Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness, while Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform basic maintenance tasks independently, increasing equipment reliability and reducing downtime. TPM integrates planned maintenance activities with other production goals to enhance overall equipment efficiency, whereas Autonomous Maintenance focuses on operator-led routines to detect and address equipment issues swiftly. Both approaches aim to improve operational productivity but differ in the scope of responsibility and maintenance execution.
Table of Comparison
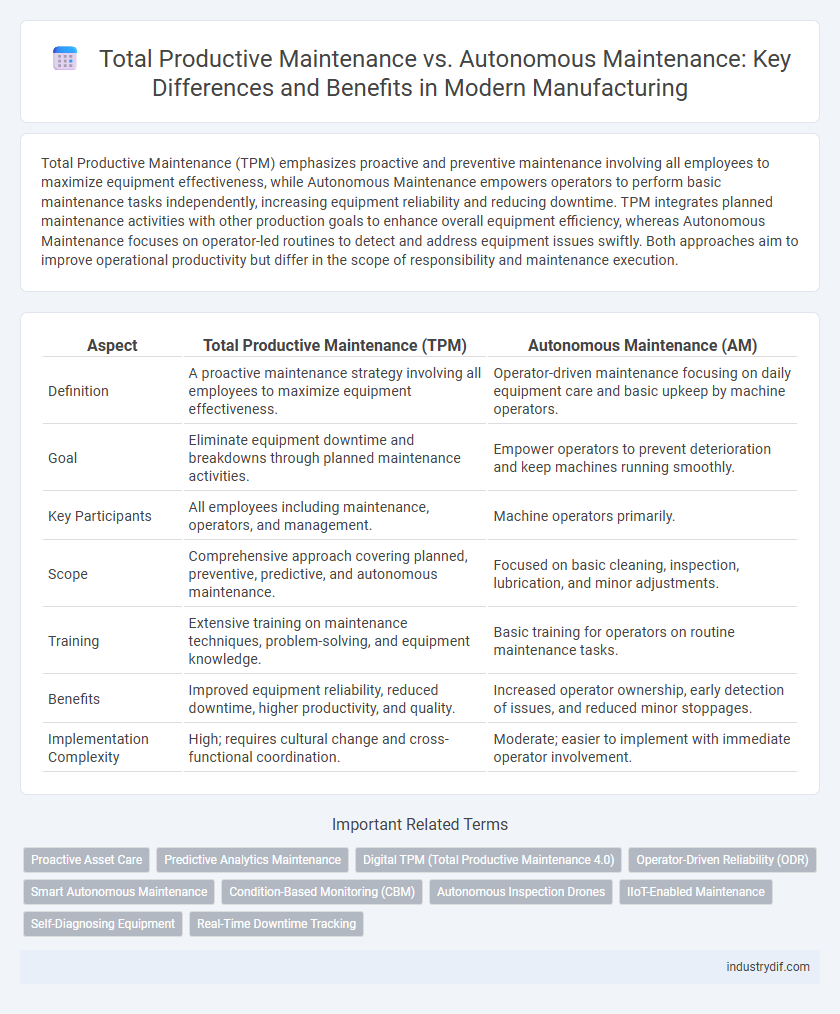
| Aspect | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) | Autonomous Maintenance (AM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A proactive maintenance strategy involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness. | Operator-driven maintenance focusing on daily equipment care and basic upkeep by machine operators. |
| Goal | Eliminate equipment downtime and breakdowns through planned maintenance activities. | Empower operators to prevent deterioration and keep machines running smoothly. |
| Key Participants | All employees including maintenance, operators, and management. | Machine operators primarily. |
| Scope | Comprehensive approach covering planned, preventive, predictive, and autonomous maintenance. | Focused on basic cleaning, inspection, lubrication, and minor adjustments. |
| Training | Extensive training on maintenance techniques, problem-solving, and equipment knowledge. | Basic training for operators on routine maintenance tasks. |
| Benefits | Improved equipment reliability, reduced downtime, higher productivity, and quality. | Increased operator ownership, early detection of issues, and reduced minor stoppages. |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires cultural change and cross-functional coordination. | Moderate; easier to implement with immediate operator involvement. |
Introduction to Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and Autonomous Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach aimed at maximizing equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive maintenance activities, minimizing downtime, and improving productivity. Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, inspection, and lubrication, fostering equipment ownership and early detection of issues. Both methodologies integrate to enhance machine reliability and operational efficiency within manufacturing environments.
Core Principles of TPM
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) centers on maximizing equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive maintenance and continuous improvement activities. Autonomous Maintenance empowers machine operators to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, inspection, and lubrication to prevent equipment deterioration. Core principles of TPM include autonomous maintenance, focused improvement, planned maintenance, quality maintenance, and early equipment management to enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
Understanding Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to take responsibility for routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, reducing machine downtime and increasing equipment reliability. It is a key pillar of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), fostering proactive involvement of front-line workers to identify and prevent potential issues early. Implementing Autonomous Maintenance enhances overall operational efficiency by promoting equipment ownership and minimizing unplanned breakdowns.
Key Differences Between TPM and Autonomous Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness, whereas Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks independently. TPM emphasizes planned maintenance and continuous improvement activities led by cross-functional teams, while Autonomous Maintenance focuses on daily cleaning, inspection, and minor repairs by machine operators to prevent equipment deterioration. Key differences lie in the scope of responsibility, with TPM integrating maintenance into overall production strategy and Autonomous Maintenance promoting operator ownership of equipment health.
