manufacturing reduces unplanned downtime by accurately forecasting equipment failures through real-time data analysis and condition monitoring. It optimizes maintenance schedules, extending machinery lifespan and lowering operational costs by preventing catastrophic breakdowns. Enhanced asset reliability and increased production efficiency result from timely interventions based on predictive analytics.
Advantages of Prescriptive Maintenance Strategies
Prescriptive maintenance optimizes manufacturing operations by not only predicting equipment failures but also recommending specific actions to prevent downtime, resulting in enhanced asset utilization and reduced maintenance costs. This strategy leverages real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to provide actionable insights, enabling proactive decision-making and efficient resource allocation. Manufacturers adopting prescriptive maintenance experience improved operational efficiency, increased equipment lifespan, and minimized unexpected breakdowns compared to predictive maintenance alone.
Data Analytics in Predictive vs Prescriptive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance utilizes data analytics techniques such as machine learning algorithms and historical equipment data to forecast potential failures and schedule timely interventions. Prescriptive maintenance advances this by integrating real-time sensor data with predictive insights to recommend specific corrective actions, optimizing maintenance schedules and resource allocation. The combination of these analytics enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and lowers maintenance costs in manufacturing environments.
Implementation Challenges in Manufacturing Environments
Implementing predictive maintenance in manufacturing often faces challenges such as data integration complexity from diverse machinery and ensuring sensor accuracy under harsh production conditions. Prescriptive maintenance adds layers of difficulty by requiring advanced analytics and AI models capable of delivering actionable recommendations, which demands significant investment in skilled personnel and infrastructure. Both approaches struggle with real-time data processing limitations and the need for seamless interoperability with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES).
Impact on Equipment Uptime and Reliability
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, significantly enhancing uptime by addressing issues before they cause disruptions. Prescriptive maintenance builds on these insights by recommending specific corrective actions, further improving reliability and minimizing unplanned downtime. Together, these approaches optimize manufacturing operations by maximizing equipment performance and extending asset lifespan.
Cost Implications for Manufacturing Operations
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and analytics to anticipate equipment failures, reducing unplanned downtime and lowering repair costs in manufacturing operations. Prescriptive maintenance builds on predictive models by recommending specific actions, optimizing resource allocation, and minimizing both maintenance expenses and production disruptions. Implementing prescriptive maintenance can yield higher cost savings despite initial investments due to enhanced decision-making and improved asset performance.
Future Trends in Maintenance Technologies
Predictive maintenance leverages AI-driven data analytics and sensor technologies to forecast equipment failures, while prescriptive maintenance integrates advanced machine learning algorithms to recommend precise corrective actions. Future trends emphasize the convergence of IoT, digital twins, and edge computing to enhance real-time decision-making and automate complex maintenance workflows. These innovations aim to reduce downtime, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational efficiency in manufacturing environments.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Analytics
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and machine learning algorithms within digital twin analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Prescriptive maintenance extends this by leveraging digital twin simulations to recommend specific actions, optimizing maintenance schedules and operational efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Failure Mode Prediction
Predictive maintenance leverages machine learning algorithms and sensor data to identify patterns and forecast equipment failure modes before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime. Prescriptive maintenance extends this approach by recommending specific corrective actions based on failure mode predictions, optimizing repair strategies and minimizing maintenance costs.
Root Cause Prescriptions
Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and machine learning to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions before breakdowns occur. Prescriptive maintenance advances this approach by not only identifying potential failures but also recommending specific root cause prescriptions and corrective actions to optimize asset performance and reduce downtime.
Prescriptive Analytics Loop
Prescriptive maintenance leverages the prescriptive analytics loop by analyzing real-time sensor data and historical maintenance records to recommend specific actions that prevent equipment failures and optimize operational efficiency. This loop integrates data ingestion, advanced analytics, and decision-making models to continuously refine maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and lower overall maintenance costs.
Anomaly Detection Models
Predictive maintenance leverages anomaly detection models to identify deviations from normal equipment behavior, enabling early fault detection and reducing unplanned downtime. Prescriptive maintenance advances this approach by not only detecting anomalies but also recommending optimal corrective actions through AI-driven insights, maximizing operational efficiency and asset lifespan.
Remaining Useful Life (RUL) Algorithms
Predictive maintenance leverages Remaining Useful Life (RUL) algorithms to estimate the time before equipment failure, enabling timely interventions that minimize downtime. Prescriptive maintenance builds upon RUL predictions by integrating advanced analytics and optimization techniques to recommend specific actions that extend asset life and maximize operational efficiency.
Maintenance Action Recommendation Systems
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that minimize downtime and extend machinery life. Prescriptive maintenance builds on these predictions by integrating advanced analytics and optimization models within maintenance action recommendation systems to suggest specific, data-driven repair or replacement actions, maximizing operational efficiency and cost savings.
Condition-Based Prescription
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data to forecast equipment failures, while prescriptive maintenance takes this a step further by recommending specific corrective actions based on condition-based prescriptions. Condition-based prescription integrates sensor data and advanced analytics to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and enhance asset lifecycle management in manufacturing environments.
Asset Health Indexing
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that minimize downtime. Prescriptive maintenance integrates asset health indexing with AI-driven recommendations to optimize maintenance schedules, improving asset reliability and operational efficiency in manufacturing environments.
Real-Time Intervention Automation
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling timely interventions that minimize downtime. Prescriptive maintenance advances this approach by automating decision-making processes and real-time intervention, prescribing specific actions to optimize equipment performance and extend asset life.
Predictive Maintenance vs Prescriptive Maintenance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com