Supply Chain Management relies on linear processes to coordinate the flow of goods, information, and resources across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Digital Supply Networks leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing to create interconnected, real-time data-driven ecosystems that enhance agility and responsiveness. This shift enables manufacturers to proactively manage disruptions, optimize inventory, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
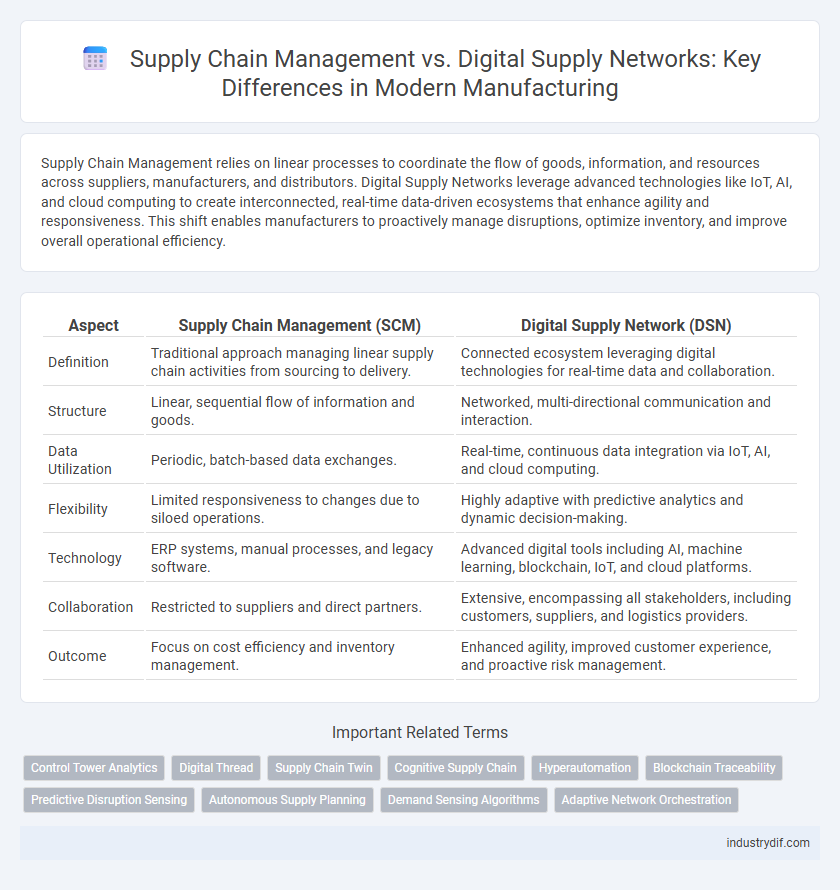
| Aspect | Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Digital Supply Network (DSN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional approach managing linear supply chain activities from sourcing to delivery. | Connected ecosystem leveraging digital technologies for real-time data and collaboration. |
| Structure | Linear, sequential flow of information and goods. | Networked, multi-directional communication and interaction. |
| Data Utilization | Periodic, batch-based data exchanges. | Real-time, continuous data integration via IoT, AI, and cloud computing. |
| Flexibility | Limited responsiveness to changes due to siloed operations. | Highly adaptive with predictive analytics and dynamic decision-making. |
| Technology | ERP systems, manual processes, and legacy software. | Advanced digital tools including AI, machine learning, blockchain, IoT, and cloud platforms. |
| Collaboration | Restricted to suppliers and direct partners. | Extensive, encompassing all stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and logistics providers. |
| Outcome | Focus on cost efficiency and inventory management. | Enhanced agility, improved customer experience, and proactive risk management. |
Introduction to Supply Chain Management and Digital Supply Networks
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves the coordinated planning, sourcing, production, and distribution of goods to optimize efficiency and reduce costs across the supply chain. Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) extend traditional SCM by leveraging advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to create dynamic, interconnected systems that enable real-time data sharing and adaptive decision-making. Emphasizing agility and transparency, DSNs transform linear supply chains into intelligent ecosystems that respond proactively to market changes and disruptions.
