Six Sigma emphasizes reducing defects and variability through data-driven methodologies, enhancing product quality and process efficiency. Industry 5.0 integrates advanced technologies like AI and IoT with human-centered approaches to foster collaboration between humans and machines for customized manufacturing. Combining Six Sigma's precision with Industry 5.0's innovation can lead to optimized production, increased flexibility, and sustainable growth.
Table of Comparison
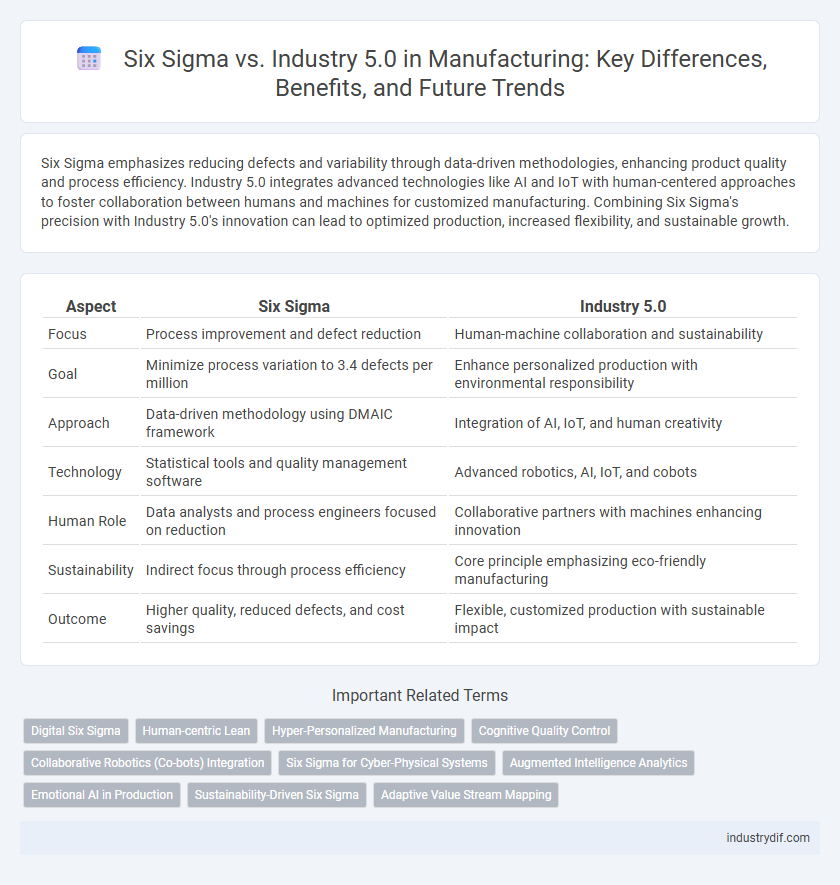
| Aspect | Six Sigma | Industry 5.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Process improvement and defect reduction | Human-machine collaboration and sustainability |
| Goal | Minimize process variation to 3.4 defects per million | Enhance personalized production with environmental responsibility |
| Approach | Data-driven methodology using DMAIC framework | Integration of AI, IoT, and human creativity |
| Technology | Statistical tools and quality management software | Advanced robotics, AI, IoT, and cobots |
| Human Role | Data analysts and process engineers focused on reduction | Collaborative partners with machines enhancing innovation |
| Sustainability | Indirect focus through process efficiency | Core principle emphasizing eco-friendly manufacturing |
| Outcome | Higher quality, reduced defects, and cost savings | Flexible, customized production with sustainable impact |
Understanding Six Sigma: Principles and Applications
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at reducing defects and improving quality by identifying and eliminating process variability through DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) cycles. Its core principles emphasize customer focus, process improvements, and fact-based decision-making to achieve near-perfect production performance with defect rates as low as 3.4 per million opportunities. Widely applied across manufacturing sectors, Six Sigma drives operational excellence by integrating statistical tools and cross-functional teamwork to optimize processes and enhance product reliability.
