Supply chain digitalization transforms traditional supply chain management by integrating advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enhance transparency, efficiency, and responsiveness. Unlike conventional supply chains that often rely on manual processes and fragmented data, digitalized supply chains enable real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making. This shift not only reduces operational costs but also improves risk management and customer satisfaction in manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
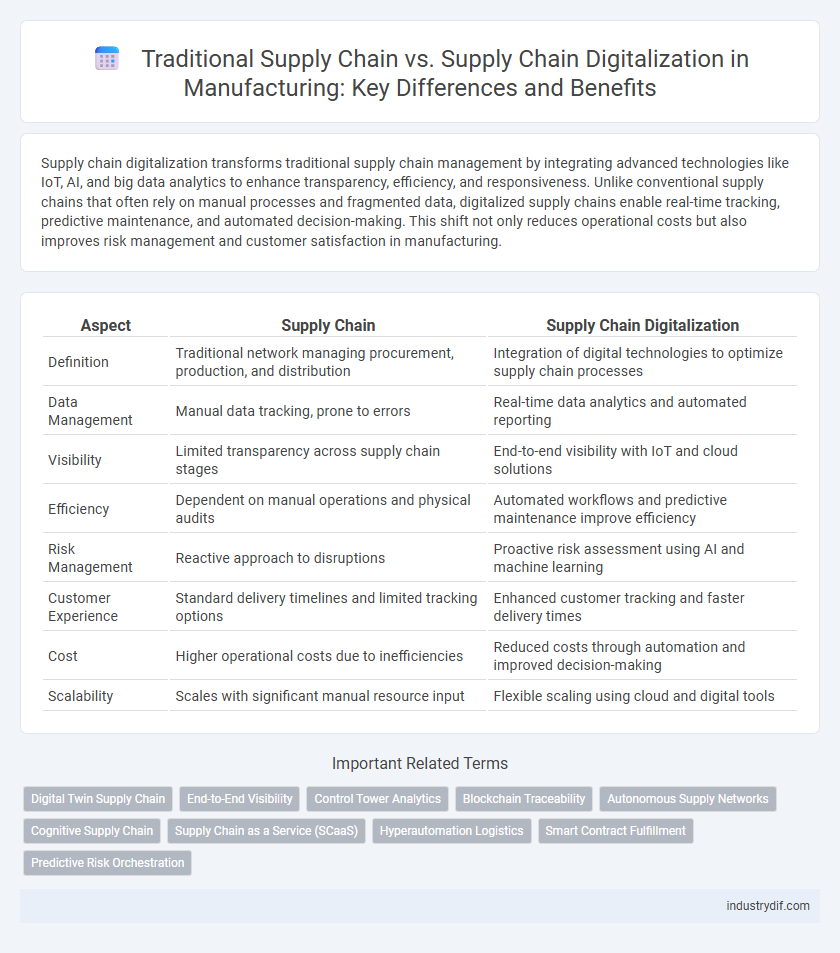
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Supply Chain Digitalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional network managing procurement, production, and distribution | Integration of digital technologies to optimize supply chain processes |
| Data Management | Manual data tracking, prone to errors | Real-time data analytics and automated reporting |
| Visibility | Limited transparency across supply chain stages | End-to-end visibility with IoT and cloud solutions |
| Efficiency | Dependent on manual operations and physical audits | Automated workflows and predictive maintenance improve efficiency |
| Risk Management | Reactive approach to disruptions | Proactive risk assessment using AI and machine learning |
| Customer Experience | Standard delivery timelines and limited tracking options | Enhanced customer tracking and faster delivery times |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to inefficiencies | Reduced costs through automation and improved decision-making |
| Scalability | Scales with significant manual resource input | Flexible scaling using cloud and digital tools |
Understanding Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional supply chain management involves coordinating activities such as procurement, production, inventory management, and distribution to ensure efficient product flow. It relies on manual processes, legacy systems, and limited real-time visibility, which can lead to delays, errors, and higher operational costs. Understanding these limitations is crucial for manufacturers aiming to transition toward supply chain digitalization, which leverages technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance transparency, agility, and decision-making.
Defining Supply Chain Digitalization
Supply Chain Digitalization refers to the integration of advanced digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain into traditional supply chain processes to enhance visibility, efficiency, and real-time decision-making. It transforms conventional supply chains by automating data exchange, improving inventory management, and enabling predictive analytics for demand forecasting. This digital shift drives agile, responsive manufacturing networks capable of reducing costs and accelerating time-to-market.
Key Differences Between Conventional and Digitalized Supply Chains
Conventional supply chains rely heavily on manual processes, paper-based documentation, and fragmented communication, resulting in slower response times and limited visibility across the entire network. Digitalized supply chains leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to enable real-time data sharing, predictive analytics, and enhanced automation, leading to increased efficiency and agility. Key differences include improved inventory accuracy, faster decision-making, and enhanced collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers through integrated digital platforms.
Technology Trends Shaping Supply Chain Digitalization
Supply chain digitalization leverages advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance transparency, efficiency, and real-time decision-making across manufacturing processes. Predictive analytics and automation streamline inventory management and demand forecasting, reducing operational costs and minimizing disruptions. Cloud computing platforms enable seamless integration of supply chain partners, facilitating faster data exchange and improved collaboration throughout the manufacturing ecosystem.