Core Principles of Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional Supply Chain Management centers on linear processes including procurement, production, and distribution, emphasizing efficiency, cost reduction, and inventory control. Core principles prioritize demand forecasting, supplier relationship management, and logistics coordination to ensure timely delivery and quality control. This approach relies heavily on hierarchical structures and fixed information flows, limiting real-time responsiveness and agility compared to Digital Supply Networks.
Key Features of Digital Supply Networks
Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) leverage real-time data analytics, AI-driven demand forecasting, and integrated IoT sensors to create highly responsive and adaptive manufacturing supply chains. Unlike traditional Supply Chain Management (SCM), DSNs enable end-to-end visibility and seamless collaboration across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors through cloud-based platforms. Key features include decentralized decision-making, predictive maintenance, and dynamic risk management, resulting in enhanced agility and reduced operational costs.
Technology Integration in Modern Supply Chains
Technology integration in modern supply chains transforms traditional Supply Chain Management (SCM) into dynamic Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) by leveraging IoT, AI, and blockchain for real-time data sharing and predictive analytics. DSNs enable enhanced visibility, agility, and collaboration across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, surpassing the linear model of SCM with interconnected, intelligent nodes. Advanced technologies streamline inventory management, demand forecasting, and risk mitigation, driving efficiency and responsiveness in global manufacturing ecosystems.
Real-Time Data and Visibility Enhancements
Supply Chain Management traditionally involves linear processes with limited real-time data access, leading to delayed response times and reduced visibility across stages. Digital Supply Networks leverage IoT sensors, AI analytics, and cloud platforms to provide comprehensive, real-time data flows that enhance transparency and predictive decision-making. This transformation enables manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, streamline logistics, and respond swiftly to disruptions through improved situational awareness.
Resilience and Flexibility: Comparing SCM and DSN
Supply Chain Management (SCM) traditionally focuses on linear processes and transactional efficiency, which can limit resilience and flexibility during disruptions. Digital Supply Networks (DSN), leveraging real-time data integration and advanced analytics, enable dynamic adaptation and proactive risk management across interconnected nodes. This interconnectedness in DSN enhances supply chain resilience by allowing rapid response to changes and improved collaboration among stakeholders.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Supply Chain Management (SCM) focuses on streamlining processes and improving supplier coordination, which enhances operational efficiency by reducing lead times and minimizing inventory costs. Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) leverage real-time data integration, AI, and IoT to enable dynamic decision-making, predictive analytics, and improved visibility across the entire supply chain. This advanced connectivity in DSNs drives greater cost reduction through optimized resource allocation and rapid response to disruptions compared to traditional SCM approaches.
Collaboration and Connectivity Across the Value Chain
Supply Chain Management (SCM) primarily emphasizes coordination among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors using linear, transactional processes. In contrast, Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) leverage real-time data integration, advanced analytics, and IoT connectivity to enable dynamic collaboration across the entire value chain. Enhanced visibility and seamless information exchange in DSNs drive faster decision-making and greater agility in manufacturing operations.
Scalability and Future Trends in Supply Chain Transformation
Supply Chain Management (SCM) traditionally focuses on linear, process-driven workflows, which can limit scalability in rapidly changing markets, whereas Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) leverage interconnected, data-rich platforms that enable real-time decision-making and adaptive resource allocation. Scalability in DSNs is enhanced by advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, facilitating seamless integration of new partners and global expansion without compromising efficiency. Future trends emphasize the transition toward autonomous supply networks that prioritize agility, predictive analytics, and resilience to disruptions, marking a fundamental shift from static supply chain models to dynamic, scalable ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Approach for Manufacturing Success
Manufacturing success hinges on selecting between traditional Supply Chain Management (SCM) and an advanced Digital Supply Network (DSN), where SCM focuses on linear processes and DSN emphasizes interconnected, real-time data-driven decision-making across all stakeholders. Embracing a Digital Supply Network enhances agility, reduces lead times, and improves demand forecasting through integrated IoT, AI, and blockchain technologies, driving smarter manufacturing operations. Companies prioritizing DSN adoption witness increased responsiveness to market shifts and optimized resource allocation, making it crucial for future-ready manufacturing strategies.