Introduction to Industry 5.0 in Manufacturing
Industry 5.0 in manufacturing emphasizes human-centric automation, integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and the Internet of Things to enhance collaboration between humans and machines. Unlike Six Sigma, which primarily focuses on process improvement and defect reduction through statistical analysis, Industry 5.0 aims to personalize production, boost sustainability, and foster innovation by leveraging cognitive computing and human creativity. This paradigm shift enables manufacturers to create more customized, efficient, and resilient production systems tailored to evolving market demands.
Core Differences: Six Sigma vs Industry 5.0
Six Sigma emphasizes defect reduction and process improvement through statistical analysis and data-driven methodologies, targeting near-zero defects in manufacturing. Industry 5.0 integrates human creativity with advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and IoT to create personalized, sustainable, and resilient production systems. Unlike Six Sigma's process-centric approach, Industry 5.0 prioritizes human-centric innovation and collaboration between humans and machines to enhance flexibility and customization.
Evolution from Industry 4.0 to 5.0
Six Sigma, with its focus on reducing defects and improving process efficiency, laid the foundation for quality management within Industry 4.0's automation and data-driven manufacturing. Industry 5.0 evolves beyond by integrating human creativity and collaboration with advanced technologies like AI and robotics, emphasizing personalized production and sustainability. This transition marks a shift from fully automated systems to a more human-centric approach, optimizing both operational excellence and worker interaction.
Human-Centric Approach in Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 emphasizes a human-centric approach by integrating advanced technologies with human creativity and expertise to enhance manufacturing processes. Unlike Six Sigma, which primarily focuses on defect reduction and process optimization through data-driven methodologies, Industry 5.0 prioritizes collaboration between humans and machines to achieve customized production and sustainability. This alignment fosters innovation, improved worker well-being, and flexible manufacturing systems tailored to individual customer needs.
Data-Driven Decision Making in Six Sigma
Six Sigma employs rigorous data-driven decision making through statistical analysis and process monitoring to reduce defects and improve quality in manufacturing. Industry 5.0 enhances traditional Six Sigma methods by integrating advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and human-centric automation for more adaptive and intelligent production systems. Data analytics in Six Sigma remains foundational, enabling precise identification of process variations and facilitating continuous improvement aligned with Industry 5.0's emphasis on collaboration between humans and machines.
Integration of Six Sigma within Industry 5.0 Frameworks
Integration of Six Sigma within Industry 5.0 frameworks enhances precision and sustainability by combining data-driven quality control with human-centric automation. Six Sigma methodologies optimize process efficiency and defect reduction, while Industry 5.0 emphasizes collaborative robots and personalized production, creating resilient manufacturing ecosystems. This synergy drives advanced quality management and innovation, aligning operational excellence with adaptive, smart manufacturing environments.
Benefits and Challenges: Six Sigma vs Industry 5.0
Six Sigma emphasizes defect reduction and process optimization through data-driven methodologies, enhancing quality and operational efficiency while facing challenges in flexibility and employee engagement. Industry 5.0 integrates human creativity with advanced technologies like AI and robotics, fostering personalized manufacturing and sustainability but requires significant investment and workforce upskilling. Balancing Six Sigma's structured approach with Industry 5.0's collaborative innovation can drive superior manufacturing outcomes by combining precision with adaptability.
Real-World Case Studies: Six Sigma and Industry 5.0
Real-world case studies highlight Six Sigma's proven efficacy in reducing defects and improving process efficiency in manufacturing plants such as General Electric, where defect rates dropped by up to 70%. In contrast, Industry 5.0 introduces human-centric automation exemplified by collaborations between robots and workers at Toyota, enhancing customization and worker satisfaction. Combining Six Sigma's data-driven quality control with Industry 5.0's adaptive technologies offers manufacturing firms a pathway to optimized productivity and innovation.
Future Outlook: Synergy Between Six Sigma and Industry 5.0
Six Sigma's data-driven quality control methods complement Industry 5.0's focus on human-centric, collaborative automation by integrating advanced AI and IoT technologies. The future of manufacturing envisions a synergy where Six Sigma optimizes process efficiency while Industry 5.0 enhances customization and sustainability through human-machine collaboration. This strategic alignment fosters innovation, operational excellence, and resilient supply chains in smart factories.