Benefits of Supply Chain Digitalization for Manufacturers
Supply chain digitalization enhances manufacturers' operational efficiency by enabling real-time data visibility and predictive analytics, reducing delays and minimizing inventory costs. Automated processes and integrated systems improve collaboration across suppliers and logistics partners, leading to faster decision-making and increased responsiveness to market changes. Enhanced traceability and transparency also ensure compliance with quality standards and foster greater customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Transitioning to a Digital Supply Chain
Transitioning to a digital supply chain presents challenges such as data integration across legacy systems, ensuring cybersecurity in interconnected platforms, and managing workforce skill gaps in digital technologies. Manufacturing companies often face resistance to change and require substantial investment in IoT, AI, and cloud computing infrastructures. Overcoming these obstacles is critical to achieving real-time visibility, improved demand forecasting, and enhanced operational efficiency in supply chain management.
Impact of Digitalization on Supply Chain Collaboration
Supply chain digitalization enhances real-time data sharing, improving transparency and coordination among manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors. Advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain facilitate seamless communication, reduce delays, and optimize inventory management. This digital transformation drives greater supply chain agility and collaborative decision-making, ultimately boosting overall manufacturing efficiency.
Digital Tools and Platforms in Modern Supply Chains
Digital tools and platforms revolutionize modern supply chains by enhancing real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making processes. Advanced supply chain digitalization integrates IoT sensors, cloud computing, and AI-driven software to optimize inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics coordination. These technologies enable manufacturers to reduce lead times, minimize operational costs, and improve overall supply chain resilience and agility.
Measuring Success: KPIs in Digital vs Traditional Supply Chains
Measuring success in traditional supply chains relies on KPIs such as on-time delivery, inventory turnover, and order accuracy, which emphasize efficiency and cost control. In contrast, digital supply chains incorporate advanced KPIs like real-time data accuracy, predictive analytics effectiveness, and supply chain responsiveness, reflecting enhanced agility and decision-making capabilities. The integration of IoT sensors, AI algorithms, and cloud platforms enables continuous performance monitoring and rapid adjustment, driving higher overall supply chain resilience and customer satisfaction.
Future Outlook: Evolving Trends in Manufacturing Supply Chains
Future manufacturing supply chains will increasingly integrate digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance transparency, agility, and efficiency. Digitalization enables real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing inventory management. Embracing these evolving trends positions manufacturers to respond swiftly to market changes and drive sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Supply Chain
Supply Chain Digitalization leverages advanced technologies like digital twins to create real-time, virtual replicas of physical supply chains, enabling predictive analytics and optimized decision-making. This transformation enhances visibility, agility, and efficiency compared to traditional supply chain models by simulating scenarios and proactively addressing disruptions.
End-to-End Visibility
End-to-end visibility in supply chain digitalization leverages IoT sensors, AI analytics, and blockchain technology to provide real-time tracking of inventory, shipments, and production status, significantly enhancing decision-making and risk management. Traditional supply chain models lack this comprehensive transparency, often resulting in delayed responses to disruptions and inefficiencies across procurement, logistics, and fulfillment processes.
Control Tower Analytics
Supply Chain Digitalization enhances traditional supply chain management by integrating Control Tower Analytics, providing real-time visibility, predictive insights, and proactive disruption management. This transformation enables manufacturers to optimize inventory, streamline operations, and improve decision-making through centralized data analytics and AI-driven monitoring.
Blockchain Traceability
Supply Chain Digitalization leverages blockchain traceability to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency by providing immutable, real-time tracking of materials and products throughout the manufacturing process. This contrasts with traditional supply chains, which often face challenges in data accuracy, provenance verification, and timely information sharing among stakeholders.
Autonomous Supply Networks
Supply Chain Digitalization transforms traditional supply chains into Autonomous Supply Networks (ASNs) by integrating advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain to enable real-time data exchange, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making. These ASNs enhance manufacturing efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve resilience against disruptions through autonomous coordination and adaptive resource management.
Cognitive Supply Chain
Supply Chain Digitalization integrates advanced AI and machine learning technologies, transforming traditional supply chains into Cognitive Supply Chains capable of real-time data analysis, predictive insights, and autonomous decision-making. This shift enhances manufacturing efficiency by optimizing inventory management, demand forecasting, and supplier collaboration through intelligent automation and adaptive learning systems.
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS)
Supply Chain as a Service (SCaaS) transforms traditional manufacturing supply chains by leveraging cloud-based platforms and real-time analytics to enhance flexibility, scalability, and end-to-end visibility. This digitalization enables manufacturers to optimize inventory management, reduce lead times, and improve supplier collaboration through integrated, on-demand services.
Hyperautomation Logistics
Supply chain digitalization leverages hyperautomation logistics to streamline end-to-end processes, integrating AI-driven robotics, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics to reduce operational costs and enhance delivery speed. Traditional supply chains lack the agility and predictive capabilities provided by hyperautomation platforms, resulting in increased downtime and inefficiencies across manufacturing workflows.
Smart Contract Fulfillment
Supply chain digitalization transforms traditional supply chain processes by integrating smart contract fulfillment, enabling automated, transparent, and secure execution of agreements without manual intervention. This innovation reduces operational delays, enhances traceability, and minimizes disputes by leveraging blockchain technology for real-time verification and enforcement of contract terms.
Predictive Risk Orchestration
Supply Chain digitalization integrates advanced analytics and AI to enhance Predictive Risk Orchestration, enabling real-time identification and mitigation of potential disruptions across manufacturing networks. This transformation improves supply chain resilience by forecasting risks such as supplier delays, demand fluctuations, and logistical bottlenecks more accurately than traditional supply chain management methods.
Supply Chain vs Supply Chain Digitalization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com