Related Important Terms
Control Tower Analytics
Control Tower Analytics enhances supply chain management by providing real-time visibility, predictive insights, and proactive issue resolution across the entire supply chain. Digital Supply Networks leverage Control Tower Analytics to create interconnected, adaptive systems that optimize inventory, improve demand forecasting, and increase operational agility.
Digital Thread
Digital Supply Networks (DSNs) enhance Supply Chain Management (SCM) by integrating real-time data flows and interconnected processes through a Digital Thread, enabling seamless traceability and agile decision-making across manufacturing operations. The Digital Thread captures and links detailed product lifecycle information, facilitating predictive analytics and optimized resource allocation for smarter, more responsive supply chains.
Supply Chain Twin
Supply Chain Management (SCM) traditionally coordinates procurement, production, and distribution processes to optimize efficiency and cost, while Digital Supply Networks (DSN) integrate real-time data, AI, and IoT to create adaptive, interconnected supply ecosystems. Supply Chain Twin technology enables DSNs by providing dynamic, digital replicas of physical supply chains, allowing manufacturers to simulate scenarios, predict disruptions, and optimize decision-making with high precision.
Cognitive Supply Chain
Cognitive supply chains leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to transform traditional supply chain management into a dynamic digital supply network (DSN) that enhances real-time decision-making and predictive analytics. By integrating IoT sensors, advanced data analytics, and cloud computing, cognitive systems enable adaptive, interconnected supply networks that optimize inventory levels, reduce downtime, and improve demand forecasting accuracy.
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation in Supply Chain Management integrates AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline operations and reduce human intervention, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Digital Supply Networks leverage hyperautomation to create adaptive, interconnected ecosystems that enable real-time data exchange and predictive analytics, driving agile decision-making across the manufacturing supply chain.
Blockchain Traceability
Supply Chain Management traditionally involves linear tracking of goods, while Digital Supply Networks leverage blockchain traceability to provide real-time, immutable data across interconnected suppliers and partners. Blockchain enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and enables end-to-end visibility in manufacturing supply chains, improving efficiency and accountability.
Predictive Disruption Sensing
Supply Chain Management (SCM) primarily reacts to disruptions through historical data analysis, whereas Digital Supply Networks (DSN) utilize real-time data and AI-driven predictive disruption sensing to proactively identify and mitigate risks. By integrating IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms, and advanced analytics, DSNs enhance supply chain resilience and operational efficiency beyond traditional SCM capabilities.
Autonomous Supply Planning
Autonomous supply planning within digital supply networks leverages real-time data analytics, AI, and machine learning to optimize inventory, demand forecasting, and production scheduling more efficiently than traditional supply chain management systems. This shift enables dynamic decision-making, reduces lead times, enhances responsiveness, and improves overall supply network agility in manufacturing operations.
Demand Sensing Algorithms
Demand sensing algorithms in supply chain management utilize historical sales data to enhance inventory forecasting, improving production efficiency and reducing stockouts. In contrast, digital supply networks integrate real-time data across interconnected systems, enabling demand sensing algorithms to deliver more accurate, dynamic forecasts that adapt rapidly to market fluctuations.
Adaptive Network Orchestration
Supply Chain Management traditionally emphasizes linear processes and inventory optimization, whereas Digital Supply Networks leverage adaptive network orchestration to enable real-time data integration, dynamic decision-making, and enhanced collaboration across multiple stakeholders. This adaptive orchestration transforms manufacturing by fostering resilience, agility, and predictive capabilities, ensuring seamless operations amid market volatility and demand fluctuations.
Supply Chain Management vs Digital Supply Network Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com