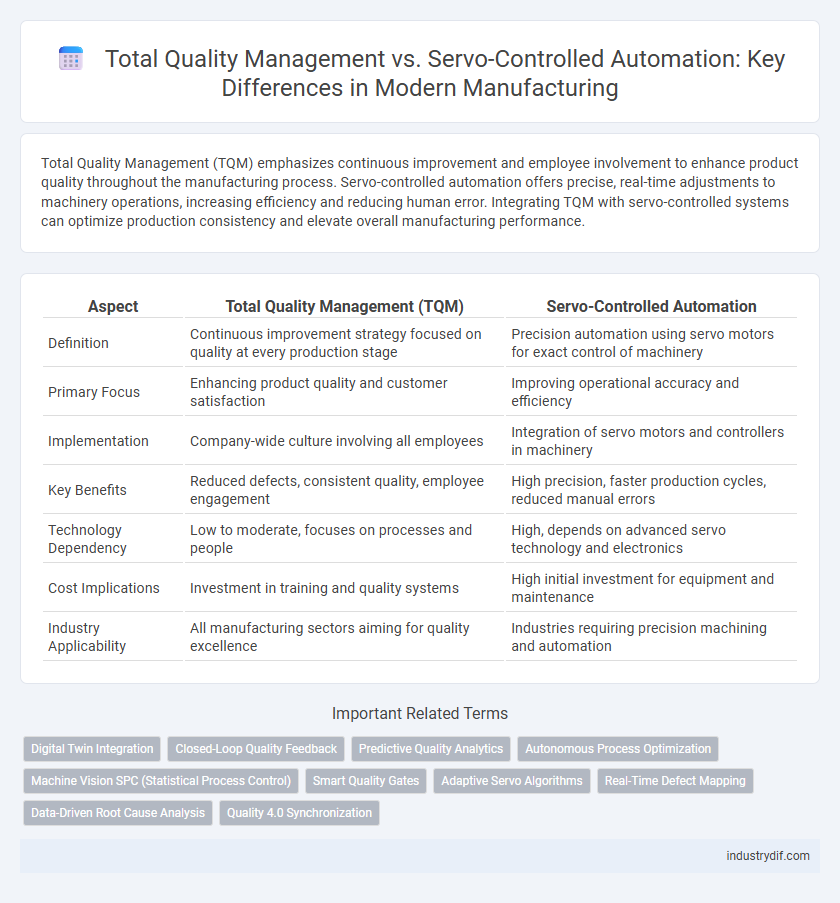
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Servo-controlled automation offers precise, real-time adjustments to machinery operations, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Integrating TQM with servo-controlled systems can optimize production consistency and elevate overall manufacturing performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Total Quality Management (TQM) | Servo-Controlled Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous improvement strategy focused on quality at every production stage | Precision automation using servo motors for exact control of machinery |
| Primary Focus | Enhancing product quality and customer satisfaction | Improving operational accuracy and efficiency |
| Implementation | Company-wide culture involving all employees | Integration of servo motors and controllers in machinery |
| Key Benefits | Reduced defects, consistent quality, employee engagement | High precision, faster production cycles, reduced manual errors |
| Technology Dependency | Low to moderate, focuses on processes and people | High, depends on advanced servo technology and electronics |
| Cost Implications | Investment in training and quality systems | High initial investment for equipment and maintenance |
| Industry Applicability | All manufacturing sectors aiming for quality excellence | Industries requiring precision machining and automation |
Understanding Total Quality Management in Manufacturing
Total Quality Management (TQM) in manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. Unlike servo-controlled automation, which relies on precise, computer-controlled machinery for consistency in production, TQM integrates quality into every process through systematic feedback and corrective actions. Implementing TQM leads to reduced defects, lower costs, and improved competitiveness by fostering a culture of quality across all departments.
Introduction to Servo-Controlled Automation
Servo-controlled automation integrates precision feedback mechanisms and programmable controls to enhance manufacturing accuracy and efficiency. Unlike traditional Total Quality Management (TQM) which emphasizes continuous process improvement and human-centric quality assurance, servo-controlled systems automate complex tasks with minimal error rates and real-time adjustments. This technology reduces variability and improves production consistency by enabling machines to respond adaptively to operational deviations.
Key Principles of Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement, customer focus, and employee involvement to enhance product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Key principles include process-centered approaches, integrated system management, and fact-based decision making, which prioritize reducing defects and increasing efficiency. In contrast to servo-controlled automation, which relies on precise machine control for production accuracy, TQM focuses on holistic quality improvements across all organizational levels.
Core Components of Servo-Controlled Automation Systems
Servo-controlled automation systems rely on core components such as servo motors, feedback devices, and precise controllers to achieve accurate and repeatable motion control in manufacturing processes. These components work together to optimize performance by continuously monitoring and adjusting position, velocity, and torque, enhancing product quality and operational efficiency. Unlike Total Quality Management, which focuses on organizational processes and continuous improvement, servo-controlled automation emphasizes real-time control and mechanical precision for high-speed and high-accuracy production environments.
Impact of TQM on Manufacturing Efficiency
Total Quality Management (TQM) significantly enhances manufacturing efficiency by fostering continuous improvement, reducing defects, and minimizing waste throughout production processes. Unlike servo-controlled automation, which primarily focuses on precision and speed, TQM integrates employee involvement and systematic quality checks to ensure long-term operational excellence. Implementing TQM can lead to higher product reliability, reduced rework costs, and improved customer satisfaction, ultimately driving sustainable manufacturing performance.