Related Important Terms
Digital Six Sigma
Digital Six Sigma integrates advanced data analytics and AI tools to enhance traditional Six Sigma methodologies, driving greater process efficiency and defect reduction in manufacturing. Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-centric automation and collaboration between workers and intelligent machines, complementing Digital Six Sigma's precision in optimizing quality and operational performance.
Human-centric Lean
Six Sigma emphasizes data-driven process improvement with a focus on defect reduction, while Industry 5.0 integrates human-centric Lean principles by combining advanced automation with personalized workforce involvement to enhance productivity and innovation. This approach prioritizes human creativity and collaboration within smart manufacturing systems, fostering sustainable and adaptive production environments.
Hyper-Personalized Manufacturing
Six Sigma enhances manufacturing quality by reducing defects through data-driven process improvements, while Industry 5.0 emphasizes hyper-personalized manufacturing by integrating human creativity with advanced robotics and AI to create customized products at scale. The fusion of Six Sigma's precision and Industry 5.0's collaborative technologies drives efficiency and flexibility in producing tailored solutions that meet individual customer demands.
Cognitive Quality Control
Six Sigma emphasizes structured data-driven methodologies to minimize defects and improve process efficiency, while Industry 5.0 integrates human creativity with advanced cognitive technologies like AI and IoT to enhance quality control through real-time, intelligent decision-making. Cognitive Quality Control in Industry 5.0 leverages machine learning algorithms and human expertise collaboration to predict, detect, and resolve production anomalies beyond traditional statistical methods used in Six Sigma.
Collaborative Robotics (Co-bots) Integration
Six Sigma emphasizes data-driven process improvement and defect reduction, while Industry 5.0 prioritizes human-centric collaboration with advanced technologies like collaborative robotics (Co-bots) to enhance productivity and flexibility. Integrating Co-bots in Industry 5.0 enables seamless human-robot interaction on manufacturing floors, promoting adaptive automation and personalized production without compromising quality standards established by Six Sigma methodologies.
Six Sigma for Cyber-Physical Systems
Six Sigma methodologies enhance Cyber-Physical Systems in manufacturing by minimizing process variability and defects through data-driven analysis and control, improving system reliability and quality. Integrating Six Sigma with Industry 5.0 technologies supports precision in automation and fosters human-machine collaboration for optimized production efficiency.
Augmented Intelligence Analytics
Six Sigma utilizes statistical analysis to minimize defects and improve process quality, whereas Industry 5.0 emphasizes augmented intelligence analytics to enhance human-machine collaboration, driving personalized manufacturing and real-time decision-making. Augmented intelligence in Industry 5.0 leverages AI and advanced data analytics to complement human expertise, increasing productivity and innovation beyond traditional Six Sigma methodologies.
Emotional AI in Production
Six Sigma emphasizes defect reduction and process efficiency through statistical analysis, while Industry 5.0 integrates Emotional AI to enhance human-machine collaboration, improving worker well-being and decision-making in production. Emotional AI in Industry 5.0 monitors operators' emotional states to optimize task allocation, increase productivity, and reduce workplace stress in manufacturing environments.
Sustainability-Driven Six Sigma
Sustainability-Driven Six Sigma integrates environmental and social metrics into traditional Six Sigma quality management to minimize waste and enhance resource efficiency, aligning with Industry 5.0's emphasis on human-centric, sustainable manufacturing. This approach optimizes processes while reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles, supporting manufacturers in achieving resilient and eco-friendly production systems.
Adaptive Value Stream Mapping
Six Sigma emphasizes defect reduction through statistical analysis and process control, while Industry 5.0 integrates human-centric customization and advanced technologies like IoT and AI to enhance flexibility in production. Adaptive Value Stream Mapping (AVSM) in Industry 5.0 dynamically incorporates real-time data and human insights, enabling continuous optimization of manufacturing workflows beyond traditional Six Sigma methods.
Six Sigma vs Industry 5.0 Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com