Benefits of Implementing TPM in Manufacturing
Implementing Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) in manufacturing enhances equipment reliability by reducing downtime and minimizing breakdowns, leading to higher production efficiency. TPM fosters a proactive maintenance culture by involving all employees in routine machine care, which improves safety and quality standards. The integration of TPM decreases overall maintenance costs while boosting asset longevity, contributing to sustainable manufacturing operations.
Advantages of Autonomous Maintenance for Shop Floor Teams
Autonomous Maintenance empowers shop floor teams to take ownership of routine equipment upkeep, leading to reduced downtime and improved machine reliability. By involving operators directly, this approach fosters early detection of abnormalities and quicker response times, enhancing overall production efficiency. This hands-on involvement also boosts worker skills and morale, driving a culture of continuous improvement on the manufacturing floor.
Integration of Autonomous Maintenance Within TPM
Integration of Autonomous Maintenance (AM) within Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances equipment reliability by empowering operators to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, inspection, and lubrication. This collaborative approach reduces downtime and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by fostering early detection of abnormalities and promoting proactive maintenance culture. Embedding AM into TPM frameworks streamlines maintenance workflows, aligning operator involvement with advanced TPM strategies for sustained manufacturing productivity.
Challenges Faced During TPM and Autonomous Maintenance Adoption
Challenges faced during Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) adoption include resistance to cultural change, insufficient training for operators, and lack of management commitment, which hinder the implementation of proactive maintenance practices. Autonomous Maintenance struggles often involve inadequate skill development among frontline workers, inconsistent execution of standard operating procedures, and difficulties in sustaining long-term engagement. Both TPM and Autonomous Maintenance require strong leadership, continuous education, and robust communication strategies to overcome these barriers and achieve effective maintenance outcomes.
Best Practices for Successful Maintenance Strategies
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes cross-functional team involvement and continuous improvement to maximize equipment effectiveness, while Autonomous Maintenance (AM) empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks, fostering ownership and early problem detection. Best practices include thorough training programs, standardized procedures, and real-time performance monitoring to ensure consistent execution and rapid response to issues. Integrating data analytics and predictive maintenance tools enhances both TPM and AM by enabling proactive decision-making and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Maintenance Approaches
Future trends in manufacturing maintenance emphasize integration of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) with Autonomous Maintenance to enhance equipment reliability and operator involvement. Advancements in IoT and AI enable predictive analytics, allowing TPM to evolve from reactive to proactive strategies while empowering operators with real-time data for autonomous decision-making. Embracing digital twin technology and machine learning algorithms fosters continuous improvement in maintenance efficiency, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Related Important Terms
Proactive Asset Care
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive asset care by involving all employees in scheduled maintenance activities to prevent equipment failure, while Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks, enhancing early detection and quick resolution of issues. Both strategies drive improved equipment reliability and operational efficiency through proactive, preventive actions that minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan.
Predictive Analytics Maintenance
Predictive Analytics Maintenance leverages data-driven insights and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, enhancing Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) by minimizing unplanned downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules. Autonomous Maintenance, while empowering operators to perform routine upkeep, relies less on predictive data and more on frontline engagement, making Predictive Analytics a critical advancement for proactive asset management in manufacturing.
Digital TPM (Total Productive Maintenance 4.0)
Digital TPM (Total Productive Maintenance 4.0) integrates IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time data monitoring to enhance equipment reliability and operational efficiency beyond traditional Total Productive Maintenance and Autonomous Maintenance methods. This evolution empowers operators with predictive insights and automated alerts, reducing downtime and enabling proactive maintenance in smart manufacturing environments.
Operator-Driven Reliability (ODR)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) integrates Autonomous Maintenance, empowering operators through Operator-Driven Reliability (ODR) to identify, prevent, and resolve equipment issues, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). ODR emphasizes proactive operator engagement in routine maintenance tasks, fostering real-time problem-solving and reducing downtime in manufacturing operations.
Smart Autonomous Maintenance
Smart Autonomous Maintenance integrates IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics to enhance proactive equipment monitoring, enabling operators to identify and resolve potential issues without specialized maintenance intervention. This approach advances traditional Total Productive Maintenance by reducing downtime and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) through real-time data and autonomous decision-making capabilities.
Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive equipment upkeep involving all employees, while Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks; Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) enhances both by using real-time data from sensors to predict machine failures and optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and increasing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Integration of CBM technologies like vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and IoT-enabled sensors allows for precise detection of equipment anomalies, bridging the gap between TPM's structured maintenance plans and Autonomous Maintenance's operator-driven inspections.
Autonomous Inspection Drones
Autonomous inspection drones enhance Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) by providing real-time, precise equipment monitoring that enables early detection of anomalies and reduces unplanned downtime. Integrating these drones into Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform consistent inspections, improve asset reliability, and optimize maintenance schedules through high-resolution data collection and AI-driven analytics.
IIoT-Enabled Maintenance
IIoT-enabled Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) integrates advanced sensors and predictive analytics to maximize equipment uptime and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by systematically involving all employees in proactive maintenance activities. In contrast, IIoT-driven Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators with real-time machine data and automated alerts to perform routine maintenance tasks, reducing dependency on specialized technicians and enhancing immediate fault detection.
Self-Diagnosing Equipment
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes cross-functional team involvement to enhance overall equipment effectiveness, while Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators with self-diagnosing equipment capabilities to detect and address minor abnormalities proactively. Self-diagnosing technology integrated into Autonomous Maintenance reduces downtime by enabling real-time fault identification and corrective action before failures escalate.
Real-Time Downtime Tracking
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) incorporates real-time downtime tracking through integrated data analytics tools that enable systematic identification and elimination of equipment inefficiencies. Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators with real-time monitoring dashboards to promptly record and address downtime events, enhancing immediate response and continuous operational uptime.
Total Productive Maintenance vs Autonomous Maintenance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com