Advantages of Servo-Controlled Automation in Production
Servo-controlled automation enhances production precision by enabling real-time adjustments, reducing human error and increasing repeatability. This technology significantly boosts efficiency through faster cycle times and improved machine utilization, leading to higher throughput and lower operational costs. The integration of servo systems also facilitates better process control and adaptability to complex manufacturing tasks, supporting consistent product quality and scalability.
Quality Assurance: TQM vs Servo-Controlled Automation
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to ensure consistent product quality, relying on comprehensive processes and standards. Servo-Controlled Automation enhances quality assurance through precise, real-time control of manufacturing operations, reducing variability and human error. Combining TQM's strategic quality framework with servo-controlled systems' operational accuracy drives superior manufacturing quality outcomes.
Cost Implications: Manual vs Automated Quality Control
Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on continuous improvement and employee involvement, resulting in lower long-term operational costs through defect reduction and waste minimization. Servo-controlled automation in quality control significantly reduces labor costs and increases inspection speed but requires high initial capital investment and ongoing maintenance expenses. Balancing manual TQM efforts with automated quality systems can optimize cost efficiency by combining human expertise with precise, consistent servo-driven inspections.
Integration of TQM with Advanced Automation Technologies
Integrating Total Quality Management (TQM) with servo-controlled automation enhances manufacturing precision by combining continuous improvement principles with real-time, feedback-driven control systems. This synergy enables higher product consistency, reduced defects, and improved process efficiency through data-driven decision-making and adaptive machine responses. Manufacturers adopting this integration achieve superior quality standards while optimizing operational throughput and minimizing waste.
Future Trends: Harmonizing TQM and Servo Automation in Manufacturing
Future trends in manufacturing highlight the integration of Total Quality Management (TQM) and servo-controlled automation to enhance production precision and product consistency. Leveraging real-time data from servo automation systems allows continuous quality improvements aligned with TQM principles, reducing defects and operational costs. This harmonization drives smart factories toward greater efficiency, responsiveness, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Integration
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance product quality, while Servo-Controlled Automation focuses on precision and repeatability through advanced machinery. Integrating Digital Twin technology bridges TQM and servo automation by providing real-time simulation and predictive analytics, enabling proactive quality control and optimized manufacturing processes.
Closed-Loop Quality Feedback
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through comprehensive quality checks and employee involvement, creating a culture of proactive defect prevention. Servo-controlled automation enhances closed-loop quality feedback by integrating real-time sensor data with precise actuator adjustments, enabling immediate correction of process deviations and reducing variability in manufacturing outputs.
Predictive Quality Analytics
Predictive quality analytics in total quality management integrates real-time data to anticipate defects and optimize production processes, enhancing overall product reliability. Servo-controlled automation leverages precise motion control to reduce variability, enabling predictive analytics to fine-tune operations and improve quality consistency.
Autonomous Process Optimization
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through human-driven quality controls and employee involvement, while Servo-Controlled Automation leverages precise, real-time feedback loops and adaptive machinery for autonomous process optimization. Integrating servo-controlled systems enhances manufacturing efficiency by minimizing variability and enabling dynamic adjustments, surpassing traditional TQM methods in achieving consistent product quality.
Machine Vision SPC (Statistical Process Control)
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance manufacturing quality, while Servo-Controlled Automation integrates precise machine vision SPC systems for real-time defect detection and process optimization. Machine vision SPC in servo-controlled automation enables higher accuracy and faster feedback loops compared to traditional TQM approaches, reducing variability and enhancing product consistency on production lines.
Smart Quality Gates
Smart Quality Gates integrate Total Quality Management principles with servo-controlled automation to enhance real-time defect detection and process control on manufacturing lines. Implementing these gates enables continuous data-driven improvements, reduces variability, and ensures product consistency through automated feedback loops and precision monitoring.
Adaptive Servo Algorithms
Adaptive servo algorithms enhance manufacturing precision by dynamically adjusting control parameters based on real-time feedback, significantly improving the responsiveness and accuracy of servo-controlled automation systems. Integrating these algorithms within Total Quality Management frameworks promotes consistent product quality while reducing variability and operational inefficiencies on the production line.
Real-Time Defect Mapping
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through employee involvement and statistical process control, facilitating real-time defect mapping to identify and correct quality issues promptly. Servo-controlled automation enhances this process by providing precise, real-time data collection and adjustments, enabling immediate defect detection and reducing production errors with high accuracy.
Data-Driven Root Cause Analysis
Total Quality Management (TQM) relies on systematic data collection and statistical process control to identify quality issues, while servo-controlled automation integrates precise sensor feedback and real-time data monitoring to enable immediate root cause analysis. Combining TQM principles with servo-controlled systems enhances manufacturing efficiency by driving data-driven decision-making and reducing process variability.
Quality 4.0 Synchronization
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance product quality, while Servo-Controlled Automation leverages precision and real-time adjustments for consistent manufacturing accuracy. Integrating Quality 4.0 synchronization enables seamless data exchange between TQM processes and servo-controlled systems, driving predictive quality analytics and adaptive control for optimized production efficiency.
Total Quality Management vs Servo-Controlled Automation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com